What is orbital lymphoma?
Orbital lymphoma refers to a lymphoma occurring in the conjunctiva, lacrimal gland, eyelid and ocular musculature. Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL) of the orbit is a rare presentation, representing 8-10% of extranodal NHL[1] and only 1% of all NHL. [2] Generally, it has an indolent course.
What is ICD-10 marginal zone lymphoma?
ICD-10-CM Code for Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue [MALT-lymphoma] C88. 4.
What is the ICD-10 code for CNS lymphoma?
200.50 - Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma, Unspecified Site, Extranodal and Solid Organ Sites [Internet]. In: ICD-10-CM.
What does extranodal lymphoma mean?
The term extranodal disease refers to lymphomatous infiltration of anatomic sites other than the lymph nodes. Almost any organ can be affected by lymphoma, with the most common extranodal sites of involvement being the stomach, spleen, Waldeyer ring, central nervous system, lung, bone, and skin.
What is marginal zone lymphoma?
Marginal zone lymphomas are types of slow-growing (low-grade) non-Hodgkin lymphomas that develop from B cells. They are called marginal zone lymphomas because they develop in a particular region found at the edge of normal lymphoid tissues (collections of lymphocytes) called the marginal zone.
What is the ICD-10 code for lymphoma?
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, unspecified, unspecified site C85. 90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C85. 90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for secondary CNS lymphoma?
Secondary malignant neoplasm of other parts of nervous system. C79. 49 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is primary CNS lymphoma?
Primary central nervous system (CNS) lymphoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lymph tissue of the brain and/or spinal cord. Having a weakened immune system may increase the risk of developing primary CNS lymphoma.
What causes CNS lymphoma?
Causes of Primary CNS Lymphoma The cause of primary CNS lymphoma is unknown. However, since primary CNS lymphoma arises from cells of the immune system, people with impaired immune systems and certain genetic and infectious diseases are at an increased risk of developing this form of cancer.
What is the difference between nodal and extranodal lymphoma?
Extranodal lymphoma, by definition, involves sites other than lymph nodes, spleen, thymus and the pharyngeal lymphatic ring. Involvement of the spleen in HD is considered as nodal disease but in the case of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) the spleen is regarded as an extranodal site.
What are the 3 main types of lymphoma?
Each type of lymphoma can cause different symptoms and need different treatment.Hodgkin lymphoma. ... Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. ... Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL) and small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) ... Lymphoma in children and young people.
What are the four stages of lymphoma?
The staging system used for Hodgkin lymphoma is the Lugano classification, which is based on the older Ann Arbor system. It has 4 stages, labeled I, II, III, and IV. For limited stage (I or II) HL that affects an organ outside of the lymph system, the letter E is added to the stage (for example, stage IE or IIE).
What does extranodal spread mean?
Extranodal extension refers to the growth of a nodal cancer metastasis beyond the confines of the capsule of a lymph node into adjacent tissues. Less preferred synonyms include extranodal spread, extracapsular extension, or extracapsular spread.
Where is extranodal?
The most frequent site of primary extranodal lymphoma is in the gastrointestinal tract, and almost all of these are NHL. The next most frequent site after the GI tract is the skin. However, when the NHL starts only in the skin, it's called a skin lymphoma, or cutaneous lymphoma.
How do you treat extranodal marginal zone lymphoma?
The current recommended regimen is a PPI and clarithromycin with either amoxicillin or metronidazole (27-29). In a large systematic review of over 1400 patients from 32 studies treated with up front H. pylori eradication for early stage gastric MALT lymphoma, the remission rate was 78%.
What does extranodal extension mean?
Extra-nodal extension is defined as tumor cells perforating the lymph node capsule into the peri-nodal tissue. Tumor tissue within the lymph node capsule itself was not considered as extra-capsular invasion [8].
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will C85.91 be available?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C85.91 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What is the name of the tumor that is found in the eye?
A primary or metastatic tumor involving the structures of the eye (conjunctiva, cornea, uvea, retina), the lacrimal gland, and the orbit. Representative examples are melanoma, carcinoma, lymphoma, and retinoblastoma. Cancer of the eye is uncommon.
What is a malignant neoplasm?
Malignant neoplasm of unspecified site of eye 1 A primary or metastatic tumor involving the structures of the eye (conjunctiva, cornea, uvea, retina), the lacrimal gland, and the orbit. Representative examples are melanoma, carcinoma, lymphoma, and retinoblastoma. 2 Cancer of the eye is uncommon. It can affect the outer parts of the eye, such as the eyelid, which are made up of muscles, skin and nerves. If the cancer starts inside the eyeball it's called intraocular cancer. The most common intraocular cancers in adults are melanoma and lymphoma. The most common eye cancer in children is retinoblastoma, which starts in the cells of the retina. Cancer can also spread to the eye from other parts of the body.treatment for eye cancer varies by the type and by how advanced it is. It may include surgery, radiation therapy, freezing or heat therapy, or laser therapy. 3 Cancer that forms in tissues of and around the eye. Some of the cancers that may affect the eye include melanoma (a rare cancer that begins in cells that make the pigment melanin in the eye), carcinoma (cancer that begins in tissues that cover structures in the eye), lymphoma (cancer that begins in immune system cells), and retinoblastoma (cancer that begins in the retina and usually occurs in children younger than 5 years).
What is the most common intraocular cancer?
The most common intraocular cancers in adults are melanoma and lymphoma. The most common eye cancer in children is retinoblastoma, which starts in the cells of the retina. Cancer can also spread to the eye from other parts of the body.treatment for eye cancer varies by the type and by how advanced it is.
What is the most common eye cancer?
If the cancer starts inside the eyeball it's called intraocular cancer. The most common intraocular cancers in adults are melanoma and lymphoma. The most common eye cancer in children is retinoblastoma, which starts in the cells of the retina. Cancer can also spread to the eye from other parts of the body.treatment for eye cancer varies by the type and by how advanced it is. It may include surgery, radiation therapy, freezing or heat therapy, or laser therapy.
When will the ICd 10 C69.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C69.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Can multiple neoplasms be coded?
For multiple neoplasms of the same site that are not contiguous, such as tumors in different quadrants of the same breast, codes for each site should be assigned. Malignant neoplasm of ectopic tissue. Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, ...
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 C88.4 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C88.4 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Which chapter is a neoplasm classified?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 C82.01 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C82.01 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the pathophysiology of orbital lymphoma?
Pathophysiology. Immunosuppression due to any cause—including AIDS, immunosuppressive drugs, or increasing age—has long been established as the main factor contributing to the pathophysiology of orbital lymphoma. More recently, however, the role of various pathogens has entered into the debate.
Where does orbital lymphoma originate?
Orbital lymphoma is a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) that originates in the conjunctiva, lacrimal gland, soft tissues of the eyelid, or extraocular muscles; it is most commonly extraconal in location. Orbital lymphoma is said to be primary when it arises spontaneously from one of these locations, and secondary when it is associated ...
Why is radiotherapy used for orbital lymphoma?
Because most orbital lymphomas are localized, radiotherapy is the most common and preferred treatment modality. The entire orbit must be encompassed in the radiation field, irrespective of how much of the orbit is involved. This reduces the chance of recurrence in previously uninvolved areas.
What percentage of NHL cases are orbital lymphoma?
While lymphoma constitutes more than half of all orbital malignancies (55 percent), 1 the incidence of orbital lymphoma has been reported to account for between 1 and 10 percent of NHL cases. 2
What is orbital presentation?
Orbit. Orbital presentation is most commonly observed as a painless palpable mass in the superolateral quadrant. It may lead to proptosis, ptosis, diplopia, or abnormal ocular movement.
What are the four patterns of lymphoma?
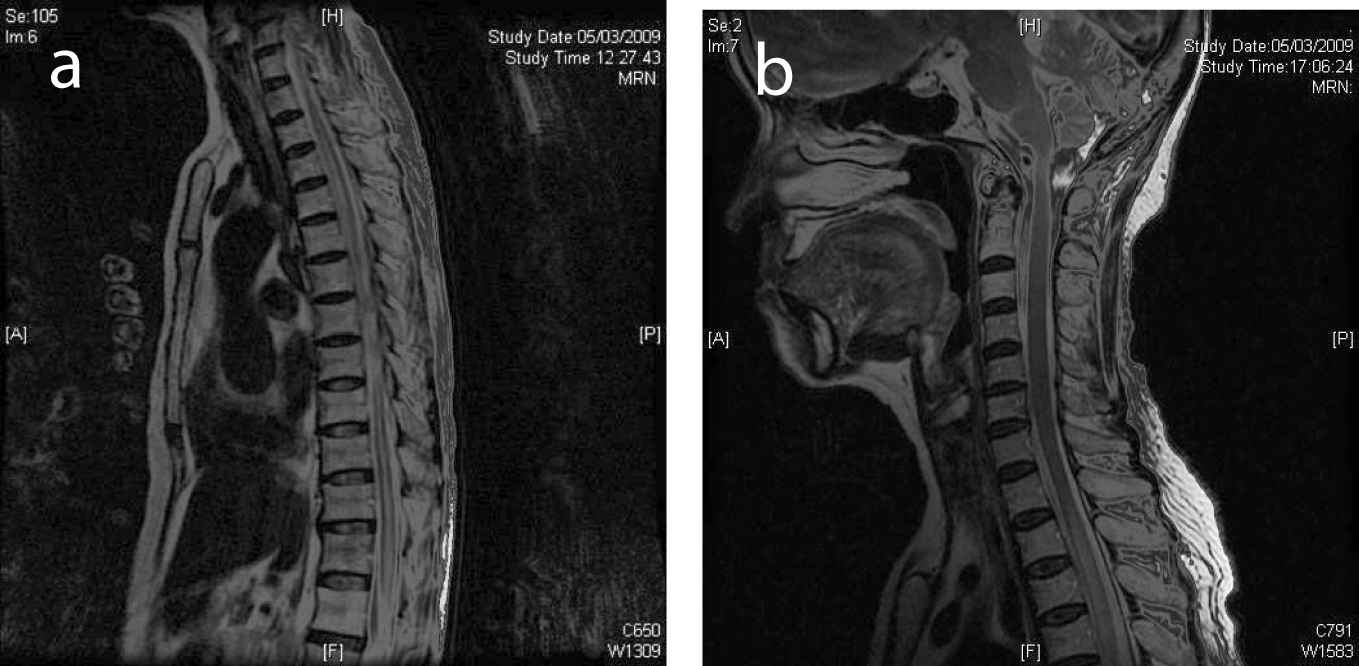
It may exhibit any of the following four patterns: retroocular, anterior preseptal, lacrimal gland involvement, or extension of an adnexal lesion. Lesions that are heterogeneous, with bony destruction, are indicative of high-grade lymphomas, which are usually accompanied by pain. Magnetic resonance imaging.
Which antigen is expressed by neoplastic cells of malignant lymphoma?
Neoplastic cells of MALT lymphomas have been shown to express the antigen CD20 on their surfaces. Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody that is directed against CD20, ultimately leading to cell destruction by various mechanisms including apoptosis, complement-mediated cytolysis, and antibody-dependent cytotoxicity.
General Information
CPT codes, descriptions and other data only are copyright 2020 American Medical Association. All Rights Reserved. Applicable FARS/HHSARS apply.
CMS National Coverage Policy
Title XVIII of the Social Security Act §1833 (a) (2) (E) related to outpatient hospital radiology services.
Article Guidance
The information in this article contains billing, coding or other guidelines that complement the Local Coverage Determination (LCD) for Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Orbit, Face, and/or Neck L34425.
Bill Type Codes
Contractors may specify Bill Types to help providers identify those Bill Types typically used to report this service. Absence of a Bill Type does not guarantee that the article does not apply to that Bill Type.
Revenue Codes
Contractors may specify Revenue Codes to help providers identify those Revenue Codes typically used to report this service. In most instances Revenue Codes are purely advisory. Unless specified in the article, services reported under other Revenue Codes are equally subject to this coverage determination.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd-10 code for perfusion of extremity
- 2. icd 10 code for dvt unspecified leg
- 3. icd 10 code for subcutaneous tumor arm
- 4. icd 10 code for groin hernia pain
- 5. icd code for peptic ulcer disease
- 6. icd 10 code for anemia of chronic disease
- 7. icd 10 code for bilateral pulmonary embolus
- 8. icd 10 code for acutesmall bowel obstruction
- 9. icd 9 code for streptococcus exposure
- 10. icd 10 code for atherosclerosis disease