Are You newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation?
The patient with newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation. The NHFA’s AF guidelines recommend opportunistic AF screening in patients aged ≥65 years with either radial pulse palpation followed by a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) or a single-lead handheld ECG. 9 Therefore, AF can be diagnosed: during routine cardiac screening; because of new onset symptoms
What is the ICD 10 code for rapid AFIB?
Unspecified atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation; Atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I48.91. Unspecified atrial fibrillation. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I48.0 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation.
How does a doctor diagnose atrial fibrillation?
Your doctor will likely start by asking if you have any of these afib symptoms:
- Feeling weak, dizzy or tired
- Racing heartbeat
- Skipped heartbeats
- Sweating with chest pain
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.

What is the 2021 ICD-10 code for AFib with RVR?
The code for “atrial fibrillation with RVR” is I48. 91 Unspecified atrial fibrillation.
What is diagnosis code I48 92?
I48. 92 - Unspecified atrial flutter. ICD-10-CM.
What is RVR?
Rapid ventricular rate or response (RVR) These chambers fibrillate, or quiver, rapidly. The result is a rapid and irregular pumping of blood through the heart. In some cases of AFib, the fibrillation of the atria causes the ventricles, or lower chambers of the heart, to beat too fast.
What I48 91?
ICD-10 code I48. 91 for Unspecified atrial fibrillation is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What is AFib with RVR?
A-fib with RVR is the common term for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response. A common disorder that involves a rapid heart rate, it requires medical attention and, in many cases, hospitalization.
Is atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation the same?
Atrial flutter is similar to atrial fibrillation, a common disorder that causes the heart to beat in irregular patterns. People with atrial flutter have a heart rhythm that's more organized and less chaotic than that of atrial fibrillation.
How can you tell the difference between AFib and SVT?
Sinus tach and most SVTs have only one P wave for each QRS complex. They may or may not be buried in the preceding T waves. But there are other supra-ventricular tachycardias that have more than one P wave for each QRS or no P waves. Atrial fibrillation has no P waves.
What is paroxysmal AFib?
When your heartbeat returns to normal within 7 days, on its own or with treatment, it's known as paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. It can happen a few times a year or as often as every day. It often becomes a permanent condition that needs regular treatment.
How is RVR determined?
Measurement. Originally RVR was measured by a person, either by viewing the runway lights from the top of a vehicle parked on the runway threshold, or by viewing special angled runway lights from a tower at one side of the runway. The number of lights visible could then be converted to a distance to give the RVR.
What is diagnosis code Z51 81?
ICD-10 code Z51. 81 for Encounter for therapeutic drug level monitoring is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Factors influencing health status and contact with health services .
What I48 19?
I48. 19 - Other persistent atrial fibrillation | ICD-10-CM.
What is atypical atrial flutter?
Atypical atrial flutter, while similar in heartbeat abnormality to Type 1 Atrial Flutter, refers to the clockwise pattern of electrical impulses of the heart beat pattern.
How to regulate heartbeat?
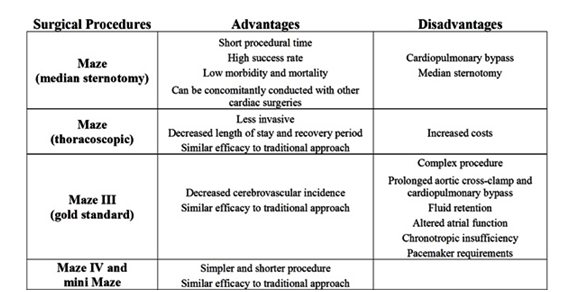
Heartbeat patterns can be regulated with medications and/or electrocardioversion ( an electrical shock of the heart). There are also procedures and surgeries that can be done to regulate abnormal heartbeat patterns. The following may be options of surgical procedures to treat atrial fibrillation: Catheter Ablation.
What is a type 1 flutter?
Typical Atrial Flutter (Type I Atrial Flutter) An atrial flutter is an abnormal heart rhythm where the heart beats regularly but at a much faster beat than normal. In this condition they actually beat faster and the ventricles beat at their normal rate, so the atria can beat at a rate of 4:1 with the ventricles.
How many beats does a heart beat?
What we normally refer to as one heart beat, can actually be divided into two beats. (Think “lub-dub, lub-dub, lub-dub”). The first is usually a little softer and the second is has more emphasis. During this first beat, or the ‘lub’ beat, the atria and ventricles are relaxed and are filling with blood.
What causes atrial fibrillation?
The causes of atrial fibrillation is oftentimes unknown, but can be the result of damage to the heart’s electrical system caused by conditions such as uncontrolled hypertension and coronary artery disease.
What is the name of the heart that causes a patient to have a stroke?
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heartbeat or arrhythmia sometimes called a quivering heart. This arrhythmia can cause a patient to develop blood clots, have a stroke, heart failure or other conditions. The heart rate is most often rapid and causes poor blood flow.
Is a patient with erratic heartbeat still atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is still reported in patients that are not currently experiencing the erratic rhythm as long as the patient is requiring ongoing medication to help control the rate. Atrial fibrillation is very common in postoperative patients and should be verified as a complication before coding as such.
Does atrial fibrillation go away?
Sometimes treating and controlling the underlying cause will make the atrial fibrillation go away. If this does not help the erratic rhythm, then the patient may require treatment with beta blockers and calcium channel blockers to help slow the heart rate. The rhythm should be restored to a normal rhythm to reduce the high heart rate.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for neck pain due to car accident
- 2. icd 10 code for scapular pain
- 3. icd 10 code for foot abscess unspecified
- 4. icd 10 code for lymphangioleiomyomatosis
- 5. icd 10 code for right hand oa
- 6. icd 10 cm code for sepsis with septic shock
- 7. icd 10 code for vesicle hip fracture
- 8. icd 10 code for left inguinal mass
- 9. icd 9 code for diabetic ulcer of foot
- 10. icd 10 code for stage 3 sacral pressure ulcer