What is the ICD 10 code for NSTEMI myocardial infarction?
Non-ST elevation (NSTEMI) myocardial infarction. I21.4 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I21.4 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the latest version of ICD 10 for heart disease?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I25.2 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I25.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 I25.2 may differ. Past myocardial infarction diagnosed by ECG or other investigation, but currently presenting no symptoms
What does include myocardial infarction mean?
"Includes" further defines, or give examples of, the content of the code or category. myocardial infarction specified as acute or with a stated duration of 4 weeks (28 days) or less from onset A disorder characterized by gross necrosis of the myocardium; this is due to an interruption of blood supply to the area.
What are the signs and symptoms of Type 1 myocardial infarction (I22)?
subsequent type 1 myocardial infarction ( I22.-) tobacco dependence ( F17.-) Necrosis of the myocardium, as a result of interruption of the blood supply to the area. It is characterized by a severe and rapid onset of symptoms that may include chest pain, often radiating to the left arm and left side of the neck, dyspnea, sweating, and palpitations.
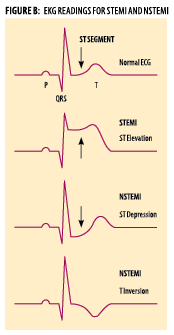
What is a type 2 myocardial infarction?
Type 2 myocardial infarction (MI) is defined by a rise and fall of cardiac biomarkers and evidence of ischemia without unstable coronary artery disease (CAD), due to a mismatch in myocardial oxygen supply and demand. Myocardial injury is similar but does not meet clinical criteria for MI.
Is type 2 MI the same as NSTEMI?
(NSTEMI) is a common diagnosis in hospitalized patients. Type 2 has been reported up to 25% of cases of MI depending on the population studied. Type 2 NSTEMI is defined as myocardial ischemia resulting from mismatched myocardial oxygen supply and demand that is not related to unstable coronary artery disease (CAD).
What is the difference between Type 1 and type 2 myocardial infarction?
Type 1 myocardial infarction occurs in those with atherosclerotic plaque rupture and thrombosis, whereas type 2 myocardial infarction occurs due to myocardial oxygen supply and demand imbalance in the context of an acute illness causing tachyarrhythmia, hypoxia, or hypotension without acute atherothrombosis.
Is type 2 MI stemi or NSTEMI?
Figure 1: Classification of MIMI TypeClassification1STEMI (acute coronary artery thrombosis) NSTEMI (acute coronary artery plaque rupture/erosion)2Supply/demand mismatch (heterogeneous underlying causes)3Sudden cardiac death with ECG evidence of acute myocardial ischemia before cardiac troponins could be drawn2 more rows•Feb 18, 2020
Do we treat type 2 MI?
Treatment of type 2 MI is to treat the underlying condition and hence remove the cardiac insult. To adequately assess the prognosis and determine appropriate further treatment in patients with type 2 MI, information about whether the patient has (or is likely to have) significant underlying CAD is essential.
Is myocarditis a type 2 MI?
Type 2 MI is distinguished from myocardial injury without acute ischemia, for example, acute heart failure and myocarditis.
Is Type 1 or Type 2 MI worse?
Three studies reported 30-day mortality, five studies reported in-hospital mortality, and four studies reported one-year mortality. Two studies reported 30-day MACEs. In-hospital and 30-day death rates were almost three times higher in patients with type 2 MI compared to type 1 MI [in-hospital: 15% for type 2 vs.
What are the 2 types of heart attacks?
Type 1 describes patients with a plaque rupture. Type 2 involves a condition other than coronary artery disease (the plaque-caused hardening of arteries) contributing to an imbalance between the heart's oxygen supply and demand, such as bleeding or a stroke.
What are the 5 types of myocardial infarction?
A heart attack is also known as a myocardial infarction....The three types of heart attacks are:ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)coronary spasm, or unstable angina.
What causes a type 2 myocardial infarction?
Causes of Type II MI The main causes were anemia, followed by sepsis, arrhythmia and post-operation. Sepsis as a cause of type-II MI was more common among patients presenting with STEMI compared with those presenting with NSTEMI (40.7% vs. 19.2%, p = 0.02). Other causes did not differ between STEMI and NSTEMI patients.
What is difference between NSTEMI and STEMI?
NSTEMI is caused by a block in a minor artery or a partial obstruction in a major artery. STEMI occurs when a ruptured plaque blocks a major artery completely.
What can cause Type 2 NSTEMI?
Causes of Type II MI The main causes were anemia, followed by sepsis, arrhythmia and post-operation. Sepsis as a cause of type-II MI was more common among patients presenting with STEMI compared with those presenting with NSTEMI (40.7% vs. 19.2%, p = 0.02). Other causes did not differ between STEMI and NSTEMI patients.
What are the 2 types of heart attacks?
Type 1 describes patients with a plaque rupture. Type 2 involves a condition other than coronary artery disease (the plaque-caused hardening of arteries) contributing to an imbalance between the heart's oxygen supply and demand, such as bleeding or a stroke.
How many types of NSTEMI are there?
Types 1 and 2 MI are spontaneous events, while type 4 and type 5 are procedure-related; type 3 MI is identified only after death. Most type 1 and type 2 MI present as non-ST-elevation MI (NSTEMI), although both types can also present as ST-elevation MI.
What does NSTEMI mean?
Overview. Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) is a type of involving partial blockage of one of the coronary arteries, causing reduced flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.
How long does a myocardial infarction last?
myocardial infarction specified as acute or with a stated duration of 4 weeks (28 days) or less from onset. A disorder characterized by gross necrosis of the myocardium; this is due to an interruption of blood supply to the area. Coagulation of blood in any of the coronary vessels.
What is the code for myocardial infarction?
Codes. I21 Acute myocardial infarction.
What causes a heart muscle to die?
A blockage that is not treated within a few hours causes the affected heart muscle to die. Gross necrosis of the myocardium, as a result of interruption of the blood supply to the area, as in coronary thrombosis. Gross necrosis of the myocardium, as a result of interruption of the blood supply to the area.
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
What is type 1 MI?
Type 1 MI is myocardial necrosis, or cell death, caused by an anatomic blockage of blood flow for a prolonged period of time. This is usually due to atherosclerotic plaque and rupture or thrombosis, causing mechanical coronary artery obstruction. Type 2 MI is also cell death, but in a non-anatomic distribution due to generalized hypoperfusion, ...
What causes Type 2 MI?
There is always an underlying condition or disease process that causes the Type 2 MI. Ischemia means insufficient blood perfusion, and prolonged ischemia leads to infarction, i.e., cell death. When cells die and break down, they release their contents, including troponin, a heart-muscle protein.
Can a second MI be a type 1?
A second Type 1 MI can either be reinfarction in the same anatomic distribution, as an extension of the first MI, or a patient can have another Type 1 MI in a different vessel , with a different area of the heart being affected. Treatment of myocardial infarction has always been informed by the desire to prevent death, reinfarction, ...
Who is Erica Remer?
She was a physician advisor of a large multi-hospital system for four years before transitioning to independent consulting in July 2016. Her passion is educating CDI specialists, coders, and healthcare providers with engaging, case-based presentations on documentation, CDI, and denials management topics. She has written numerous articles and serves as the co-host of Talk Ten Tuesdays, a weekly national podcast. Dr. Remer is a member of the ICD10monitor editorial board, a former member of the ACDIS Advisory Board, and the board of directors of the American College of Physician Advisors.
Does heart tissue regenerate after death?
In general, once heart tissue dies, it does not regenerate and the patient develops scar tissue. It is awesome that we finally have a unique code for Type 2 MI, I21.A1. It does not need artery site specification because that is not relevant.
What is the ICD-10 code for myocardial infarction type 2?
I21.A1 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Myocardial infarction type 2 . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also: Infarct, infarction.
What is the ICd 10 code for acute myocardial infarction?
Acute myocardial infarction, unspecified 1 I21.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM I21.9 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I21.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 I21.9 may differ.
What is Z72.0 in medical terms?
tobacco use ( Z72.0) Acute myocardial infarction. Clinical Information. Necrosis of the myocardium, as a result of interruption of the blood supply to the area. It is characterized by a severe and rapid onset of symptoms that may include chest pain, often radiating to the left arm and left side of the neck, dyspnea, sweating, and palpitations. ...
What is the release of cardiac biomarkers?
The release of cardiac biomarkers indicates myocardial injury. A significant trending of troponin indicates myocardial infarction. Typical signs and symptoms suggestive of ischemia are chest, jaw, or arm pain, dyspnea, and diaphoresis, but other symptoms may predominate, such as fatigue, nausea, or syncope.
What is MI in cardiology?
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) is the term for myocardial necrosis, or cell death, in a clinical setting, consistent with myocardial ischemia. “Ischemia” implies insufficient blood perfusion, and prolonged ischemia results in cell death.
What is the third universal definition of myocardial infarction?
Such is the case with troponin. In October 2012, the Third Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (TUDMI) was published by the American Heart Association, redefining myocardial infarction (MI).
What is a type 5 MI?
Type 5 MI, related to coronary artery bypass grafting. If the troponin is elevated but it does not constitute a Type 2 MI, there are numerous ways to refer to it, such as troponinemia, troponin leak, and non-zero troponin.
What is the implication of Type 2 MI?
There is always an underlying etiology. The implication of a Type 2 MI is that it portends a worse prognosis for the causative condition.
Who is Erica Remer?
She was a physician advisor of a large multi-hospital system for four years before transitioning to independent consulting in July 2016. Her passion is educating CDI specialists, coders, and healthcare providers with engaging, case-based presentations on documentation, CDI, and denials management topics. She has written numerous articles and serves as the co-host of Talk Ten Tuesdays, a weekly national podcast. Dr. Remer is a member of the ICD10monitor editorial board, a former member of the ACDIS Advisory Board, and the board of directors of the American College of Physician Advisors.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for vulvitis
- 2. icd 10 code for recurrent asuteros
- 3. icd 9 code for knee derangement
- 4. icd 10 code for skin tag on labia
- 5. icd 10 code for fecal impaction in rectum
- 6. icd 10 cm code for herpangina
- 7. icd 10 code for acute bilateral knee pain
- 8. icd 10 code for palmar erythema
- 9. icd 10 code for nubian gastrointestinal
- 10. icd 10 code for right labial barthlin cyst