What does a positive occult blood test indicate?
– Occult blood in the stool may indicate colon cancer or polyps in the colon or rectum, though not all cancers or polyps bleed. – Your test could show a positive result when you have no cancer (false-positive result) if you have bleeding from other sources, such as a stomach ulcer, hemorrhoid, or even blood swallowed from your mouth or your nose.
What does it mean if they find occult blood in my stool?
Occult blood in the stool may indicate colon cancer or polyps in the colon or rectum - though not all cancers or polyps bleed. Typically, occult blood is passed in such small amounts that it can be detected only through the chemicals used in a fecal occult blood test.
Does occult blood in urine indicate kidney disease?
What does occult blood in urine mean for kidney disease patients? Occult blood in urine is often diagnosed by a urine test, which means minority red blood cells in urine, and occult in urine is often a common symptoms for people with kidney disease. Occult blood in urine is not the same as blood urine, and occult blood in urine cant be observed under the microscope and naked eyes. Occult blood in urine is often said as the occult blood +, which means there are 10 red blood cells which is ...
What is the CPT code for occult blood?
CPT Code: 82270 Fecal Occult Blood Test Frequency Limitations: Screening fecal occult blood tests are covered at a frequency of once every 12 months for beneficiaries who have attained age 50. A written order from the beneficiary's attending physician is required. Attending physician means a doctor or medicine or osteopathy…
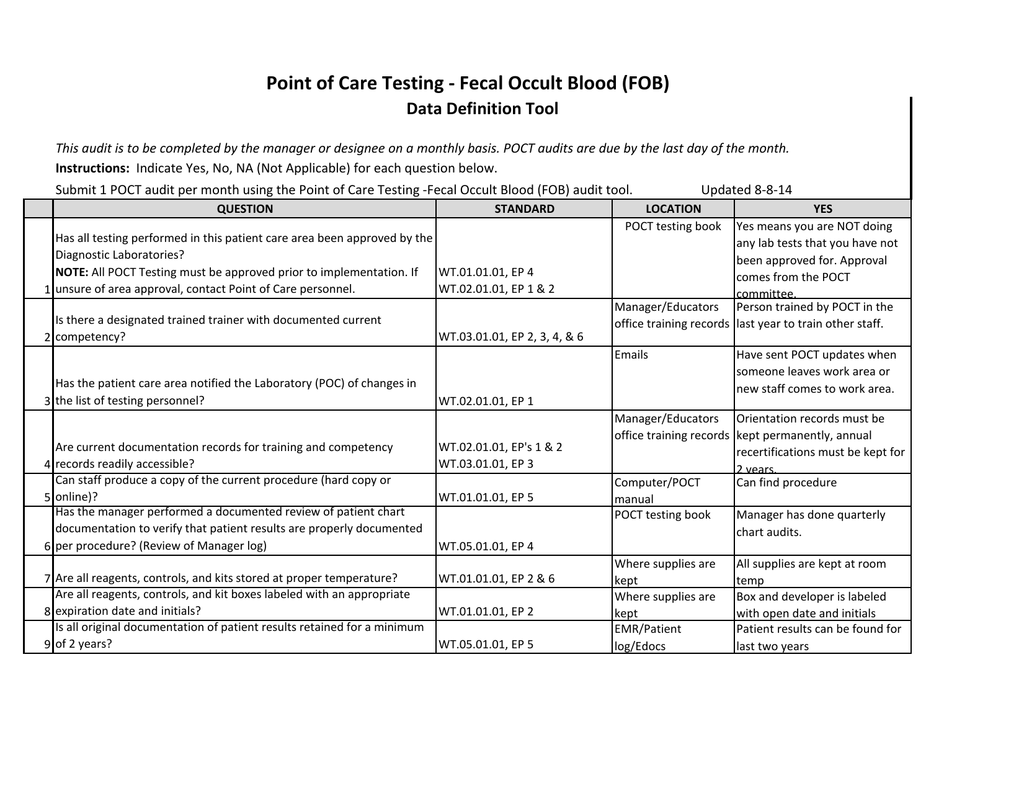
What is the ICD-10 code for abnormal stool?
The ICD10 code for the diagnosis "Other fecal abnormalities" is "R19. 5". R19. 5 is a VALID/BILLABLE ICD10 code, i.e it is valid for submission for HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the ICD-10 code for gastrointestinal occult blood loss?
ICD-10 code K92. 2 for Gastrointestinal hemorrhage, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the digestive system .
What is the ICD-10 code for blood in stools?
578.1 - Blood in stool. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD 9 code for occult blood?
Decision Summary. CMS has determined that ICD-9-CM codes 863.91 through 863.99 flow from the existing narrative for conditions for which PT and FOBT tests are reasonable and necessary.
What is the ICD 10 code for positive cologuard test?
When a patient undergoes colonoscopy for a positive Cologuard test and there are no abnormal findings, the coder would report the diagnosis as R19. 5 (other fecal abnormalities).
Why is stool tested for occult blood?
The fecal occult blood test (FOBT) is a lab test used to check stool samples for hidden (occult) blood. Occult blood in the stool may indicate colon cancer or polyps in the colon or rectum — though not all cancers or polyps bleed.
What is the ICD 10 code for bright red blood in stool?
K62. 5 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is ICD 9 code blood in stool?
578.1 Blood in stool - ICD-9-CM Vol. 1 Diagnostic Codes.
What is the ICD 10 code for loose stool?
R19. 7 - Diarrhea, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the CPT code for blood in stool?
CPT Code: 82270 Fecal Occult Blood Test.
The ICD code R195 is used to code Fecal occult blood
Fecal occult blood (FOB) refers to blood in the feces that is not visibly apparent (unlike other types of blood in stool such as melena or hematochezia). A fecal occult blood test (FOBT) checks for hidden (occult) blood in the stool (feces).
Coding Notes for R19.5 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
MS-DRG Mapping
DRG Group #391-392 - Esophagitis, gastroent and misc digest disorders with MCC.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'R19.5 - Other fecal abnormalities'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code R19.5. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Codes GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official approximate match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that while there is no exact mapping between this ICD10 code R19.5 and a single ICD9 code, 792.1 is an approximate match for comparison and conversion purposes.
What is the blood test for occult bleeding?
As you know, the hemoccult test screens for blood in the stool. It detects a small trace of blood visible to the naked eye. Blood which is hidden from view is referred to as "occult" bleeding. Hemoccult = hidden blood=729.1
What blood test should I use for a hemoccult?
I agree with Lisa and LRing#N#Occult blood means the blood is hidden to the eye. When a hemoccult test comes back positive for this hidden blood, you should use 792.1 (Nonspecific abnormal findings in stool contents). Blood in the stool that is visible, appearing as either bright red streaks or tarry black stools, you should use 578.1
How often should I test for occult blood?
In patients who are taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and have a history of gastrointestinal bleeding but no other signs, symptoms, or complaints associated with gastrointestinal blood loss, testing for occult blood may generally be appropriate no more than once every three months.
What is the most widely used test for GI bleeding?
The guaiac-based test is the most widely used.
Can a guaiac test be false positive?
Similarly, this test's sensitiv ity may result in a false positive if the patient has recently ingested meat.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for charcot marie tooth
- 2. what is the icd 10 pcs code for blood test
- 3. icd 10 code for congential laryngomalacia
- 4. icd 10 code for chronic otitis externa bilateral
- 5. icd 10 code for microvascular ischemic changes
- 6. icd 10 code for new diagnosis of diabetes mellitus
- 7. icd 9 code for strep pharyngitis
- 8. icd code for ppd test placement
- 9. icd 10 code for cystocele with rectocele
- 10. icd 10 dx code for hypothyroidism