What is the ICD 10 code for osteomyelitis?
Oct 01, 2021 · Osteomyelitis of vertebra, sacral and sacrococcygeal region. M46.28 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M46.28 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is osteomyelitis M86?
M86.0 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis. M86.00 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, unspecified... M86.01 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, shoulder. M86.011 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, right shoul... M86.012 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, left should... M86.019 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, unspecified...
What is the M86 code for excluded bone disease?
Oct 01, 2021 · Osteomyelitis, unspecified. M86.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.9 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M86.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 M86.9 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for pyogenic bone disease?
Oct 01, 2021 · Osteomyelitis of vertebra, lumbar region. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. M46.26 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M46.26 became effective on October 1, 2021.
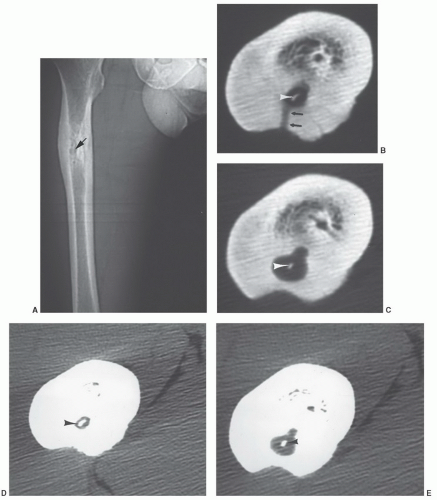
What is the ICD-10 code for osteomyelitis of the sacrum?
What is the ICD-10 code for ischial osteomyelitis?
What is the ICD-10 code for acute on chronic osteomyelitis?
What is the code for osteomyelitis of the lumbosacral region?
| ICD-10: | M46.26 |
|---|---|
| Short Description: | Osteomyelitis of vertebra, lumbar region |
| Long Description: | Osteomyelitis of vertebra, lumbar region |
What is pelvic osteomyelitis?
What part of the pelvis is the Ischium?
What is chronic osteomyelitis?
What is osteomyelitis unspecified?
What is the CPT code for osteomyelitis?
Is Discitis the same as osteomyelitis?
What is L89 154?
What K57 92?
What does the title of a manifestation code mean?
In most cases the manifestation codes will have in the code title, "in diseases classified elsewhere.". Codes with this title are a component of the etiology/manifestation convention. The code title indicates that it is a manifestation code.
Can osteomyelitis kill bone?
Osteomyelitis can cause severe pain in the infected bone. If it is not treated , it can kill bone tissue. Inflammation of the bone marrow and adjacent bone caused by a pyogenic organism; it may remain localized or may spread through the bone to involve the marrow, cortex, cancellous tissue, and periosteum. Codes.
What is the code for osteomyelitis?
M46.28 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of osteomyelitis of vertebra, sacral and sacrococcygeal region. The code M46.28 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What are the symptoms of bone infection?
Symptoms of bone infections include. Pain in the infected area. Chills and fever. Swelling, warmth, and redness.
How to tell if you have a bone infection?
A blood test or imaging test such as an x-ray can tell if you have a bone infection. Treatment includes antibiotics and often surgery.
What is the disease of osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the bone caused by an infectious organism. The condition develops rapidly during the course of several days. It is characterized by localized pain, soft-tissue swelling, and tissue warmth at the site of the infection, plus systemic symptoms such as fever, irritability, fatigue, and nausea.
What is chronic multifocal osteomyelitis?
Chronic multifocal osteomyelitis is a rare condition that also is referred to as chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, or SAPHO syndrome (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis). The cause of the condition is unknown, and tissue cultures typically fail to identify any infectious organism.
What is the code for an infectious agent?
As with all infectious processes in which the infectious agent is not a component of the code that describes the condition, an additional code from categories B95-B97 should be assigned to identify the infectious agent, assuming it can be identified. Any major osseous defects also should be identified with a code from subcategory M89.7.
Which code includes Brodie's abscess?
Multiple sites. Other osteomyelitis (M86.8) which includes Brodie’s abscess, requires only the general region (shoulder, upper arm, forearm, hand, thigh, lower leg, ankle/foot, other site, and unspecified site). Laterality is not a component of codes in category M86.8. Unspecified osteomyelitis (M86.9) is not specific to a site.
Is osteomyelitis a chronic disease?
Osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the bone that typically is further differentiated as acute, sub-acute, or chronic. In ICD-9-CM, documentation of the general site of the inflammation/infection (such as shoulder region, forearm, or ankle), along with identification of the inflammation/infection as a current acute/sub-acute infection or a chronic condition, is all that is required to assign the most specific code.
Can osteomyelitis cause sinus drainage?
Chronic osteomyelitis is a severe, persistent inflammation/infection that can recur and be difficult to treat. A chronic infection also may present with a draining sinus, presenting a greater risk for complications, such as major bo ny defects.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for pyogenic meningitis
- 2. www. library .ahima.org// icd-10-cm pcs code for total knee replacement ??
- 3. icd 10 code for diabetes with hypercalcemia
- 4. icd 10 code for digital mucous cyst
- 5. icd 9 code for cor atherosclerosis unspecified vesel
- 6. icd 10 code for ischemic ecg
- 7. icd 10 code for right orbital fracture
- 8. icd 9 code for generalized anxiety
- 9. icd 10 code for liarthalgia
- 10. icd 10 code for stage 1 pressure ulcer coccyx