What does neonatal abstinence syndrome mean?
The ICD code P961 is used to code Neonatal withdrawal. Neonatal withdrawal or neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) is a withdrawal syndrome of infants, caused by the cessation of the administration of licit or illicit drugs. Tolerance, dependence, and withdrawal may occur as a result of repeated administration of drugs or even after short-term high dose use—for example …
When does a newborn suffered neonatal abstinence syndrome?
ICD10 codes matching "Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome" Codes: = Billable. P96.1 Neonatal withdrawal symptoms from maternal use of drugs of addiction
What is the prognosis of Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS)?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code O09.29. Supervision of pregnancy with other poor reproductive or obstetric history. Suprvsn of pregnancy w poor reprodctv or obstetric history; Supervision of pregnancy with history of neonatal death; Supervision of pregnancy with history of stillbirth. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code O09.29.
What is the abbreviation for neonatal abstinence syndrome?
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index is designed to allow medical coders to look up various medical terms and connect them with the appropriate ICD codes. There are 5 terms under the parent term 'Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome' in the ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index . Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome - see also Newborn acne L70.4 bradycardia P29.12
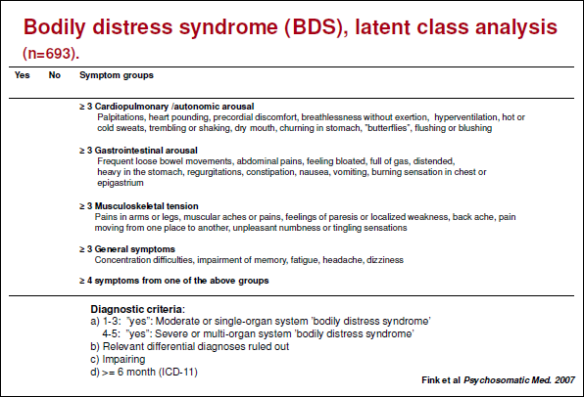
What is newborn abstinence syndrome?
Neonatal abstinence syndrome (also called NAS) is a group of conditions caused when a baby withdraws from certain drugs he's exposed to in the womb before birth. NAS is most often caused when a woman takes drugs called opioids during pregnancy.
Is neonatal abstinence syndrome a medical diagnosis?
How is neonatal abstinence syndrome diagnosed? The diagnosis is made based on a history of medicine or substance use in the mother, or on a baby's symptoms. An accurate report of the mother's drug use is important. This includes the time the last drug was taken.
What is neonatal abstinence syndrome CDC?
Neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS) is a withdrawal syndrome that can occur in newborns exposed to certain substances, including opioids, during pregnancy. A new CDC article looked at laws enacted in six states that make health departments or hospitals report all babies born with NAS for public health monitoring.
What are some examples of neonatal abstinence syndrome?
Neonatal abstinence syndrome, or NAS, develops after a baby is born and no longer gets certain drugs or medicine from the mother. Some examples might be methadone, heroin and percocet.
What is neonatal abstinence syndrome NHS?
Once delivered and the umbilical cord has been cut, your baby's drug supply suddenly ceases causing your baby to begin the withdrawal process known as Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome (NAS). This withdrawal process is similar to the effects you would feel if you suddenly stopped taking your drugs.
What is the 1st line of treatment indicated in infants presenting with neonatal abstinence syndrome?
Even though non-pharmacological treatment remains the first line, AAP endorses the use of pharmacotherapy when indicated, keeping in mind that it is also associated with a more extended overall stay in the hospital, which is detrimental to the mother-infant dyad.
What is total abstinence?
While stimulant addicts are of course at the highest risk when using stimulants, “total abstinence” means avoiding other psychoactive substances as well.
Who is at risk for neonatal abstinence syndrome?
Infants who have been exposed to opioids in the womb are at risk of developing symptoms of opioid dependence and withdrawal, known as neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), at birth.Jan 8, 2019
How do you manage neonatal abstinence syndrome?
Pharmacologic Treatment of NAS. Several medications including paregoric, tincture of opium, phenobarbital, morphine, methadone, buprenorphine and clonidine have been employed to treat NAS. The AAP and Cochrane Reviews have concluded that opioids are ideal treatment for neonates exposed to opioids in utero [25, 35, 36].Jun 16, 2014
How many babies are born with neonatal abstinence syndrome?
Over 20,000 babies are born each year dependent on illegal or prescription drugs and suffer neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), a type of opiate withdrawal.
Can neonatal abstinence syndrome be prevented?
Neonatal abstinence syndrome can be prevented. Avoid opiates and other drugs during pregnancy. You also should avoid alcohol and tobacco. Talk to your doctor about the medicines you take or if you have an addiction.Jul 24, 2019
What is a neonatal drug withdrawal syndrome?
Clinical Information. A constellation of signs and symptoms observable in a neonate that are consistent with maternal substance abuse or withdrawal while pregnant. Fetal and neonatal addiction and withdrawal as a result of the mother's dependence on drugs during pregnancy.
What are the symptoms of fetal addiction?
Withdrawal or abstinence symptoms develop shortly after birth. Symptoms exhibited are loud, high-pitched crying, sweating, yawning and gastrointestinal disturbances.
What is the P58.4?
jaundice due to drugs or toxins transmitted from mother or given to newborn ( P58.4-) reactions and intoxications from maternal opiates, tranquilizers and other medication ( P04.0- P04.1, P04.4-) withdrawal symptoms from maternal use of drugs of addiction ( P96.1)
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. A constellation of signs and symptoms observable in a neonate that are consistent with maternal substance abuse or withdrawal while pregnant.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for acute otitis media bilateral
- 2. icd 10 cm code for l leg burn,
- 3. icd 10 code for wernickes encephalopathy
- 4. icd 10 code for elevated ebv
- 5. icd 10 code for icd9 373.11
- 6. icd 9 code for thrombocytopathy
- 7. icd 10 code for lumbalgia with radiculitis
- 8. icd-10-pcs code for diverting loop ileostomy
- 9. icd 10 code for fx of pip
- 10. icd 10 code for right hip surgical wound