What is a Grade 1 neuroendocrine tumour?
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) are classified by tumor grade, which describes how quickly the cancer is likely to grow and spread. Grade 1 (also called low-grade or well-differentiated) neuroendocrine tumors have cells that look more like normal cells and are not multiplying quickly.
How can neuroendocrine tumors be prevented?
What you can do
- Be aware of any pre-appointment restrictions. ...
- Write down any symptoms you're experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to the reason for which you scheduled the appointment.
- Write down key personal information, including any major stresses or recent life changes.
- Make a list of all medications, vitamins or supplements that you're taking.
What are neuroendocrine tumours?
There are several types of neuroendocrine tumours including:
- gastro-intestinal which start in the large and small bowel
- pancreatic which account for about 7% of neuroendocrine tumours
- lung
- merkel cell carcinoma which involves the Merkel cells in the top layer of the skin
- neuroblastoma which usually starts in the adrenal glands and affects immature or developing nerve cells in children.
Who is at risk for neuroendocrine tumors?
The risk of neuroendocrine tumors is higher in people who inherit genetic syndromes that increase the risk of cancer. Examples include: There is a problem with information submitted for this request.
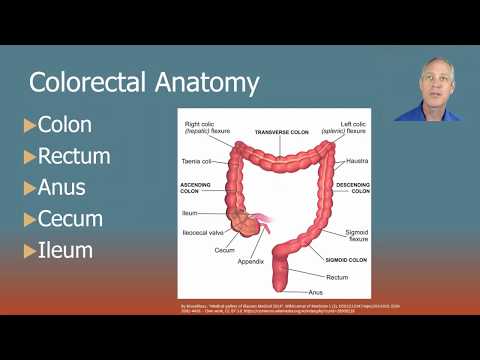
What is the diagnosis code for neuroendocrine tumor?
C7A. 1 - Malignant poorly differentiated neuroendocrine tumors | ICD-10-CM.
Is small cell lung cancer the same as neuroendocrine?
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is the most common form of neuroendocrine lung cancer. A rare form of neuroendocrine lung cancer is called large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma.
What is Neuroendocrine Tumours?
A neuroendocrine tumour is a rare tumour that can develop in many different organs of the body. It affects the cells that release hormones into the bloodstream (neuroendocrine cells).
Are carcinoid and neuroendocrine tumors the same?
Overview. Carcinoid tumors are a type of slow-growing cancer that can arise in several places throughout your body. Carcinoid tumors, which are one subset of tumors called neuroendocrine tumors, usually begin in the digestive tract (stomach, appendix, small intestine, colon, rectum) or in the lungs.
Is neuroendocrine tumor lung cancer?
This type of tumor is called a “non-functional" NET. There are other types of NETs that develop in the lung. They include small cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (also called small cell lung cancer) and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma (a type of non-small cell lung cancer).
What type of cancer is neuroendocrine cancer?
Neuroendocrine tumors are cancers that begin in specialized cells called neuroendocrine cells. Neuroendocrine cells have traits similar to those of nerve cells and hormone-producing cells. Neuroendocrine tumors are rare and can occur anywhere in the body.
What is the difference between endocrine and neuroendocrine?
Endocrine – adrenocorticol carcinoma (ACC) arises within the cortex, and may be associated with excess secretion of steroidal hormones. TNM staging. Neuroendocrine – pheochromocytoma arises within the medulla, and may be associated with the overproduction of catecholamines.
Where is neuroendocrine tumor?
They are distributed throughout the body, but the most common places for tumors to develop from them are in the lungs, small intestines and pancreas. Are all neuroendocrine tumors cancerous? The short answer is yes.
What is the most common neuroendocrine tumor?
Insulinoma. Insulinomas are the most common functioning pancreatic endocrine tumors.
What is the difference between adenocarcinoma and neuroendocrine?
While each type of tumor can spread (metastasize) from the pancreas to other organs, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors usually spread over a period of years. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, on the other hand, typically spreads over a period of months.
What are types of neuroendocrine tumors?
Types of Neuroendocrine TumorsCarcinoid tumors in the lungs, gastrointestinal tract or thymus.Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (islet cell cancer)Medullary thyroid carcinoma.Merkel cell carcinoma (neuroendocrine carcinoma of the skin)Pheochromocytoma of the adrenal gland.Adrenal cancer.More items...
What is typical carcinoid tumor of lung?
What is a lung carcinoid tumor? A lung carcinoid tumor is a type of cancerous tumor made up of neuroendocrine cells. These cells are found throughout the body, including the lungs. They are similar to endocrine cells because both produce hormones or hormone-like substances.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for fracture r humerus
- 2. icd 10 code for left trimalleolar fracture
- 3. icd-9 code for adjustment disorder with mixed disturbance of emotions and conduct
- 4. icd 10 cm code for medication request
- 5. icd-10 cm code for overanxious disorder icd 10
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for peripheral arterial disease
- 7. icd 10 code for secondary peritoneal cancer
- 8. icd 10 code for cva prophylaxis
- 9. icd 9 code for severe renal insufficiency, gfr 20
- 10. icd 10 code for keloid formation