What is the ICD 10 code for Mycobacterium infection?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code B99.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J18.9 Mycobacterium, mycobacterial (infection) A31.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code A31.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code A31.9 ICD-10-CM Codes Adjacent To A31.0 Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
What is the ICD 10 code for dissem Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex?
Disseminated mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (DMAC) A31.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Dissem mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (DMAC) The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM A31.2 became effective on October 1,...
What is cutaneous mycobacterial infection?
Cutaneous mycobacterial infection. A cutaneous infection caused by mycobacterium ulcerans. It presents with painless nodular swelling of the skin, leading to the formation of necrotizing ulcers. A lesion in the skin and subcutaneous tissues due to infections by mycobacterium ulcerans. It was first reported in uganda, africa.
What is non-tuberculous mycobacterial pneumonia?
Non-tuberculous mycobacterial pneumonia. Pulmonary mycobacterial avium. Pulmonary mycobacterium avium complex infection. ICD-10-CM A31.0 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 177 Respiratory infections and inflammations with mcc.
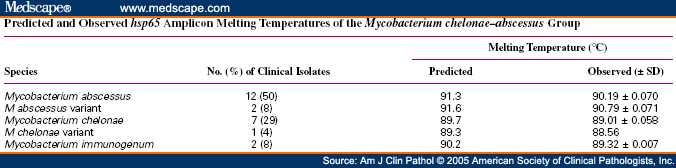
What is the ICD 10 code for Mycobacterium Abscessus?
A31. 0 - Pulmonary mycobacterial infection | ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD 10 code for MAC?
ICD-10-CM Code for Disseminated mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex (DMAC) A31. 2.
What is Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare infection?
MAC lung disease is an infection caused a group of bacteria called Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). MAC includes two closely related species, Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare, and may also be referred to as MAI.
What is a pulmonary mycobacterial infection?
Mycobacterial lung infections are caused by a group of bacteria, mycobacteria, that includes the causative-agents of tuberculosis (TB) and leprosy. There are also nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM), ubiquitous in soil, water, food, on the surfaces of many plants and within buildings, particularly within water pipes.
What is MAC pulmonary disease?
MAC Lung Disease is an uncommon infection caused by Mycobacterium Avium Complex (MAC). It has a thick, protective, and waxy cell wall, and found in dust, soil, and water. While most people come into contact with the MAC bacteria, only a few become infected and are severely impacted by it.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is the difference between MAC and MAI lung disease?
A: “Mycobacterium avium intracellulare” (MAI) or “Mycobacterium avium Complex” (MAC) is an atypical NON-TB germ (micro-organism). MAC is related to the tuberculosis germ, but is not contagious and the MAC microbes live in the environment. It comprises more than one type of microorganism (both M. avium and M.
Are mycoplasma and Mycobacterium the same?
The shorthand for these two diseases of cattle is the same, but they completely different bacteria: Mycobacterium bovis and Mycoplasma bovis. Every bacteria has a specific name, so that we can identify them better – the “surname” (in this case Mycobacterium and Mycoplasma) and then a “first name” (bovis).
What is the difference between MAC and TB?
M. tuberculosis is spread through the air. MAC is a common bacterium found primarily in water and soil. You can contract it when you drink or wash with contaminated water or handle soil or eat food with MAC-containing particles on it.
What is Mycobacterium other than tuberculosis?
Nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) are mycobacteria other than M. tuberculosis (the cause of tuberculosis) and M. leprae (the cause of leprosy). NTM are also referred to as atypical mycobacteria, mycobacteria other than tuberculosis (MOTT), or environmental mycobacteria.
What is mycobacterial disease?
Nontuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) lung disease is a general term for a group of disorders characterized by exposure to specific bacterial germs known as mycobacteria. These germs are found in the water and soil and are common throughout the environment as a whole. They usually do not cause illness.
What is a common disease caused by a Mycobacterium?
Mycobacteria are a type of germ. There are many different kinds. The most common one causes tuberculosis. Another one causes leprosy. Still others cause infections that are called atypical mycobacterial infections.
Coding Notes for A31.0 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #177-179 - Respiratory infections and inflammations with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'A31.0 - Pulmonary mycobacterial infection'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code A31.0. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 031.0 was previously used, A31.0 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for hitting on face
- 2. icd 10 code for grade ii diastolic dysfunction
- 3. icd 10 code for chronic right stump wound
- 4. icd 10 code for osteoporosis of forarm
- 5. icd 10 code for diabetes type 2 with osteomyelitis
- 6. icd-10-cm code for benign neoplasm of genitourinary tract, male
- 7. icd 10 code for swallowed battery proximal stomach
- 8. icd-10 code for manipulation under anesthesia left knee
- 9. icd 10 code for thrombosis of the subclavian artery
- 10. icd 10 code for knee plateau fx