What is the ICD 10 code for Mobitz type 1 block?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I44.1 Atrioventricular block, second degree 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code I44.1 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I44.1 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What does AV block mean in ICD 10?
May 26, 2021 · Question: What ICD-10-CM code should I report for Mobitz Block Type 1? I saw this diagnosis in my cardiologist’s documentation, but I have no idea which code to submit. North Carolina Subscriber. Answer: You should report I44.1 (Atrioventricular block, second degree) for Mobitz block type I. If you look under included conditions for I44.1, you will see that this code …
What are the reference codes for atrioventricular blockage?
I44.1 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of atrioventricular block, second degree. The code I44.1 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through September 30, 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code I44.1 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like ekg: mobitz type ii atrioventricular …
Is syncope a symptom of a Mobitz 1 block?
References in the ICD-10-CM Index to Diseases and Injuries applicable to the clinical term "mobitz heart block (atrioventricular)" Mobitz heart block (atrioventricular) - I44.1 Atrioventricular block, second degree. Previous Term: Mobile Mobility. Next Term: Moebius Möbius.
What is the ICD-10 code for Mobitz 1?
1.
What is Mobitz Type 1 heart block?
In second-degree heart block, the impulses are intermittently blocked. Type I, also called Mobitz Type I or Wenckebach's AV block: This is a less serious form of second-degree heart block. The electrical signal gets slower and slower until your heart actually skips a beat.May 28, 2021
Why is it called Mobitz Type 1?
Both types are named after Woldemar Mobitz. Type I is also named for Karel Frederik Wenckebach, and type II is also named for John Hay.
What is Mobitz block?
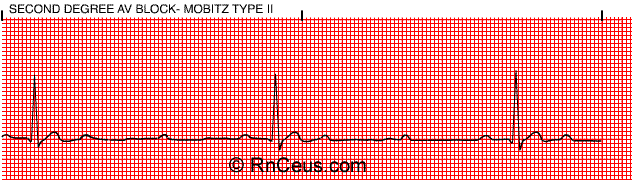
Definition of Mobitz II block (Hay Block) A form of 2nd degree AV block in which there is intermittent non-conducted P waves without progressive prolongation of the PR interval. Arrows indicate “dropped” QRS complexes (i.e. non-conducted P waves)Feb 4, 2022
What causes Mobitz type 1 AV block?
There are multiple causes of second-degree Mobitz type 1 (Wenckebach) AV block, including reversible ischemia, myocarditis, increased vagal tone, status post-cardiac surgery, or even medications that slow AV nodal conduction (e.g., beta-blockers, non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocks, adenosine, digitalis, and ...
What is the difference between Mobitz Type 1 and Mobitz Type 2?
Both Mobitz type 1 block and type 2 block result in blocked atrial impulses (ECG shows P-waves not followed by QRS complexes). The hallmark of Mobitz type 1 block is the gradual prolongation of PR intervals before a block occurs. Mobitz type 2 block has constant PR intervals before blocks occur.
What is Mobitz Type 1 second-degree AV block?
Also called Wenckebach or Mobitz type I block, type I second-degree AV block occurs when each successive impulse from the SA node is delayed slightly longer than the previous one. This pattern of progressive prolongation of the PR interval continues until an impulse fails to be conducted to the ventricles.
How do you treat Mobitz 1?
Mobitz I block Symptomatic patients should be treated with atropine and transcutaneous pacing. However, atropine should be administered with caution in patients with suspected myocardial ischemia, as ventricular dysrhythmias can occur in this situation.Jan 26, 2017
What is a 1st degree AV block?
First-degree atrioventricular (AV) block is a delay within the AV conduction system and is defined as a prolongation of the PR interval beyond the upper limit of what is considered normal (generally 0.20 s). Up until recently, first-degree AV block was considered an entirely benign condition.
Is Mobitz Type 1 regular?
Mobitz type I is a type of 2nd degree AV block, which refers to an irregular cardiac rhythm (arrhythmia), that reflects a conduction block in the electrical conduction system of the heart.
How do I know if I have type 2 Mobitz?
In Mobitz type II there is a constant PR interval across the rhythm strip both before and after the non-conducted atrial beat. Each P wave is associated with a QRS complex until there is one atrial conduction or P wave that is not followed by a QRS.Aug 29, 2021
Is Mobitz 2 regular?
Mobitz II: There will be a P-wave with every QRS. There may not always be a QRS complex with every p-wave. The rate will usually be regular.
What is an AV block?
Atrioventricular (AV) block involves impairment of the conduction between the atria and ventricles of the heart. In ICD-10-CM the codes are categorized by degree:#N#First degree AV block (I44.0 Atrioventricular block, first degree) – All atrial impulses reach the ventricles, but the conduction is delayed within the AV node. Patients are generally asymptomatic and the first-degree AV block is usually an incidental finding on electrocardiography (ECG). People with newly diagnosed first-degree AV block may be well-conditioned athletes, or they may have a history of myocardial infarction or myocarditis. First-degree AV block also may represent the first sign of degenerative processes of the AV conduction system.#N#Second degree AV block (I44.1 Atrioventricular block, second degree) – Atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles. Patients may be asymptomatic, but may experience pre-syncope or syncope and sensed irregular heartbeats. The latter usually is observed in more advanced conduction disturbances, such as Mobitz II second-degree AV block. A history of medications that affect atrioventricular node (AVN) function (e.g., digitalis, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers) may be contributory and should be obtained. Other terms for a second degree AV block are Wenckebach’s and Mobitz blocks.#N#Third degree AV block (I44.2 Atrioventricular block, complete) – No supraventricular impulses are conducted to the ventricles. Patients have symptoms of fatigue, dizziness, light-headedness, pre-syncope, or syncope. Syncopal episodes due to slow heart rates are called Morgagni-Adams-Stokes (MAS) episodes, in recognition of the pioneering work of these researchers on syncope. Patients with third-degree AV block may have associated symptoms of acute myocardial infarction either causing the block or related to reduced cardiac output from bradycardia in the setting of advanced atherosclerotic coronary artery disease.#N#Proper coding of AV block requires documentation of severity:
Who is John Verhovshek?
John Verhovshek. John Verhovshek, MA, CPC, is a contributing editor at AAPC. He has been covering medical coding and billing, healthcare policy, and the business of medicine since 1999. He is an alumnus of York College of Pennsylvania and Clemson University.
Is AV block asymptomatic?
Patients are generally asymptomatic and the first-degree AV block is usually an incidental finding on electrocardiography (ECG). People with newly diagnosed first-degree AV block may be well-conditioned athletes, or they may have a history of myocardial infarction or myocarditis.
What is it called when your heart beats too fast?
An arrhythmia is a problem with the rate or rhythm of your heartbeat. It means that your heart beats too quickly, too slowly, or with an irregular pattern. When the heart beats faster than normal, it is called tachycardia. When the heart beats too slowly, it is called bradycardia.
What is the tabular list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code I44.1:
What causes a fast heartbeat?
The most common type of arrhythmia is atrial fibrillation, which causes an irregular and fast heart beat. Many factors can affect your heart's rhythm, such as having had a heart attack, smoking, congenital heart defects, and stress. Some substances or medicines may also cause arrhythmias.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code I44.1 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
What is dysfunctional AV node?
The AV node is dysfunctional, such that it will not be able to repolarize adequately by the time the next impulse arrives, which is why the conduction will be slower than the previous and the PR interval becomes prolonged. The AV node becomes more and more exhausted (i.e more and more refractory) each time until it is completely refractory and blocks the atrial impulse. This manifests on the ECG with gradual prolongation of the PR interval until a P-wave is blocked and thus not followed by a QRS complex. The AV node then recovers (after the complete block), only to repeat the cycle again. These cycles are often referred to as Wenckebach periods.
Is Mobitz type 1 block good?
It is also common among athletes due to their high vagal tone. It is more common in older individuals. The prognosis is good, even in the elderly. Mobitz type 1 block generally does not progress to more advanced blocks. Should it progress to more advanced blocks, which typically is due to a more distal location of the block, an artificial pacemaker is needed.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for p afib
- 2. icd 1 code for gastritis
- 3. icd 10 code for need for tdap
- 4. icd-10 code for end stage copd with hypoxia
- 5. icd 10 cm code for trochanteric bursitis
- 6. which of the following will not be a seventh character for an icd-10-cm code
- 7. icd 10 code for pneumocephalus, traumatic
- 8. icd 10 code for intraabdominal abscess
- 9. icd 10 code for fell off bed
- 10. icd 10 code for malignant neoplasm of lower respiratory tract nos