Unspecified mental disorder due to known physiological condition. F09 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM F09 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What does Nos mean in ICD?
Apr 15, 2020 · Also know, what is the ICD 10 CM code for major neurocognitive disorder? G31. 84 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM G31. 84 became effective on October 1, 2019. Furthermore, what are some of the treatments for neurocognitive disorders? Medications. …
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · Mild neurocognitive disorder due to traumatic brain injury Minimal cognitive impairment ICD-10-CM G31.84 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v39.0): 056 Degenerative nervous system disorders with mcc 057 Degenerative nervous system disorders without mcc Convert G31.84 to ICD-9-CM Code History
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R41.9 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Unspecified symptoms and signs involving cognitive functions and awareness Unsp symptoms and signs w cognitive functions and awareness; Unspecified neurocognitive disorder ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code H61.10 Unspecified noninfective disorders of pinna Disorder of pinna NOS
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. R41.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Unsp symptoms and signs w cognitive functions and awareness; The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R41.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
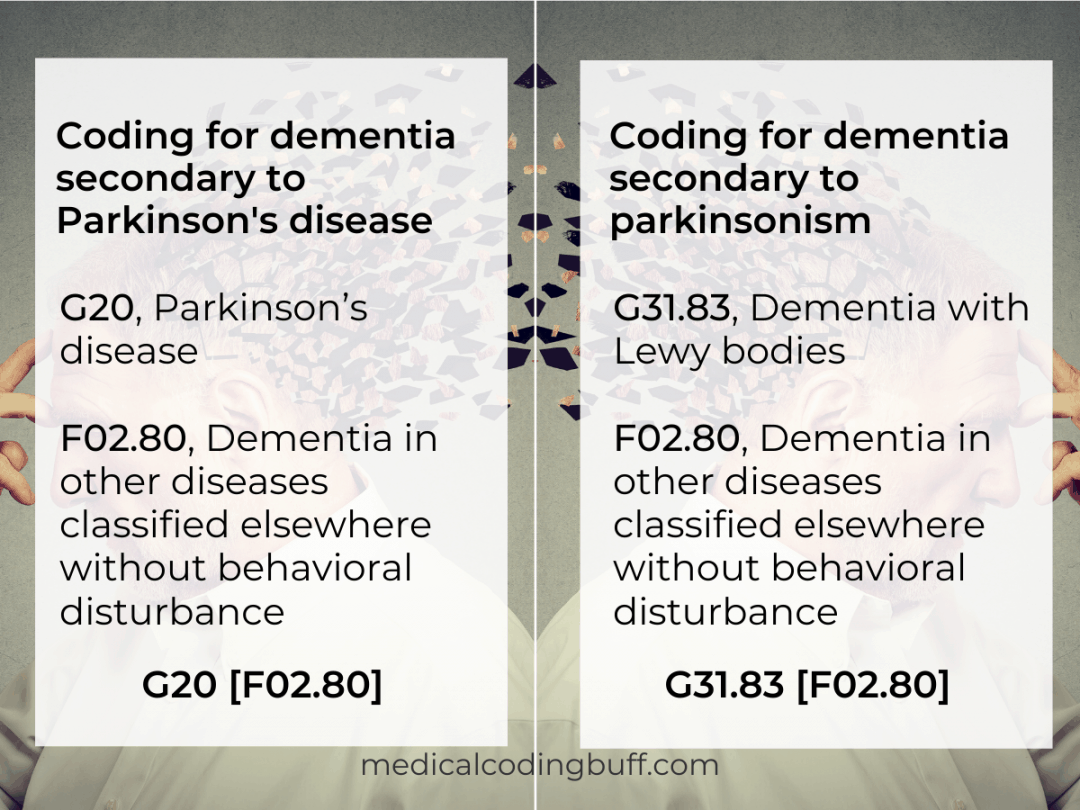
What is cognitive Disorder NOS?
What is the ICD-10 code for mild neurocognitive disorder?
Which of the following is the ICD-10 code for possible major neurocognitive disorder due to Alzheimer's disease?
What is unspecified neurocognitive disorder?
What is the most common neurocognitive disorder?
What is minor neurocognitive disorder?
How do you code major neurocognitive disorder?
What is the ICD-10 code for major neurocognitive disorder with behavioral disturbance?
What is the ICD-10 code for dementia without behavioral disturbance?
What are the three types of neurocognitive disorders?
What are the types of neurocognitive disorders?
- Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of neurocognitive disorder. ...
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. ...
- Dementia with Lewy bodies. ...
- Frontotemporal dementia. ...
- Parkinson's disease. ...
- Huntington's disease. ...
- Mixed dementia. ...
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus.
Is neurocognitive disorder the same as dementia?
Is mild cognitive impairment reversible?
How is neurocognitive disorder treated?
What does the title of a diagnosis code mean?
The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code. "In diseases classified elsewhere" codes are never permitted to be used as first listed or principle diagnosis codes. They must be used in conjunction with an underlying condition code and they must be listed following the underlying condition.
What is F02.81?
F02.81 describes the manifestation of an underlying disease, not the disease itself. Applicable To. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with aggressive behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with combative behavior. Dementia in other diseases classified elsewhere with violent behavior.
Is neurocognitive disorder a secondary diagnosis?
Since both major and mild neurocognitive disorders are used as secondary diagnosis to indicate the severity of cognitive decline in other disorders, it is typically co-morbid with at least one other disorder. When coding for mild neurocognitive disorder, it is important to note whether it is accompanied by behavioral disturbances as well ...
What is mild neurocognitive disorder?
Mild neurocognitive disorder is a sub-diagnosis used to indicate the severity of other mental disorders, including dementia, brain injury, and other cognitive disorders. It is important to note that both major and minor neurocognitive disorder are distinct from developmental and intellectual disabilities ...
Can neurocognitive disorders be treated?
While there are no direct treatments for mild neurocognitive disorder or the dementia it is typically associated with, many of the other co-morbid diseases diagnosed along with mild neurocognitive disorder. There is evidence that group-based cognitive remediation treatment in patients with mild neuro cognitive disorder and bipolar disorder shows improved verbal memory, attention, executive function, and psychosocial function, indicating that this treatment option may be viable for patients diagnosed with mild neurocognitive disorder caused by other etiologies (Demant, Almer, Vinberg, Kessing, & Miskowiak, 2013).
Is mild neurocognitive disorder co-morbid?
Since both major and mild neurocognitive disorders are used as secondary diagnosis to indicate the severity of cognitive decline in other disorders, it is typically co-morbid with at least one other disorder. When coding for mild neurocognitive disorder, it is important to note whether it is accompanied ...

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for status post small bowel resection
- 2. icd 10 code for hronuic use opioid analgesia
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for follow up for surgery on heart
- 4. icd-10 code for callus left foot
- 5. icd 10 code for viral pneumonia due to covid
- 6. icd 10 cm code for burn cooking oil, work
- 7. icd 10 cm code for soft tissue amputation-right thumb.
- 8. 2016 icd 10 code for fractured proximal tibia
- 9. icd 10 code for seryum prptein
- 10. icd 10 code for gluten sensitive enteropathy