What is multiple epiphyseal dysplasia?
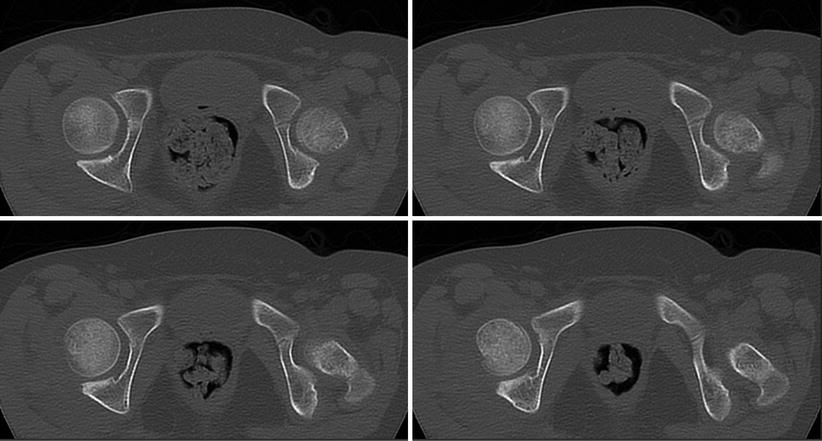
Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia is a condition that affects the ends of the long bones, otherwise known as epiphysis. The condition results from a problem in the cartilage oligomeric matrix protein, which accumulates in the cartilage and causes premature destruction, and can lead to early arthritis.
Is multiple epiphyseal dysplasia a form of dwarfism?
Multiple Epiphyseal Dysplasia is a congenital disorder caused most commonly by an autosomal mutation in cartilage oligomeric matrix protein on chromosome 19. Patients present with a form of dwarfism characterized by irregular, delayed ossification at multiple epiphyses.
What is the ICD 10 code for skeletal dysplasia?
Congenital malformation of musculoskeletal system, unspecified. Q79. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q79.
How common is multiple epiphyseal dysplasia?
The incidence of dominant multiple epiphyseal dysplasia is estimated to be at least 1 in 10,000 newborns. The incidence of recessive multiple epiphyseal dysplasia is unknown. Both forms of this disorder may actually be more common because some people with mild symptoms are never diagnosed.
What is the difference between achondroplasia and Pseudoachondroplasia?
Achondroplasia, the single most common form of human dwarfism, results in most cases from one of two very specific mutations in the gene encoding fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3). Pseudoachondroplasia is caused by a variety of mutations in the gene encoding cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP).
Is multiple epiphyseal dysplasia a genetic disorder?
Recessive multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (rMED) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by skeletal malformations (dysplasia) including those affecting bones of the hands, feet, and knees. Joint pain, particularly of the hips or knees, is also common and develops during childhood.
How many types of skeletal dysplasia are there?
There are about 400 types of skeletal dysplasia. The descriptions below include some of the more common types of skeletal dysplasia.
What is Kniest dysplasia?
Kniest dysplasia is an extremely rare disorder of bone growth that leads to short stature, malformed bones and joints, and skeletal abnormalities. It's diagnosed only once out of every 1 million births.
What is the ICD-10 code for short stature?
ICD-10 Code for Short stature (child)- R62. 52- Codify by AAPC.
Is Fairbanks disease hereditary?
Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) encompasses a spectrum of skeletal disorders, most of which are inherited in an autosomal dominant form. However, there is an autosomal recessive form. Associated genes include COL9A1, COL9A2, COL9A3, COMP, and MATN3....Genetics.TypeOMIMGeneEDM5607078MATN3EDM6120210COL9A14 more rows
What is Trevor's disease?
Dysplasia epiphysealis hemimelica (DEH), also known as Trevor's disease, is a developmental bone disease of childhood. It is rare and clinical experience with this condition is limited. Most cases are diagnosed before 8 years of age.
What does epiphyseal mean?
1 : a part or process of a bone that ossifies separately and later becomes ankylosed to the main part of the bone especially : an end of a long bone. 2 : pineal gland.
What is a pseudo dwarf?
The condition is also referred to as pseudoachondroplastic dysplasia or pseudoachondroplastic spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia. It is a form of dwarfism. People with pseudoachondroplasia have normal intelligence, head size, and facial features.
What is Diastrophic dwarfism?
Diastrophic dysplasia is a disorder of cartilage and bone development that leads to an onset of joint pain and deformity. It is a rare genetic condition that causes dwarfism, where a child's legs and arms do not grow and develop to the typical adult length.
Is Fairbanks a disease?
Fairbank's disease or multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) is a rare genetic disorder (dominant form: 1 in 10,000 births) that affects the growing ends of bones. Long bones normally elongate by expansion of cartilage in the growth plate (epiphyseal plate) near their ends.
Is Fairbanks disease genetic?
Fairbanks disease or multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) is a rare genetic disorder (dominant form--1 in 10,000 births) which affects the growing ends of bones.
The ICD code Q788 is used to code Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia
Fairbank's disease or multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) is a rare genetic disorder (dominant form — 1 in 10,000 births) that affects the growing ends of bones. Bones usually elongate by a process that involves the depositing of cartilage at the ends of the bones, called ossification. This cartilage then mineralizes and hardens to become bone.
Coding Notes for Q78.8 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #564-566 - Other musculoskeletal system and connective tissue diagnoses with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'Q78.8 - Other specified osteochondrodysplasias'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code Q78.8. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Codes GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code Q78.8 and a single ICD9 code, 756.59 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is osteochondrodysplasia?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. An osteochondrodysplasia disease that has material basis in defective cartilage mineralization into bone, which results in irregular ossification centers of the hip or the knee. Symptoms can include fatigue and joint pain. Medical condition.
When did the European Skeletal Dysplasia Network start?
Since 2003, the European Skeletal Dysplasia Network has used an online system to diagnose cases referred to the network before mutation analysis to study the mutations causing PSACH or MED.
What is the most common mutation in COL9A1?
The COMP gene is mutated in 70% of the molecularly confirmed MED patients. Mutations are in the exons encoding the type III repeats (exons 8–14) and C-terminal domain (exons 15–19). The most common mutations in COL9A1 are in exons 8-10, in COL9A2 in exons 2-4, and in COL9A3 in exons 2-4. Altogether, those mutations cover 10% of the patients. The other 20% of affected people have mutations in MATN3 gene, all found within exon 2. The following testing regime has been recommended by the European Skeletal Dysplasia Network:
What are the pathological mechanisms involved in MED and PSACH?
With this new model, they were able to demonstrate that reduced cell proliferation and increased apoptosis are significant pathological mechanisms involved in MED and PSACH. In 2010, this mouse model allowed a new insight into myopathy and tendinopathy, which are often associated with PSACH and MED. These patients show increased skeletal muscle stress, as indicated by the increase in myofibers with central nuclei. Myopathy in the mutant mouse results from underlying tendinopathy, because the transmission of forces is altered from the normal state. There is a higher proportion of larger diameter fibrils of collagen, but the cross-sectional area of whole mutant tendons was also significantly less than that of the wild-type tendons causing joint laxity and stiffness, easy tiring and weakness. This study is important because those diseases are often mistaken for neurological problems, since the doctor can detect a muscle weakness. This includes many painful and useless clinical neurological examination before the correct diagnosis. In this work, the researchers suggest to the pediatric doctor to perform x-rays before starting the neurological assessment, to exclude the dysplasia.
Is multiple epiphyseal dysplasia autosomal dominant?
Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) encompasses a spectrum of skeletal disorders, most of which are inherited in an autosomal dominant form. However, there is an autosomal recessive form.
Popular Posts:
- 1. the icd-10-cm code assigned for: congestive heart failure
- 2. what is the correct icd-9-cm code for addison's anemia
- 3. icd-10 code for vre
- 4. icd code for surgical site infection
- 5. icd 10 code for vitamin c supplement
- 6. icd-10-pcs code for open reduction internal fixation
- 7. icd 10 code for bacterial cystitis
- 8. what is the correct icd 10 code for volume overload
- 9. icd 10 code for associated aphasia unspecified
- 10. icd 10 code for central retinal artery occlusion left eye