What is the ICD 10 code for narrow angle eye?
Anatomical narrow angle, unspecified eye. H40.039 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H40.039 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for glaucoma with angle closure?
Unspecified primary angle-closure glaucoma, stage unspecified. H40.20X0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the H40 ICD-10 reference for glaucoma?
ICD-10 Glaucoma Reference Guide H40.00 Preglaucoma, unspecified H40.001 Right eye H40.002 Left eye H40.003 Bilateral Excludes1 Absolute glaucoma H44.51-Congenital glaucoma Q15.0 Traumatic glaucoma due to birth injury P15.3 H40.01 Open angle with borderline findings, low risk (1–2 risk factors) Open angle, low risk H40.011 Right eye H40.012 Left eye
What is the ICD 10 code for trauma to the eye?
H40.039 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H40.039 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H40.039 - other international versions of ICD-10 H40.039 may differ. injury (trauma) of eye and orbit ( S05.-)
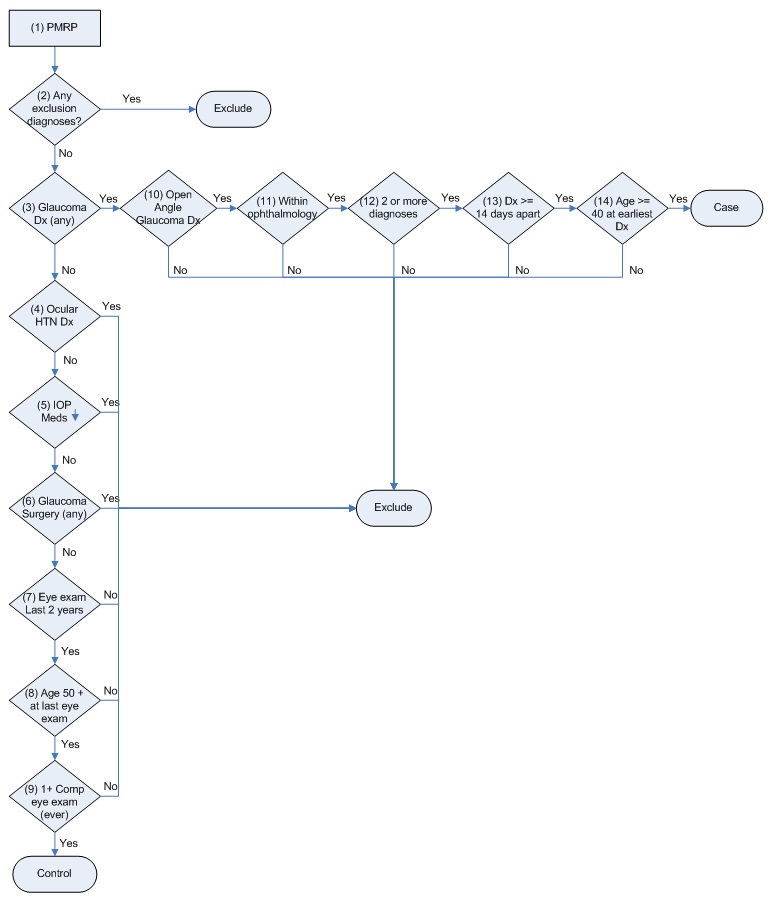
What is the ICD-10 code for narrow angle glaucoma?
ICD-10 code H40. 03 for Anatomical narrow angle is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the eye and adnexa .
Is narrow angles the same as glaucoma?
Anatomically Narrow Angles However, it is important to understand that being at risk for glaucoma and having glaucoma are different. People with anatomically narrow angles carry only the predisposition to glaucoma without any evidence of glaucoma itself.
What does narrow angles in the eye mean?
Narrow angles refers to the anatomy at the front of the eye called the drainage angle. This is where fluid called aqueous humor drains from the eye. In someone with narrow angles, the iris and the cornea are too close together.
What is narrow lens glaucoma?
Narrow-angle glaucoma is a type of glaucoma that occurs when the structure inside the eye that allows fluid to drain normally from the eye (called the drainage angle) becomes restricted.
What is the difference between iridotomy and iridectomy?
Iridectomy is a similar procedure to iridotomy, and it is usually performed for similar reasons. The difference is that rather than creating a hole in the iris, the surgeon removes part of it.
What is the difference between narrow angle and closed angle glaucoma?
There are also some important differences: In open-angle, eye pressure builds gradually, but in closed-angle, it's far more sudden. Open-angle glaucoma is not a medical emergency, but can cause vision issues over time; closed-angle is a medical emergency requiring immediate medical attention.
Do all people with narrow angles get glaucoma?
Not all people with narrow angles need to be treated as not everyone will get acute angle closure glaucoma. At Skouras Eye and Cosmetic Centre, we provide patients with a comprehensive eye examination and advanced tests and imaging to assess your risk for acute angle closure glaucoma.
How common is narrow-angle glaucoma?
The term narrow angle refers to an anatomical condition in which there is irido-trabecular apposition caused by any number of factors. The incidence of narrow-angle glaucoma in the general population is around 1 percent, increasing in Inuit Eskimo and East Asian individuals.
Which drug should not be used in narrow-angle glaucoma?
Here is a list of numerous narrow angle glaucoma medications to avoid: Allergy/Cold Remedies: Diphenhydramine, Ephedrine. Anxiety: Vistaril (hydroxyzine) Asthma/COPD: Atrovent (ipratroprium bromide), Spiriva (tiotropium bromide)
What is anatomical narrow angle bilateral?
Anatomical narrow angles are characterized by the abnormally small space/ angle between the cornea and the iris (colored part of the eye). This condition leaves one predisposed to the development of angle closure events or glaucoma (where the flow of fluid out of the eye is impeded).
What is subcapsular glaucomatous flecks?
Clinical Information. A condition in which there is a build-up of fluid in the eye, which presses on the retina and the optic nerve. The retina is the layer of nerve tissue inside the eye that senses light and sends images along the optic nerve to the brain.
What is ocular disease?
An ocular disease, occurring in many forms, having as its primary characteristics an unstable or a sustained increase in the intraocular pressure which the eye cannot withstand without damage to its structure or impairment of its function . The consequences of the increased pressure may be manifested in a variety of symptoms, depending upon type and severity, such as excavation of the optic disk, hardness of the eyeball, corneal anesthesia, reduced visual acuity, seeing of colored halos around lights, disturbed dark adaptation, visual field defects, and headaches. (dictionary of visual science, 4th ed)
What causes blindness in the eye?
Glaucoma damages the eye's optic nerve. It is a leading cause of blindness in the United States. It usually happens when the fluid pressure inside the eyes slowly rises, damaging the optic nerve. Often there are no symptoms at first, but a comprehensive eye exam can detect it.
When will the ICD-10-CM H40.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H40.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How to protect eyes from vision loss?
early treatment can help protect your eyes against vision loss. Treatments usually include prescription eyedrops and/or surgery. nih: national eye institute. Group of diseases characterized by increased intraocular pressure resulting in damage to the optic nerve and retinal nerve fibers.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for abraision insde throat
- 2. icd 10 code for excess abdominal fat
- 3. icd 10 code for premature 28 weeks
- 4. icd 10 code for uti pregnancy
- 5. icd 10 code for loa
- 6. 2016 icd 10 code for retained products of blood
- 7. icd 10 code for chronic leg ulcer bilateral
- 8. icd 10 code for hepatitis b s antibody
- 9. icd-10-cm code for respiratory failure
- 10. icd 10 code for back apin