Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · Hyponatremia of newborn 2019 - New Code 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Code on Newborn Record P74.22 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM P74.22 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How many codes in ICD 10?
ICD-10 code P74.22 for Hyponatremia of newborn is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period .
What is diagnosis code k08.121 in the ICD 10?
Oct 01, 2021 · P74.22. P74.22 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Hyponatremia of newborn . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
What is hyponatremia ICD 10?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code P74.22. Hyponatremia of newborn. 2019 - New Code 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code Code on Newborn Record. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Y93. Activity codes. for an injury or health condition, such as a heart attack while shoveling snow, which resulted from, or was contributed to, by the activity.
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for hyponatremia?
ICD-10 | Hypo-osmolality and hyponatremia (E87. 1)
What is the code for hyponatremia?
ICD-10 code E87. 1 for Hypo-osmolality and hyponatremia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is R53 81 diagnosis?
Other malaise2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R53. 81: Other malaise.
What is the ICD-10 code for newborn screening?
ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for newborn, infant and child health examinations Z00. 1.
What is the ICD-10 code for hypomagnesemia?
E83.42ICD-10 | Hypomagnesemia (E83. 42)
What is Hypoosmolality and hyponatremia?
Hyponatremia with hypo-osmolality of serum is produced by retention of water, by loss of sodium or both. It is always maintained by a defect in excretion of free water.
What is R53 82 diagnosis?
ICD-10 | Chronic fatigue, unspecified (R53. 82)
What is diagnosis code R53 83?
ICD-10 | Other fatigue (R53. 83)
What is ICD-10 code for PNA?
9.
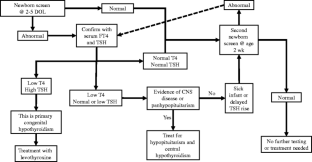
What is newborn baby screening test?
New-born Screening allows these conditions to be detected at birth, allowing the child to potentially lead a normal and healthy life. The test simply requires a few drops of blood, which is collected on a special filter paper by pricking the heel of the baby.
What is dat positive in newborn?
What is DAT? DAT tests for evidence of a reaction between the mother's and baby's blood groups. If your baby's DAT is positive, there is a risk that he/she could develop anaemia (low number of red blood cells) and/or jaundice (yellow colour to the skin).
What is the universal newborn screening?
Newborn screening is a public health service done in each U.S. state. Every newborn is tested for a group of health disorders that aren't otherwise found at birth. With a simple blood test, doctors can check for rare genetic, hormone-related, and metabolic conditions that can cause serious health problems.
Why are electrolytes important?
They are in your blood, urine, tissues, and other body fluids. Electrolytes are important because they help. Balance the amount of water in your body. Balance your body's acid/base (pH) level. Move nutrients into your cells.
What are the electrolytes in the body?
Make sure that your nerves, muscles, the heart, and the brain work the way they should. Sodium, calcium, potassium, chlorine, phosphate, and magnesium are all electrolytes. You get them from the foods you eat and the fluids you drink. The levels of electrolytes in your body can become too low or too high.
How does sodium affect blood pressure?
Your kidneys control how much sodium is in your body. If you have too much and your kidneys can't get rid it, sodium builds up in your blood. This can lead to high blood pressure.
How much salt should I eat a day?
The Dietary Guidelines recommend that most adults eat less than 2.3 grams per day. That equals about 1 teaspoon of table salt a day. Some people are more sensitive to the effects of salt than others and should eat less.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for alcohol induced depressive disorder
- 2. icd 10 code for mass right ring finger
- 3. icd 10 cm code for closed displaced shaft humerus fracture
- 4. icd 10 code for on anticoagulation
- 5. icd 10 code for immunocompromised due to medication
- 6. icd 10 code for transurethral resection of prostate
- 7. icd 10 code for tsh with reflex
- 8. assign the icd-10-cm code for pica in an adult.
- 9. icd 10 code for gianotti crosti syndrome
- 10. icd 10 code for anticoagulation status