How to code MRSA?
Oct 01, 2021 · Colonization MRSA Z22.322 (Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus) Positive culture (nonspecific) nose R84.5 staphylococcus (Methicillin susceptible) Z22.321 Methicillin resistant Z22.322 Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
Does MSSA colonization reduce risk for MRSA infection?
Oct 01, 2021 · This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B95.62 - other international versions of ICD-10 B95.62 may differ. Applicable To Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infection as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere The following code (s) above B95.62 contain annotation back-references that may be applicable to B95.62 : A00-B99
What is MRSA colonization?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J15.212 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Pneumonia due to Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Bronchopneumonia due to methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus; Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (mrsa) bronchopneumonia; Methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus (mrsa) pneumonia.
Is MRSA a viral infection?
Oct 01, 2021 · Colonization MSSA Z22.321 (Methicillin susceptible Staphylococcus aureus) Positive culture (nonspecific) nose R84.5 staphylococcus (Methicillin susceptible) Z22.321 Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, …
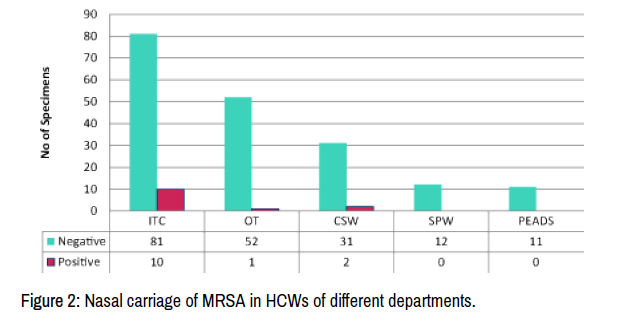
What is MRSA nasal colonization?
Being colonized with MRSA means you carry it in your nose or on your skin but you are not sick with a MRSA infection. If you have signs and symptoms of a MRSA infection (boil, abscess, pain, swelling) you are much more likely to spread MRSA because the infected area contains many MRSA germs.Jul 7, 2020
How do you code MRSA bacteremia?
Many conditions require you to report MRSA with B95. 62, and a second code to identify the site/type of infection, such as the skin site or specific heart valve. The drug resistance is inherent in the MRSA code, and ICD-10-CM guidelines tell you to leave Z16. 11 out.Jan 12, 2017
Where is MRSA colonized?
The most common site of colonisation is the anterior nares, but MRSA can also be found in other areas such as the axillae, abnormal skin (e.g., eczema, wounds), urine, rectum, and throat. There should be no signs or symptoms of infection.Nov 13, 2015
What is MRSA nasal swab?
MRSA screening tests include: Bacterial culture - a nasal swab is collected from the nares (nostrils) of an asymptomatic person and cultured (put onto a special nutrient medium, incubated, and then examined for the growth of characteristic MRSA colonies).
How do you code MRSA in ICD-10?
ICD-10-CM Code for Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere B95. 62.
What is the ICD-10 code for bacteremia?
What's the diagnosis in ICD-10? Bacteremia – Code R78. 81 (Bacteremia).
How does MRSA colonization occur?
A person can get MRSA by touching someone or something that has the bacteria on it and then touching their skin or nose. In the hospital, the most common way to get MRSA is when a caregiver or visitor touches the patient or objects in the patient's room without properly washing their hands first.
How do you know if you have colonized MRSA?
Colonization by MRSA does not lead to symptoms unless the bacteria cause an active infection. Most people who have an active community-acquired MRSA infection show symptoms of a skin infection. You might have a raised, red lump or a large, tender lump that drains pus.
How common is MRSA colonization?
MRSA is often resistant to other antibiotics, as well. While 33% of the population is colonized with staph (meaning that bacteria are present, but not causing an infection with staph), approximately 1% is colonized with MRSA.
What is the code for MRSA pneumonia?
Exceptions include a patient with MRSA sepsis or MRSA pneumonia, which have specific codes: A41.02 Sepsis due to Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Only one code is needed for sepsis; additional codes are reported to capture severe sepsis and accompanying organ failure.
What is the code for Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus?
B95.62 Methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection as the cause of diseases classified elsewhere. The infection site is known, and reported secondarily (e.g., skin of the groin). One of these two codes usually is the first-listed code when a patient is treated for an MRSA infection.
What is the P code for staph infection?
There are instances, however, when Z16.11 for staph infections is appropriate. When a newborn or neonate has MRSA pneumonia or MRSA sepsis, for example, the P code captures the staphylococcal infection, but not the penicillin resistance. P36.39 Sepsis of newborn due to other staphylococci.
What is a nasal swab?
Patients undergoing hospitalization or outpatient elective surgery usually are tested for colonization using a nasal swab. The cost of this test is bundled into the Medicare Severity-Diagnosis Related Groups payment, but the preventive value of the test makes it financially advantageous for facilities.
Where does MRSA lurk?
MRSA lurks on the skin and in the nasal cavities of many people, increasing the risk of infection for the colonized persons and those around them. A person who has been “colonized” has MRSA present, without necessarily having an active MRSA infection.
Can you report MRSA colonization?
A patient may have MRSA colonization and an active MRSA infection, in which case, code both conditions. Report this code anytime a true screening is performed, as for hospital admission or when a skin or other accessible infection site is suspect.
Can you report Z16.11 with B95.62?
Never Report Z16.11 with the Four MRSA Codes. To do so would be redundant. Z16.11 Resistance to penicillins [Methicillin is a form of penicillin.] Many conditions require you to report MRSA with B95.62, and a second code to identify the site/type of infection, such as the skin site or specific heart valve.
What is the subcategory of R65.2?
If a patient has sepsis and an acute organ dysfunction, but the medical record documentation indicates that the acute organ dysfunction is related to a medical condition other than the sepsis, do not assign a code from subcategory R65.2, Severe sepsis.
What is the term for the condition of being colonized or carrying MSSA?
The condition or state of being colonized or carrying MSSA or MRSA is called colonization or carriage, while an individual person is described as being colonized or being a carrier.
How many codes are needed for severe sepsis?
The coding of severe sepsis requires a minimum of 2 codes: first a code for the underlying systemic infection, followed by a code from subcategory R65.2, Severe sepsis. If the causal organism is not documented, assign code A41.9, Sepsis, unspecified organism, for the infection.
What does colonization mean in a swab?
Colonization means that MSSA or MSRA is present on or in the body without necessarily causing illness. A positive MRSA colonization test might be documented by the provider as "MRSA screen positive" or "MRSA nasal swab positive.".
When should sepsis be assigned first?
If the patient is admitted with a localized infection, such as pneumonia, and sepsis/severe sepsis doesn't develop until after admission, the localized infection should be assigned first, followed by the appropriate sepsis/severe sepsis codes. 5.Sepsis due to a post-procedural infection. a.
Is severe sepsis a non-infectious condition?
6.Sepsis and severe sepsis associated with a noninfectious process. In some cases a noninfectious process (condition), such as trauma, may lead to an infection which can result in sepsis or severe sepsis. If sepsis or severe sepsis is documented as associated with a noninfectious condition, such as a burn or serious injury, ...
When should a non-infectious condition be sequenced?
If the infection meets the definition of principal diagnosis it should be sequenced before the non-infectious condition. When both the associated non-infectious condition and the infection meet the definition of principal diagnosis either may be assigned as principal diagnosis.

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2018 icd 10 code for acute appendicitis
- 2. 2016 icd 10 code for pancreatitis due to alcohol
- 3. icd 10 code for anterior abdominal wall abscess
- 4. icd 10 code for icu admission
- 5. icd 10 code for adnexal pain
- 6. icd 10 code for extreme tricep pain
- 7. icd 10 code for ulcer of toe
- 8. icd 10 code for newborn hydronephrosis
- 9. icd-10 code for fall riding bike
- 10. icd 10 code for toe pain right