Is there a cure for otitis externa?
Otitis externa sometimes gets better without treatment, but it can take several weeks. Your GP can prescribe ear drop medication that usually improves the symptoms within a few days. There are a number of different types of ear drops that may be used to treat otitis externa, but they all tend to be used several times a day for about a week.
How can otitis externa be prevented?
Prevention • Otitis externa after swimming can be prevented by thorough drying of the ear canal. • Prompt treatment of acute otorrhea in patients with tympanostomy tubes with antibiotic-glucocorticoid drops can prevent secondary otitis externa.
What is the prognosis of untreated otitis externa (OE)?
- AOE can lead to localised abscess formation; this is usually as a result of Staphylococcus aureus
- This presents with localised fluctuant swelling, which may form in or around the affected ear
- Occlusion of the ear canal may lead to a conductive hearing deficit; If the abscess ruptures, there may be evidence of purulent discharge
What infection is called otitis externa?
Swimmer's ear (also called otitis externa) is a type of ear infection. The infection occurs in the ear canal. Because the ear canal is dark, warm, and can hold water, it makes a perfect environment for water-loving bacteria and fungus to grow. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
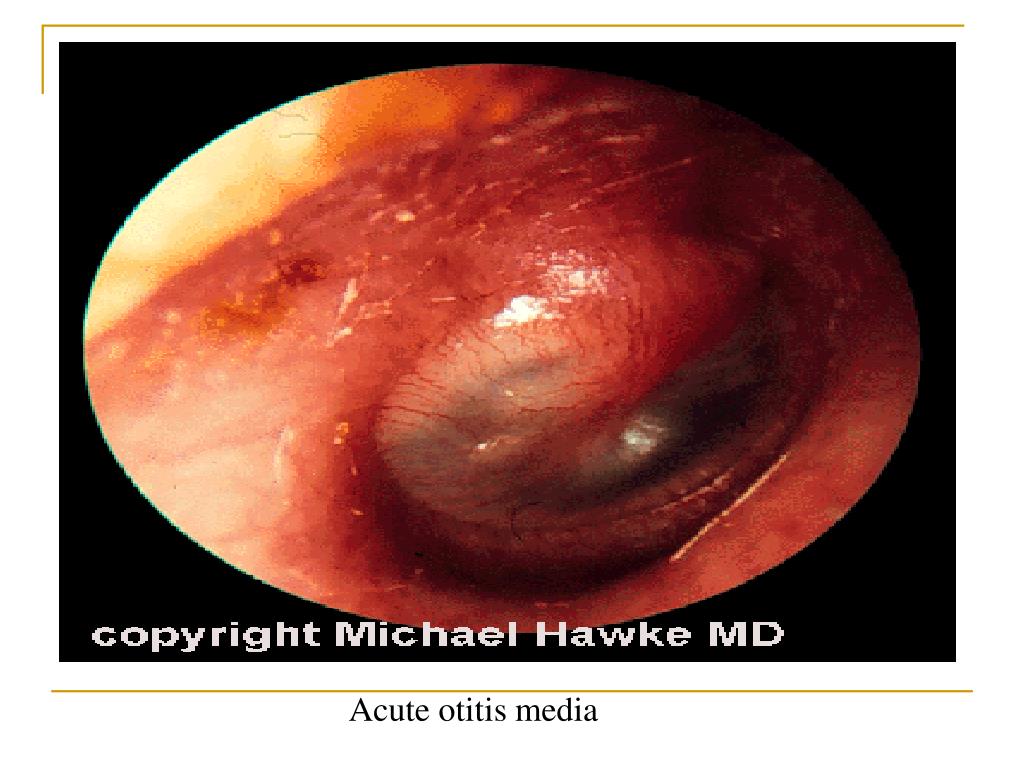
What is the ICD-10 code for Acute otitis media left ear?
ICD-10 code H66. 92 for Otitis media, unspecified, left ear is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the ear and mastoid process .
What is the DX code for otitis media?
ICD-10-CM Code for Otitis media, unspecified H66. 9.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
What is acute serous otitis media?
Acute Serous Otitis Media Acute otitis media (AOM) is the most common ear infection, causing pain and swelling in the ear. A doctor can diagnose AOM simply by looking into your child's ears with an otoscope.
What is otitis media with effusion?
Otitis media with effusion (OME) is a collection of non-infected fluid in the middle ear space. It is also called serous or secretory otitis media (SOM). This fluid may accumulate in the middle ear as a result of a cold, sore throat or upper respiratory infection.
What is Nonsuppurative otitis media?
Acute nonsuppurative otitis media refers to the tubal pharynx, mouth, and cartilage segments, inflammatory mucosal hyperemia, swelling, and congestion after acute upper respiratory tract infection and may be accompanied by bacteria or viruses via the eustachian tube, directly into the middle ear cavity, resulting in an ...
Is R51 a billable code?
R51. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM R51. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for altered mental status?
82 Altered mental status, unspecified.
What is the ICD-10 code for acute tonsillitis?
ICD-10 code J03. 90 for Acute tonsillitis, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is the difference between acute otitis media and serous otitis media?
Ear Infection. Be aware that serous otitis media is not an ear infection, otherwise known as acute otitis media. While both have fluid in the middle ear space, fluid with acute otitis media is infected, whereas that is not the case with serous otitis media.
What is the difference between otitis media and otitis media with effusion?
Otitis media is a generic term that refers to an inflammation of the middle ear. The middle ear is the space behind the eardrum. Otitis media with effusion means there is fluid (effusion) in the middle ear, without an infection.
What is the difference between serous and suppurative otitis media?
Acute suppurative otitis media is distinguished from secretory (serous) otitis media by the presence of purulent fluid in the middle ear. Pathogenic bacteria may be cultured from the majority of needle aspirates of this purulent fluid.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for cervico-occipital neuralgia
- 2. icd 10 code for right lip dysesthesia
- 3. icd 10 cm code for l abscess buttocks
- 4. icd 9 code for neck fusion
- 5. icd-10-pcs code for peg tube placement
- 6. icd 10 code for sprain shoulfer right
- 7. icd-10-cm code for acute and chronic duodenal ulcer
- 8. icd 10 code for disuse toxic myopathy
- 9. icd 10 code for pain in right groin
- 10. icd 10 code for liver cept