Thoracic aortic ectasia. I77.810 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM I77.810 became effective on October 1, 2018.
How is a dilated aortic root repaired?
Valve sparing surgery becomes very much essential to cure the enlarged aortic root or its aneurysm. Surgeons thus remove the enlarged section and replace them with the synthetic tube referred as graft. During the surgical procedure, doctors keep the aortic valve of a patient aside and use it again.
What causes a mildly ectatic aorta?
A Guide to the Causes, Signs and Symptoms, and Available Treatments
- About. Mild aortic ectasia is defined as an enlargement of the aorta that is mild in degree. ...
- Risk of Rupture. Though the term ‘mild’ may indicate a lack in the seriousness of the condition, aortic aneurysms are serious.
- Echocardiography. ...
- Other Factors. ...
- Symptoms. ...
- Treatment. ...
- Summary. ...
- References. ...
What is treatment for enlarged aortic root?
With our minimally invasive aortic root valve replacement procedure, patients can generally expect:
- Shorter hospital stay
- Less post-surgical pain due to a smaller incision, better chest wall stability, and no broken sternum
- Less blood loss during surgery
- Less downtime and restrictions – our patients can resume normal exercise, daily movement, driving, and work in a few weeks compared to several months with traditional open-heart surgery
What is new in dilatation of the ascending aorta?
What Are the Clinical Implications?
- Aortic root dilatation and mid‐ascending aortic dilatation deserve new and different management.
- A surgical threshold of 5.0 cm should be considered for the aortic root.
- A surgical threshold of 5.25 cm should be considered for the mid‐ascending aorta.
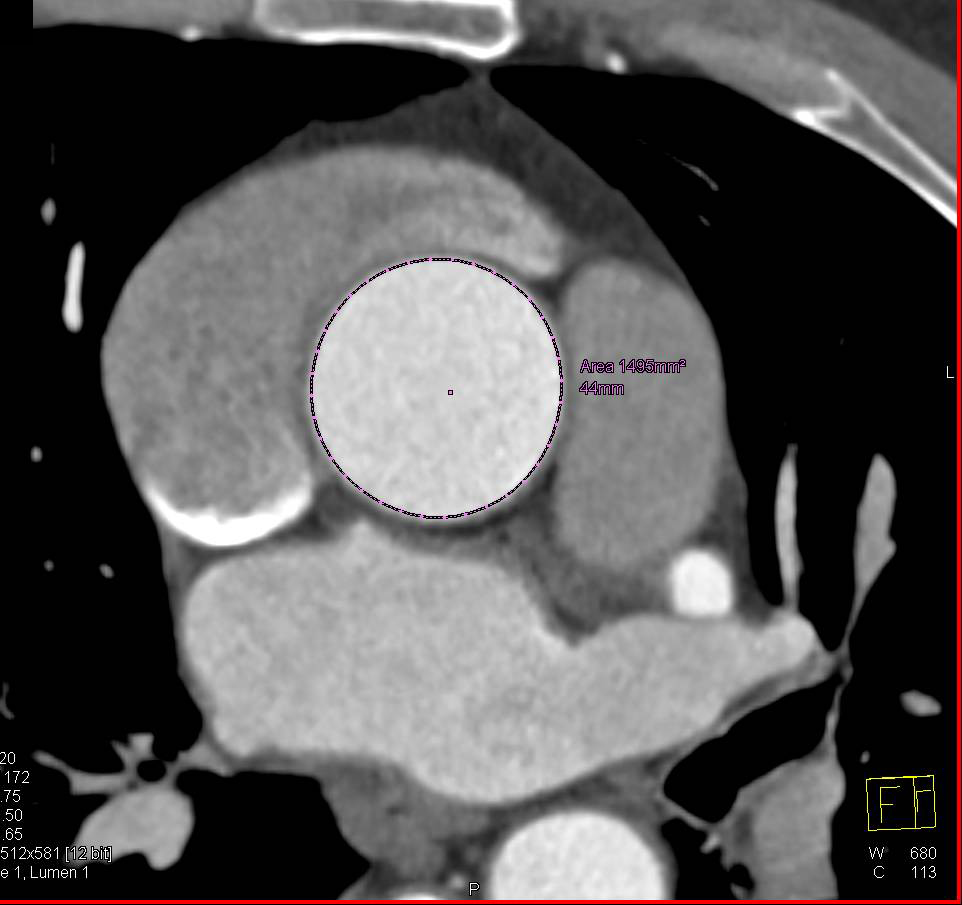
What is mild aortic root dilation?
Otherwise known as an aortic root aneurysm, a dilated aortic root is when the first section of the aorta, where the aortic valve resides, becomes enlarged. When this enlargement reaches a critical size, there is a risk of it rupturing or tearing, leading to a life-threatening situation.
Is the aortic root part of the thoracic aorta?
The Thoracic Aorta has 4 distinct parts: Aortic Root – Lies in the front portion of the chest below the sternum. It starts at the level of the heart and includes the aortic valve and the portion where the coronary arteries arise called the Sinus of Valsalva.
Where is aortic root located?
The aorta is the large blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to the body. The aortic root is located near where the aorta and the heart connect.
Is aortic dilation the same as aortic dissection?
Aortic dilatation may lead to aortic dissection or aortic rupture. The chance of aortic dissection is related to the aortic diameter. In 2002, Davies et al15 identified that the median aortic diameter at the time of rupture for the ascending or aortic arch was 6.0 cm.
What causes a dilated aortic root?
Progressive dilatation of the aortic root is caused by medial degeneration and destruction of the elastic and collagen fibers and can be also associated with high blood pressure, high stroke volume, and inflammatory diseases [14–17].
What is the aortic root and ascending aorta?
The ascending aorta originates beyond the aortic valve and ends right before the innominate artery (brachiocephalic trunc). It is approximately 5 cm long and is composed of two distinct segments. The lower segment, known as the aortic root, encompasses the sinuses of Valsalva and sinotubular junction (STJ).
Is aortic root the same as aortic valve?
The term 'aortic root' refers to the aortic valve from its position at the left ventricular outlet to its junction with the ascending portion of the aorta. Anatomically, this whole structure is the aortic valve. The normal aortic valve is more complex than its three semilunar leaflets suggests.
What is normal aortic root dilation?
Aortic root dilatation and mid‐ascending aortic dilatation deserve new and different management. A surgical threshold of 5.0 cm should be considered for the aortic root. A surgical threshold of 5.25 cm should be considered for the mid‐ascending aorta.
How is a dilated aortic root treated?
Aortic root surgery. This type of open-chest surgery is done to treat an enlarged section of the aorta to prevent a rupture. Aortic aneurysms near the aortic root may be related to Marfan syndrome and other related condition. A surgeon removes part of the aorta and sometimes the aortic valve.
Is a dilated aorta the same as an aneurysm?
Eliason: An aortic aneurysm, also referred to as an enlarged aorta, is an abnormal enlargement of the aorta, which can occur in the chest (thoracic aortic aneurysm), abdomen (abdominal aortic aneurysm, or AAA) or both (thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm). Approximately 80 percent of aortic aneurysms are in the abdomen.
What is the difference between AAA and aortic dissection?
An abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is usually located below the kidneys. Aortic dissection can occur in the aorta and its main branches. Aneurysms and dissections are classified depending on where they occur in the aorta.
What is the difference between an aortic aneurysm and an aortic dissection?
Aneurysms can occur in any vessel, most notably in the brain, heart, thoracic aorta, and abdominal aorta. A dissection is a tear of the inside layer of a blood vessel wall that allows blood to flow between the layers that make up the vessel wall and separate these layers.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for arthritis of knee
- 2. icd 10 code for contusion of right patella
- 3. icd 10 code for right wrist pain and swelling
- 4. icd code for vitiligo
- 5. icd 10 code for laminectomy and fusion
- 6. icd 10 code for hemiparesis right leg
- 7. icd-9-cm code for insomnia
- 8. icd 10 cm code for chronic narcotic use
- 9. icd 9 code for tongue lesion
- 10. icd 10 code for c6-7 fracture