What is the ICD 10 code for osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis, unspecified. M86.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.9 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M86.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 M86.9 may differ.
What is chronic osteomyelitis and how can it be treated?
This pattern of recurring infection or failure of the bone to heal is chronic osteomyelitis. When areas of the bone die, circulation through the bone stops and treatment is very difficult. Systemic drugs may not be effective at this point and surgery is necessary.
What is an example of a history of osteomyelitis?
For example, if the record indicates a history of osteomyelitis and there is another possible cause of osteomyelitis, such as an infection due to a pressure ulcer or tuberculosis or typhoid. Another example might be if a patient has a complicated history including diabetes.
How long does it take for osteomyelitis to develop?
Acute osteomyelitis develops within two weeks after disease onset, subacute osteomyelitis within one to several months and chronic osteomyelitis after a few months. The specific organism isolated in bacterial osteomyelitis is often associated with the age of the patient or a common clinical scenario (i.e., trauma or recent surgery).
What is the ICD-10 code for spinal osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis of vertebra, site unspecified M46. 20 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M46. 20 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is osteomyelitis of vertebra?
Vertebral osteomyelitis is a rare spinal infection. Osteomyelitis, the name for a painful bone infection that develops from bacteria or fungi, is itself rare. Vertebral osteomyelitis can happen as the result of an injury to your spine or after surgery.
What is the ICD-10 code for osteomyelitis?
There are three subcategories for reporting this condition using ICD-10-CM, including M86. 0 Acute hematogenous osteomyelitis, M86. 1 Other acute osteomyelitis, and M86. 2 Sub-acute osteomyelitis.
What is the ICD-10 code for osteomyelitis of the sacrum?
M46.28ICD-10 code: M46. 28 Osteomyelitis of vertebra Sacral and sacrococcygeal region.
What is a spinal bone infection?
Vertebral osteomyelitis is a bone infection usually caused by bacteria. In the spine, it is often found in the vertebrae, although the infection can spread into the epidural and intervertebral disc spaces. Osteomyelitis is rare and most common in young children and the elderly, but it can occur at any age.
What is infection in the spine called?
Vertebral osteomyelitis refers to an infection of the vertebral body in the spine. It is a fairly rare cause of back pain, especially in young healthy adults. Generally, the infection is spread to the vertebral body by a vascular route.
What is the CPT code for osteomyelitis?
CPT® Code 21025 in section: Excision of bone (eg, for osteomyelitis or bone abscess)
What is osteomyelitis unspecified?
Osteomyelitis is an infection in a bone. Infections can reach a bone by traveling through the bloodstream or spreading from nearby tissue. Infections can also begin in the bone itself if an injury exposes the bone to germs.
What is the ICD-10 code M86 9?
Osteomyelitis, unspecifiedICD-10 code: M86. 9 Osteomyelitis, unspecified | gesund.bund.de.
What is Coccygeal osteomyelitis?
Discussion: Sacro-coccygeal osteomyelitis is a rare complication of perianal CD. Contrary to the general population, patients with perianal CD develop sacro-coccygeal osteomyelitis by direct extension from a pelvic abscess or fistula rather than hematogenous seeding from a distant source.
What is the ICD-10 Code for osteomyelitis of right foot?
ICD-10 Code for Other acute osteomyelitis, right ankle and foot- M86. 171- Codify by AAPC.
What is L89 154?
ICD-10 code L89. 154 for Pressure ulcer of sacral region, stage 4 is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What causes vertebral osteomyelitis?
Vertebral osteomyelitis is the most common form of vertebral infection. It can develop from direct open spinal trauma, infections in surrounding areas and from bacteria that spreads to a vertebra from the blood. Intervertebral disc space infections involve the space between adjacent vertebrae.
How is vertebral osteomyelitis treated?
Treatment for vertebral osteomyelitis is usually conservative (meaning nonsurgical) and based primarily on use of intravenous antibiotic treatment. Occasionally, surgery may be necessary to alleviate pressure on the spinal nerves, clean out infected material, and/or stabilize the spine.
What is the most common cause of osteomyelitis?
Most cases of osteomyelitis are caused by staphylococcus bacteria, types of germs commonly found on the skin or in the nose of even healthy individuals.
What causes vertebrae infection?
Vertebral osteomyelitis is most often caused by bacteria. The infection may develop after trauma to the spine, post-surgery, or from bacterial infections in other parts of the body that spread to the vertebra from the blood.
When will the ICd 10-CM M86.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What causes inflammation of the bone marrow and adjacent bone?
Inflammation of the bone marrow and adjacent bone caused by a pyogenic organism ; it may remain localized or may spread through the bone to involve the marrow, cortex, cancellous tissue, and periosteum.
What are the different types of osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis of vertebra, thoracic region 1 Osteomyelitis of thoracic vertebra 2 Osteomyelitis of vertebra of thoracic spine
When will the ICD-10-CM M46.24 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M46.24 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the disease of osteomyelitis?
Acute osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the bone caused by an infectious organism. The condition develops rapidly during the course of several days. It is characterized by localized pain, soft-tissue swelling, and tissue warmth at the site of the infection, plus systemic symptoms such as fever, irritability, fatigue, and nausea.
What is chronic multifocal osteomyelitis?
Chronic multifocal osteomyelitis is a rare condition that also is referred to as chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, or SAPHO syndrome (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis, osteitis). The cause of the condition is unknown, and tissue cultures typically fail to identify any infectious organism.
What is the code for an infectious agent?
As with all infectious processes in which the infectious agent is not a component of the code that describes the condition, an additional code from categories B95-B97 should be assigned to identify the infectious agent, assuming it can be identified. Any major osseous defects also should be identified with a code from subcategory M89.7.
Which code includes Brodie's abscess?
Multiple sites. Other osteomyelitis (M86.8) which includes Brodie’s abscess, requires only the general region (shoulder, upper arm, forearm, hand, thigh, lower leg, ankle/foot, other site, and unspecified site). Laterality is not a component of codes in category M86.8. Unspecified osteomyelitis (M86.9) is not specific to a site.
Is osteomyelitis a chronic disease?
Osteomyelitis is an inflammation of the bone that typically is further differentiated as acute, sub-acute, or chronic. In ICD-9-CM, documentation of the general site of the inflammation/infection (such as shoulder region, forearm, or ankle), along with identification of the inflammation/infection as a current acute/sub-acute infection or a chronic condition, is all that is required to assign the most specific code.
Can osteomyelitis cause sinus drainage?
Chronic osteomyelitis is a severe, persistent inflammation/infection that can recur and be difficult to treat. A chronic infection also may present with a draining sinus, presenting a greater risk for complications, such as major bo ny defects.
When is the ICd 10 code for osteomyelitis effective?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.8 became effective on October 1, 2020.
When will the ICd 10-CM M86.8 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICd 10 code for osteomyelitis?
Other osteomyelitis, lower leg 1 M86.8X6 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.8X6 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M86.8X6 - other international versions of ICD-10 M86.8X6 may differ.
When will the ICd 10 M86.8X6 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M86.8X6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is another possible cause of osteomyelitis?
For example, if the record indicates a history of osteomyelitis and there is another possible cause of osteomyelitis, such as an infection due to a pressure ulcer or tuberculosis or typhoid. Another example might be if a patient has a complicated history including diabetes.
Is osteomyelitis a chronic disease?
This infection occurs predominantly in children and is often disseminated via the blood stream (hematogenously). In adults, osteomyelitis is usually a subacute or chronic infection that develops secondary to an open injury to bone and surrounding soft tissue.
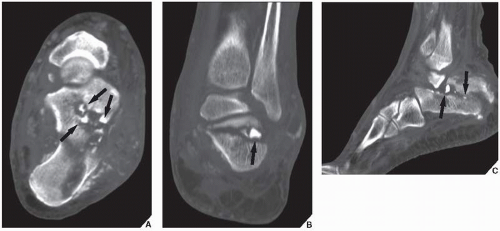
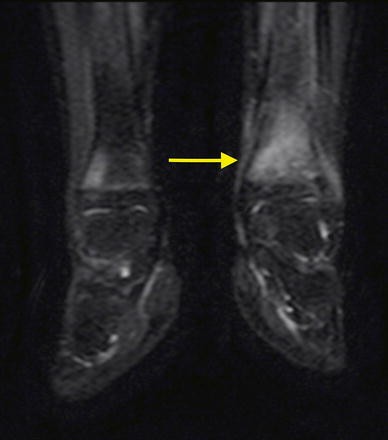
Acute and Sub-Acute Osteomyelitis
Chronic Osteomyelitis
- There are four subcategories in ICD-10-CM for chronic osteomyelitis, including M86.3 Chronic multifocal osteomyelitis, M86.4 Chronic osteomyelitis with draining sinus, M86.5 Other chronic hematogenous osteomyelitis, and M86.6 Other chronic osteomyelitis. Chronic multifocal osteomyelitis is a rare condition that also is referred to as chronic recurr...
Other Osteomyelitis
- There are two additional subcategories for the reporting of this condition in ICD-10-CM. Subcategory M86.8 reports other osteomyelitis, and this category includes Brodie’s abscess. Brodie’s abscess previously was classified as a type of chronic osteomyelitis, but most scholarly literature now refers to it as a sub-acute condition. The defining characteristic is the presence o…
Site Specificity in ICD-10-CM
- While ICD-9-CM identifies only the general region of the osteomyelitis, ICD-10-CM includes specific bones for some sites and laterality. Specific sites for subcategories M86.0-M86.6 include: 1. Shoulder 2. Humerus 3. Radius/ulna 4. Hand 5. Femur 6. Tibia/fibula 7. Ankle/foot 8. Other specified sites 9. Multiple sites Other osteomyelitis (M86.8) which includes Brodie’s abscess, re…
Additional Codes
- As with all infectious processes in which the infectious agent is not a component of the code that describes the condition, an additional code from categories B95-B97 should be assigned to identify the infectious agent, assuming it can be identified. Any major osseous defects also should be identified with a code from subcategory M89.7.
Additional Coding Changes For Bone Infections
- One additional coding change is that there are is no longer a separate designation for periostitis without mention of osteomyelitis in ICD-10-CM. In ICD-9-CM, this condition was reported with codes from subcategory 730.3. In ICD-10-CM, the Alphabetic Index provides only a limited number of specific entries for periostitis. There are specific entries for periostitis of the dentoalveolar str…
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for multiple trauma fractures
- 2. icd 10 code for mediastinal fluid collection
- 3. icd 10 code for hx of liver cancer
- 4. icd 10 code for status avr
- 5. icd 10 code for cardiolipin igg ab
- 6. what is the icd 9 code for colitis
- 7. icd 10 code for diabetic supplies
- 8. icd 10 cm code for elevated blood sugar
- 9. icd-10 code for pelvic dysfunction
- 10. icd 10 code for acute pancreatitis with pseudocyst