What is the ICD 10 code for nephropathy?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N14.2. Nephropathy induced by unspecified drug, medicament or biological substance. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code.
What is the ICD 10 code for idiopathic neuropathy?
ICD-10 codes for this scenario would be: G60.9 – Idiopathic neuropathy. Note: Neuropathy idiopathic indexes to G60.9 in the index of ICD-10 CM manual. Neuropathy is idiopathic when underlying cause is unknown.
What is the ICD 10 code for polyneuropathy?
Neuropathy, neuropathic G62.9 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G62.9 Polyneuropathy, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code Applicable To Neuropathy NOS. acute motor G62.81. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G62.81. Critical illness polyneuropathy. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To.
How to code peripheral neuropathy with diabetes?
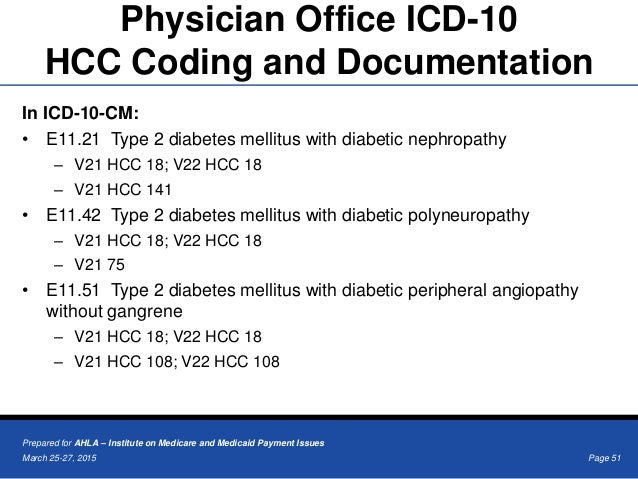
Check whether patient has diabetes or not. If yes, neuropathy and diabetes needs to be combined and coded regardless of it is polyneuropathy, autonomic neuropathy, mononeuropathy or unspecified neuropathy. Peripheral neuropathy with diabetes should be coded as E11.42 (DM with polyneuropath), not e11.40 (DM with neuropathy).
Where is the ICd 10 code for neuropathy?
What is the code for neuropathy?
What is the code for peripheral neuropathy?
What are the symptoms of autonomic neuropathy?
What tests are used to diagnose neuropathy?
Can peripheral neuropathy cause tingling?
Can neuropathy be transferred from parent to child?
See 2 more
What is a nephropathy?
Nephropathy is the deterioration of kidney function. The final stage of nephropathy is called kidney failure, end-stage renal disease, or ESRD. According to the CDC, diabetes is the most common cause of ESRD.
What is ICD-10 code for IGA nephropathy?
3.
What is the ICD-10 code for diabetic nephropathy?
ICD-10-CM Code for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with diabetic nephropathy E11. 21.
What is diagnosis code N28 9?
N28. 9, disorder of kidney and ureter, unspecified.
What code is n18 9?
9: Chronic kidney disease, unspecified.
Is IgA nephropathy a glomerulonephritis?
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is an antibody that plays a key role in your immune system by attacking invading pathogens and fighting infections. But in IgA nephropathy, this antibody collects in the glomeruli, causing inflammation (glomerulonephritis) and gradually affecting their filtering ability.
Can you code E11 22 and E11 21?
The incorrect portion of the response came as an aside at the end, where it was stated that “it would be redundant to assign codes for both diabetic nephropathy (E11. 21) and diabetic chronic kidney disease (E11. 22), as diabetic chronic kidney disease is a more specific condition.” It is true you wouldn't code both.
What is the difference between E11 21 and E11 22?
E11. 22 states within its code DM with CKD therefore it is a more accurate code than E11. 21 which is just DM with Nephropathy (any kidney condition).
What is a E11 21?
ICD-10 code: E11. 21 Type 2 diabetes mellitus With renal complications Uncontrolled.
What is R79 89?
ICD-10 code R79. 89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD-10 code for acute on chronic kidney disease?
Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease ICD-10-CM Code range N17-N19. The ICD-10 code range for Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease N17-N19 is medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO).
What is the ICD-10 code for worsening renal function?
Abnormal results of kidney function studies The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R94. 4 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is disorder of kidney and ureter?
A ureteral obstruction is a blockage in one or both of the tubes (ureters) that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder. Ureteral obstruction can be cured. However, if it's not treated, symptoms can quickly move from mild — pain, fever and infection — to severe — loss of kidney function, sepsis and death.
What is Hydro kidney?
Hydronephrosis is swelling of one or both kidneys. Kidney swelling happens when urine can't drain from a kidney and builds up in the kidney as a result. This can occur from a blockage in the tubes that drain urine from the kidneys (ureters) or from an anatomical defect that doesn't allow urine to drain properly.
What is the ICD 10 code for dementia?
F02. 8* Dementia in other specified diseases classified elsewhere.
Code for Neuropathic Pain? | Medical Billing and Coding Forum - AAPC
If this is your first visit, be sure to check out the FAQ & read the forum rules.To view all forums, post or create a new thread, you must be an AAPC Member.If you are a member and have already registered for member area and forum access, you can log in by clicking here.If you've forgotten your username or password use our password reminder tool.
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code G62.89
Approximate Synonyms. Neuropathy (nerve damage), multifocal motor; ICD-10-CM G62.89 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group(s) (MS-DRG v 39.0):. 073 Cranial and peripheral nerve disorders with mcc; 074 Cranial and peripheral nerve disorders without mcc; Convert G62.89 to ICD-9-CM. Code History. 2016 (effective 10/1/2015): New code (first year of non-draft ICD-10-CM)
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code E11.40
Free, official coding info for 2022 ICD-10-CM E11.40 - includes detailed rules, notes, synonyms, ICD-9-CM conversion, index and annotation crosswalks, DRG grouping and more.
Where is the ICd 10 code for neuropathy?
Most of the neuropathy ICD 10 codes are located in Chapter-6 of ICD-10-CM manual which is “diseases of the nervous system”, code range G00-G 99
What is the code for neuropathy?
Neuropathic pain should be coded as neuralgia M79.2, not neuropathy.
What is the code for peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy with diabetes should be coded as E11.42 (DM with polyneuropath), not e11.40 (DM with neuropathy).
What are the symptoms of autonomic neuropathy?
Autonomic neuropathy symptoms can be heart intolerance, excess sweat or no sweat, blood pressure changes, bladder, bowel or digestive problems. Physician does a thorough physical examination including extremity neurological exam and noting vitals.
What tests are used to diagnose neuropathy?
Detailed history of the patient like symptoms, lifestyle and exposure to toxins may also help to diagnose neuropathy. Blood tests, CT, MRI, electromyography, nerve biopsy and skin biopsy are the tests used to confirm neuropathy.
Can peripheral neuropathy cause tingling?
Symptoms can vary in both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy because the nerves affected are different. Peripheral neuropathy symptoms can be tingling, sharp throbbing pain, lack of coordination, paralysis if motor nerves are affected. Autonomic neuropathy symptoms can be heart intolerance, excess sweat or no sweat, blood pressure changes, bladder, bowel or digestive problems.
Can neuropathy be transferred from parent to child?
There is hereditary neuropathy also which get transferred from parent to child. Neuropathy can occur in any nerve of the body, but peripheral neuropathy is the common type seen in most of the people. As the name says peripheral neuropathy affects peripheral nerves usually extremities (hands and feet).
Where is the ICd 10 code for neuropathy?
Most of the neuropathy ICD 10 codes are located in Chapter-6 of ICD-10-CM manual which is “diseases of the nervous system”, code range G00-G 99
What is the code for neuropathy?
Neuropathic pain should be coded as neuralgia M79.2, not neuropathy.
What is the code for peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy with diabetes should be coded as E11.42 (DM with polyneuropath), not e11.40 (DM with neuropathy).
What are the symptoms of autonomic neuropathy?
Autonomic neuropathy symptoms can be heart intolerance, excess sweat or no sweat, blood pressure changes, bladder, bowel or digestive problems. Physician does a thorough physical examination including extremity neurological exam and noting vitals.
What tests are used to diagnose neuropathy?
Detailed history of the patient like symptoms, lifestyle and exposure to toxins may also help to diagnose neuropathy. Blood tests, CT, MRI, electromyography, nerve biopsy and skin biopsy are the tests used to confirm neuropathy.
Can peripheral neuropathy cause tingling?
Symptoms can vary in both peripheral and autonomic neuropathy because the nerves affected are different. Peripheral neuropathy symptoms can be tingling, sharp throbbing pain, lack of coordination, paralysis if motor nerves are affected. Autonomic neuropathy symptoms can be heart intolerance, excess sweat or no sweat, blood pressure changes, bladder, bowel or digestive problems.
Can neuropathy be transferred from parent to child?
There is hereditary neuropathy also which get transferred from parent to child. Neuropathy can occur in any nerve of the body, but peripheral neuropathy is the common type seen in most of the people. As the name says peripheral neuropathy affects peripheral nerves usually extremities (hands and feet).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for bronchitis, not specified as acute or chronic
- 2. what is the icd 10 code for after care for right tha
- 3. icd 10 code for stenosis of av fistula
- 4. icd 9 code for cat bite
- 5. what is the icd 10 code for right ventricular collapse
- 6. icd 10 code for mrsa abcess
- 7. icd 10 code for allergy to medication
- 8. what is the icd 10 code for jaw pain'
- 9. icd 10 code for thoracolumbar foraminal narro
- 10. icd 10 code for burn 2nd degree right forearm