How to pronounce orthostatic hypotension?
orthostatic hypotension pronunciation with meanings, synonyms, antonyms, translations, sentences and more The proper pronunciation of the word hurón in Spanish is? ur-ro-nn
How can one get rid of orthostatic hypotension?
- Use more salt. Experts usually recommend limiting salt in your diet because sodium can raise blood pressure, sometimes dramatically. ...
- Drink more water. Fluids increase blood volume and help prevent dehydration, both of which are important in treating hypotension.
- Wear compression stockings. ...
- Medications. ...
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
The ICD-10-CM is a catalog of diagnosis codes used by medical professionals for medical coding and reporting in health care settings. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) maintain the catalog in the U.S. releasing yearly updates.
What is the ICD 10 code for accelerated hypertension?
Instead, use the following codes:
- I15.0, Renovascular hypertension,
- I15.1, Hypertension secondary to other renal disorders,
- I15.2, Hypertension secondary to endocrine disorders,
- I15.8, Other secondary hypertension,
- I15.9, Secondary hypertension, unspecified.
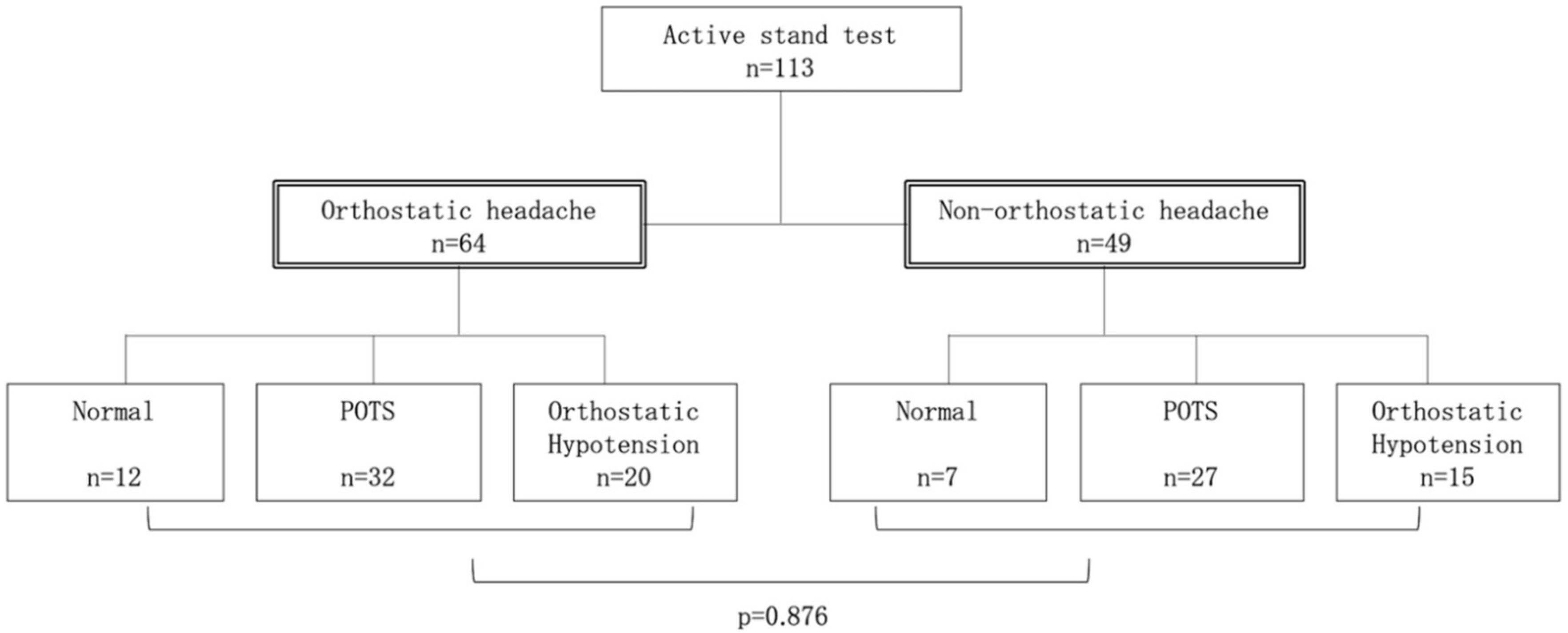
What is the ICD-10 code for I95 1?
ICD-10 code: I95. 1 Orthostatic hypotension | gesund.bund.de.
What is the ICD-10 code for orthostatic dizziness?
ICD-10 | Orthostatic hypotension (I95. 1)
What is considered orthostatic hypotension?
A drop of 20 millimeters of mercury (mm Hg) in the top number (systolic blood pressure) within 2 to 5 minutes of standing is a sign of orthostatic hypotension. A drop of 10 mm Hg in the bottom number (diastolic blood pressure) within 2 to 5 minutes of standing also indicates orthostatic hypotension.
What is the difference between orthostatic hypotension and neurogenic orthostatic hypotension?
One key difference between the two groups, they added, is that patients with neurogenic orthostatic hypotension typically have little or no heart rate (HR) increase in the upright position, while patients with nonneurogenic orthostatic hypotension may have marked tachycardia.
Is postural hypotension and orthostatic hypotension the same?
Orthostatic hypotension — also called postural hypotension — is a form of low blood pressure that happens when standing after sitting or lying down. Orthostatic hypotension can cause dizziness or lightheadedness and possibly fainting.
Is Orthostasis the same as orthostatic hypotension?
Condition: Orthostasis or orthostatic hypotension (OH) is a decrease in blood pressure that happens soon after standing or sitting up. When a person stands up, gravity causes blood to pool in the legs. This reduces blood pressure since less blood is circulating back to the heart to pump.
What is the most common cause of orthostatic hypotension?
Loss of fluid within the blood vessels is the most common cause of symptoms linked to orthostatic hypotension. This could be due to dehydration brought about by diarrhea, vomiting, and the use of medication, such as diuretics or water pills.
How do you check for orthostatic hypotension?
Subtract the systolic (top number) blood pressure while sitting or standing from the systolic blood pressure while lying down. If the difference is a decrease of 20 mmHg or more, this supports a finding of orthostatic hypotension.
How do you check for Orthostatics?
1 Have the patient lie down for 5 minutes. 2 Measure blood pressure and pulse rate. 3 Have the patient stand. 4 Repeat blood pressure and pulse rate measurements after standing 1 and 3 minutes.
What is non neurogenic orthostatic hypotension?
Non-neurogenic Causes Acute onset non-neurogenic orthostatic hypotension is one of the most common forms of the condition. It is frequently caused by a decrease in intravascular blood volume due to, vomiting, dehydration or hemorrhage. Acute orthostatic hypotension may also accompany myocardial infarcts.
What is autonomic failure in orthostatic hypotension?
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary actions such as widening or narrowing of our blood vessels. Failure in this system can lead to orthostatic hypotension, which means a sudden drastic drop in blood pressure especially from a lying or sitting down position.
What neurological disorder causes low blood pressure?
A myriad of neurologic disorders including multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, and tabes dorsalis (syphilitic myelopathy), can cause autonomic dysfunction and result in symptomatic hypotension.
What is a normal blood pressure while standing?
A healthy blood pressure reading is 120/80 milligrams of mercury (mm Hg) or lower.
When is low blood pressure an emergency?
You could have a medical emergency if any of the following signs and symptoms happen along with low blood pressure: Nausea. Cold, clammy, pale skin. Rapid, shallow breathing.
What are positive orthostatic vitals?
The test is considered positive if systolic blood pressure falls 20 mm Hg below baseline or if diastolic blood pressure falls 10 mm Hg below baseline. If symptoms occur during testing, the patient should be returned to the supine position immediately.
What is orthostatic hypotension?
orthostatic hypotension is a finding and defined as a 20 mm hg decrease in systolic pressure or a 10 mm hg decrease in diastolic pressure 3 minutes after the person has risen from supine to standing. symptoms generally include dizziness blurred vision and syncope.
What is the I95.1 code?
I95.1 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of orthostatic hypotension. The code I95.1 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What is the name of the system that controls involuntary actions?
Also called: Dysautonomia. Your autonomic nervous system is the part of your nervous system that controls involuntary actions, such as the beating of your heart and the widening or narrowing of your blood vessels. When something goes wrong in this system, it can cause serious problems, including.
What does it mean when you have a coat hanger?
Less frequently, affected individuals can experience muscle pain in the neck and shoulders (known as "coat hanger pain"), lower back pain, or weakness.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
Type 1 Excludes. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes note. It means "NOT CODED HERE!". An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note.
What is the tabular list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code I95.1:
Can the nervous system be affected by Parkinson's disease?
Autonomic nervous system disorders can occur alone or as the result of another disease, such as Parkinson's disease, alcoholism and diabetes. Problems can affect either part of the system, as in complex regional pain syndromes, or all of the system. Some types are temporary, but many worsen over time.
What is the ICd 10 code for orthostatic hypotension?
I95.1 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Orthostatic hypotension . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
Do you include decimal points in ICD-10?
DO NOT include the decimal point when electronically filing claims as it may be rejected. Some clearinghouses may remove it for you but to avoid having a rejected claim due to an invalid ICD-10 code, do not include the decimal point when submitting claims electronically. See also:

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2015 icd 9 code for static type b aortic dissection
- 2. icd 10 code for unspec fracture right hip
- 3. what icd 10 code is used for routine bloodwork
- 4. icd 10 code for general body weakness
- 5. icd 9 code for 11 year old well exam
- 6. icd 10 code for c section seroma
- 7. icd 10 code for diaper
- 8. icd 10 code for rib pain on left side
- 9. icd 10 code for puncture wound of right lower leg
- 10. icd-10-cm code for elevated troponin