What is the ICD 10 code for mood disorder?
Oct 01, 2021 · F34.81. F34.81 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
What is diagnosis code 10?
F34.81 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder. The code F34.81 is valid during the fiscal year 2022 from October 01, 2021 through September 30, 2022 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions. The ICD-10-CM code F34.81 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like disruptive mood …
What are the causes of DMDD?
ICD-10 code F34.81 for Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Mental, Behavioral and Neurodevelopmental disorders . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
Which disorders are considered moderate mood disorders?
F30 Manic episode. F31 Bipolar disorder. F32 Depressive episode. F33 Major depressive disorder, recurrent. F34 Persistent mood [affective] disorders. F39 Unspecified mood [affective] disorder. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes F30-*. F30 Manic episode. …
What is dysregulation mood disorder?
Overview. Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) is a childhood condition of extreme irritability, anger, and frequent, intense temper outbursts. DMDD symptoms go beyond a being a “moody” child—children with DMDD experience severe impairment that requires clinical attention.
What is a F34 81 diagnosis?
ICD-10 code: F34.81. Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) is part of a cluster of diagnoses called the depressive disorders. Depressive disorders are a group of psychiatric conditions that include: Major depressive disorder. Persistent depressive disorder (dysthymia)
What is disruptive mood dysregulation disorder in adults?
Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD) defined by DSM-V is characterized by severe and recurrent temper outbursts and persistently irritable or angry mood. Objectives. Our aim is to attract attention to an adult case with DMDD since the literature is lacking adult manifestations.Mar 23, 2020
Is DMDD a mental illness?
DMDD is a psychiatric condition. It's typically only diagnosed in children. The main symptoms include irritability, emotional dysregulation, and behavioral outbursts. Outbursts are usually in the form of severe temper tantrums.
What does anxiety F41 9 mean?
Code F41. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Anxiety Disorder, Unspecified. It is a category of psychiatric disorders which are characterized by anxious feelings or fear often accompanied by physical symptoms associated with anxiety.
What does F43 23 mean?
Code F43. 23 is the diagnosis code used for Adjustment Disorder (AD) with Mixed Anxiety and Depressed Mood. It is sometimes known as situational depression. It occurs when an individual is unable to adjust to or cope with a particular stress or a major life event.
What category is disruptive mood dysregulation disorder?
DMDD is a newly classified disorder, first appearing in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) in 2013. The DSM is used for the assessment and diagnosis of mental disorders; it does not include specific guidelines for the treatment of any disorder.
What is the DSM-5 code for disruptive mood dysregulation disorder?
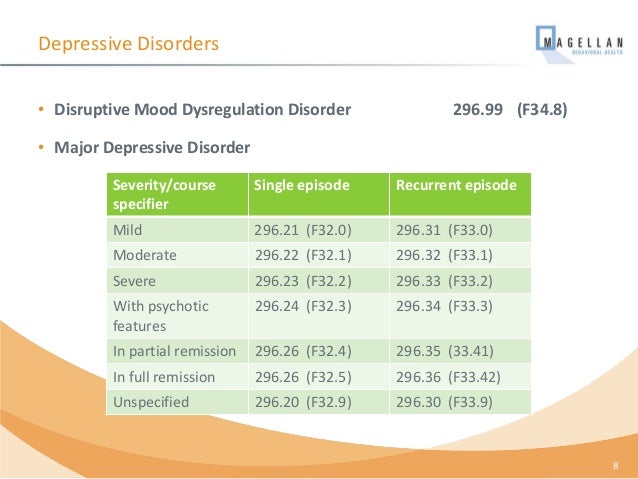
Disruptive Mood Dysregulation Disorder DSM-5 296.99(F34. 8) - Therapedia.
What are three characteristics of disruptive mood dysregulation?
The symptoms of DMDD include:Severe, recurrent temper tantrums. ... Outbursts occurring three or more times a week. ... Tantrums that are out of proportion to the situation. ... Tantrums that are inappropriate for the child's age level. ... Irritable and angry moods between tantrums. ... Symptoms happen in multiple settings.Feb 18, 2021
Is DMDD the same as bipolar?
A DMDD diagnosis is never given before the age of 6 or after the age of 18 years old, so adults cannot be diagnosed with DMDD. Bipolar disorder, which is classified as a mood disorder, typically involves cycling between periods of elevated mood (mania) and periods of significantly lower mood (depression).
Does DMDD turn into bipolar?
Research has also demonstrated that children with DMDD usually do not go on to have bipolar disorder in adulthood. They are more likely to develop problems with depression or anxiety. Many children are irritable, upset, or moody from time to time.
At what age is the rate of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder higher?
These findings generally support that SMD and/or chronic irritability in youth ages 10–13 years increase risk for depression, anxiety, and functional impairment in adulthood. Using the same sample reported in Brotman et al.Jan 20, 2016
What is the ICd 10 code for mood disorder?
F34.81 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Disruptive mood dysregulation disorder . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Disorder (of) see also Disease. disruptive F91.9.
What is the F34.81 code?
F34.81 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of disruptive mood dysregulation disorder. The code F34.81 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the GEM crosswalk?
The General Equivalency Mapping (GEM) crosswalk indicates an approximate mapping between the ICD-10 code F34.81 its ICD-9 equivalent. The approximate mapping means there is not an exact match between the ICD-10 code and the ICD-9 code and the mapped code is not a precise representation of the original code.
How do I treat mood disorders?
Mood disorders can increase a person's risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other diseases. Treatments include medication, psychotherapy, or a combination of both . With treatment, most people with mood disorders can lead productive lives. Cyclothymic disorder (Medical Encyclopedia)
How many people have mood disorders?
A mood disorder is different. It affects a person's everyday emotional state. Nearly one in ten people aged 18 and older have mood disorders. These include depression and bipolar disorder (also called manic depression). Mood disorders can increase a person's risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other diseases.
What is emotional disorder?
Emotional behavior inappropriate for one's age or circumstances, characterized by unusual excitability, guilt, anxiety, or hostility. Mental disorders characterized by a disturbance in mood which is abnormally depressed or elated. Compare emotional stability or emotionally disturbed.
How many people have mood disorders?
Nearly one in ten people aged 18 and older have mood disorders. These include. major depressive disorder. dysthymic disorder (a chronic, mild depression) bipolar disorder (also called manic depression) mood disorders can increase a person's risk for heart disease, diabetes, and other diseases.
What is a DMDD?
DMDD is characterized by persistent irritability and temper tantrums. PDD is more similar to major depression symptomatically – youth with this illness experience sad / depressed mood along with physical and cognitive symptoms.
How old do you have to be to have DMDD?
The symptoms must be present in at least two settings (and severe in at least one) The symptoms must be present by age 10 (however, a youth cannot be diagnosed with DMDD before age six or after age 18)
How common is DMDD?
Prevalence for DMDD is estimated at approximately 1-5% of youth. DMDD is characterized by chronic irritable mood (at least one year with no more than 3 months asymptomatic) during which the youth also experiences severe temper outbursts that are out of proportion to the situation and not developmentally appropriate.
What is Mindyra for?
Mindyra provides primary care doctors and other health care specialists with valid, time-saving tools to arrive at a more precise diagnosis and treatment plan for their patients who have mental health, substance abuse and learning challenges.
What is behavioral treatment?
Learn more. Behavioral treatment may also be helpful, particularly to manage the impulsive and explosive behaviors. Behavioral treatments that include parent training have demonstrated good efficacy in youth exhibiting these types of behaviors.
What are the changes that can occur with depressive disorder?
Individuals with depressive disorders often experience significant somatic changes, such as disruptions in sleep (insomnia or hypersomnia), eating (overeating or loss of appetite), or energy level. Changes in cognition, such as difficulty concentrating, indecisiveness, and morbid ideation (such as thoughts of death) are also common.
What is a depressive disorder?
Depressive disorders are a group of psychiatric conditions that include: The depressive disorders are characterized primarily by mood disturbance (sad, empty, or irritable mood). Individuals with depressive disorders often experience significant somatic changes, such as disruptions in sleep (insomnia or hypersomnia), ...
What is the ICd 10 code for mood disorder?
Mood disorder due to known physiological condition, unspecified 1 F06.30 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 Short description: Mood disorder due to known physiological condition, unsp 3 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM F06.30 became effective on October 1, 2020. 4 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of F06.30 - other international versions of ICD-10 F06.30 may differ.
What is F05 dementia?
delirium due to known physiological condition ( F05) dementia as classified in F01 - F02. other mental disorders associated with alcohol and other psychoactive substances ( F10-F19) Other mental disorders due to known physiological condition.
What is the meaning of F10-F19?
mood disorders due to alcohol and other psychoactive substances ( F10-F19 with .14, .24, .94) mood disorders, not due to known physiological condition or unspecified ( F30-F39) Mood disorder due to known physiological condition. Approximate Synonyms. Organic mood disorder.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for collapsed thoracic vertebra
- 2. icd 10 code for r97.2
- 3. icd 10 code for injection right fpl tendon
- 4. icd 10 code for right lower extremity mass
- 5. icd 9 code for klippel feil
- 6. icd 9 code for prophylaxis dvt
- 7. icd 9 code for malignant neoplasm
- 8. icd 10 code for torticollis spasmodic
- 9. icd 10 diagnosis code for presence of urinary catheter
- 10. what is the icd 10 code for reactive airway disease