Other fracture of upper and lower end of left fibula, initial encounter for closed fracture. S82.832A is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM S82.832A became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the healing time for a tibia fracture?
Recovery time for a tibia fracture typically takes 4-6 months to heal completely. If the fracture is open or comminuted, healing time may take longer. Your doctor will often prescribe medications for pain-relief for a short period of time after the injury or surgery. How long before you can walk on a broken tibia?
What does a stress fracture in your tibia feel like?
limited bending motion in and around your knee. Similarly one may ask, what does a tibia stress fracture feel like? A stress fracture typically feels like an aching or burning localized pain somewhere along a bone.
What is a left distal fracture?
When the radius breaks near the wrist, it is called a distal radius fracture. The break usually happens due to falling on an outstretched or flexed hand. It can also happen in a car accident, a bike accident, a skiing accident or another sports activity. A distal radius fracture can be isolated, which means no other fractures are involved.
What is a stress fracture of the tibia?
- Pain on the inside of the shin, usually on the lower third.
- Symptoms often occur after running long distances.
- When pressing in over the area your leg will feel tender and sore.
- You may even have swelling over the site of the fracture.
- If you have a stress fracture you may also feel a particularly tender spot at the exact point of the stress fracture.
What is the ICD code for fracture of the shaft of the left fibula?
What is a Bosworth fracture?
About this website
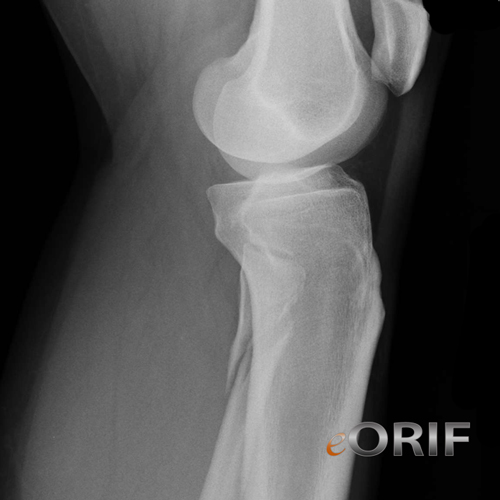
What is the ICD-10 code for fracture of the shaft of the left tibia?
S82.202 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Unspecified fracture of shaft of left tibia. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more specific code is available to choose from below.
What type of fracture is S82.202C?
Use S82.202C for initial encounter for open fracture type IIIA, IIIB, or IIIC
What is the ICD code for fracture of the shaft of the left fibula?
S82.402A is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of unspecified fracture of shaft of left fibula, initial encounter for closed fracture. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is a Bosworth fracture?
The Bosworth fracture is a rare fracture of the distal fibula with an associated fixed posterior dislocation of the proximal fibular fragment which becomes trapped behind the posterior tibial tubercle. The injury is caused by severe external rotation of the ankle. The ankle remains externally rotated after the injury, making interpretation of X-rays difficult which can lead to misdiagnosis and incorrect treatment. The injury is most commonly treated by open reduction internal fixation as closed reduction is made difficult by the entrapment of the fibula behind the tibia.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for otitis media right
- 2. icd 10 code for hearing loss
- 3. icd 10 code for thoracic arthritis
- 4. what is the icd-10 code for unspecified staphylococcus
- 5. icd 9 code for phlebitis and thrombitis of lower extremity
- 6. icd 10 cm code for coronary arteriosclerosis of a native artery
- 7. icd 10 code for obesity z68.35
- 8. icd 10 code for right knee injection
- 9. icd 10 code for screening for hepatitis b immunity
- 10. icd 10 code for use of aromatase inhibitors