What is the ICD 10 code for optic disc disease?
Other disorders of optic disc, right eye 1 H47.391 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM H47.391 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H47.391 - other international versions of ICD-10 H47.391 may differ.
What does it mean when your optic disc is swollen?
A disorder characterized by swelling around the optic disc. Swelling around the optic disc, usually due to increased intracranial pressure or pressure on the optic nerve by a tumor. Swelling around the optic disk, the area where the optic nerve (the nerve that carries messages from the eye to the brain) enters the eyeball.
What is the ICD 10 code for optic nerve damage?
2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. H47.093 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Oth disorders of optic nerve, NEC, bilateral. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H47.093 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for undifferentiated optic neuritis?
Unspecified optic neuritis. H46.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM H46.9 became effective on October 1, 2018.
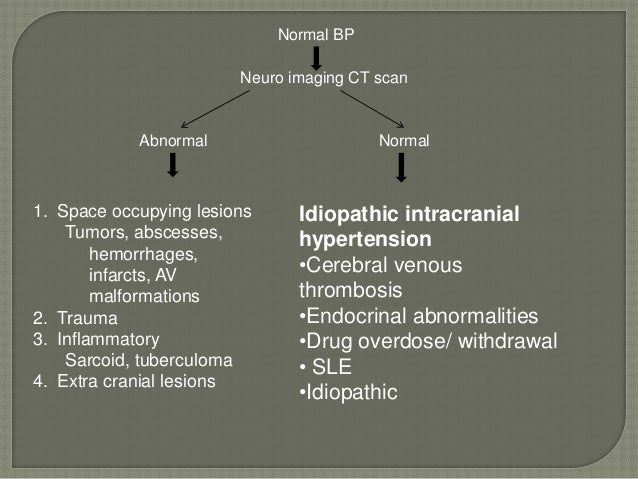
What is the ICD 10 code for optic disc edema?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM H47. 13 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of H47.
What is optic disc swelling?
Papilledema is swelling of your optic nerve, which connects the eye and brain. This swelling is a reaction to a buildup of pressure in or around your brain that may have many causes. Often, it's a warning sign of a serious medical condition that needs attention, such as a brain tumor or hemorrhage.
Is optic disc edema the same as papilledema?
Optic disc edema refers to swelling of the nerve fiber layer at the optic nerve head due to an optic neuropathy of any etiology (inflammatory, infiltrative, compressive, etc.) whereas the term papilledema refers to optic disc edema caused by raised intracranial pressure.
What is the ICD 10 code for papilledema?
ICD-10 code H47. 11 for Papilledema associated with increased intracranial pressure is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the eye and adnexa .
What is the optic disc also known as?
Optic disc: The circular area in the back of the inside of the eye where the optic nerve connects to the retina. Also called the optic nerve head.
What is the difference between papilledema and optic neuritis?
In contrast to true papilledema, with AION or optic neuritis, there is a startling loss of visual acuity, but clear-cut field defects. The presence of exudates, cotton wool spots, or hemorrhages is rare in most conditions associated with optic disc swelling other than papilledema and the non-arteritic form of AION.
How can you tell the difference between papilledema and Pseudopapilledema?
Pseudopapilledema is defined as anomalous elevation of one or both optic discs without edema of the retinal nerve fiber layer. Papilledema, on the other hand, is a swelling of the optic disc due to increased intracranial pressure.
What is the difference between papilledema and pseudotumor cerebri?
Papilledema and pseudotumor cerebri are conditions related to pressure inside your skull which can cause swelling in your optic nerve. Specifically, pseudotumor cerebri causes increased intracranial pressure, which can lead to papilloedema — swelling of your optic nerve.
How can you tell the difference between papilledema and Papillitis?
Papillitis can be differentiated from papilledema by an afferent pupillary defect (Marcus Gunn pupil), by its greater effect in decreasing visual acuity and color vision, and by the presence of a central scotoma. Papilledema that is not yet chronic will not have as dramatic an effect on vision.
What is unspecified Papilledema?
A disorder characterized by swelling around the optic disc. Swelling around the optic disc, usually due to increased intracranial pressure or pressure on the optic nerve by a tumor.
What is bilateral papilledema?
Papilledema is a sign of elevated intracranial pressure and is almost always bilateral. Causes include the following: Brain tumor. The tumors usually develop during early or middle adulthood but may develop at any age; they are... read more. or abscess.
What is the ICD-10 code for increased intracranial pressure?
H47. 11 - Papilledema associated with increased intracranial pressure | ICD-10-CM.
The ICD code H473 is used to code Optic disc drusen
Optic disc drusen (ODD) or optic nerve head drusen (ONHD) are globules of mucoproteins and mucopolysaccharides that progressively calcify in the optic disc. They are thought to be the remnants of the axonal transport system of degenerated retinal ganglion cells.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'H47.39 - Other disorders of optic disc'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code H47.39. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
What causes optic nerve pain?
A disorder characterized by inflammation of the optic nerve. Causes include autoimmune disorders, infections, toxins, drugs, and multiple sclerosis. It may manifest with acute loss of vision and pain. Inflammation of the optic nerve.
Can optic neuritis be a sarcoidosis?
Why: optic neuritis may be present in patients with sarcoidosis or reiter's syndrome ( rarely). How: clinically, patients with optic neuritis present with sudden loss of central vision and pain on moving the eye. Opthalmoscopically there may be hyperemia of the optic disc and distention of the large retinal veins.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for renal artery stenosis
- 2. icd 10 code for post covid vaccination reaction
- 3. icd 9 code for crmo
- 4. icd-10 code for hyperbilirubinemia
- 5. icd-10 code for ibs
- 6. icd 10 code for rebound hypertension
- 7. icd 10 dx code for vancomycin, trough
- 8. icd 10 code for traumatic cerebral edema
- 9. icd 10 code for problems with prosthetic
- 10. icd 10 cm code for diarrhea chronic