What is the ICD 10 code for parotid gland cancer?
2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. D37.030 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of the parotid salivary gland. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM D37.030 became effective on October 1, 2018.
What is the ICD 10 code for neoplasm of uncertain behavior?
D37.030 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of the parotid salivary gland.
What is the ICD 10 code for carotid body tumor?
Carotid body tumor ICD-10-CM D44.6 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 054 Nervous system neoplasms with mcc 055 Nervous system neoplasms without mcc
What is the CPT code for malignant neoplasm?
Malignant neoplasms of ectopic tissue are to be coded to the site mentioned, e.g., ectopic pancreatic malignant neoplasms are coded to pancreas, unspecified ( C25.9 ). Categories D37 - D44, and D48 classify by site neoplasms of uncertain behavior, i.e., histologic confirmation whether the neoplasm is malignant or benign cannot be made.
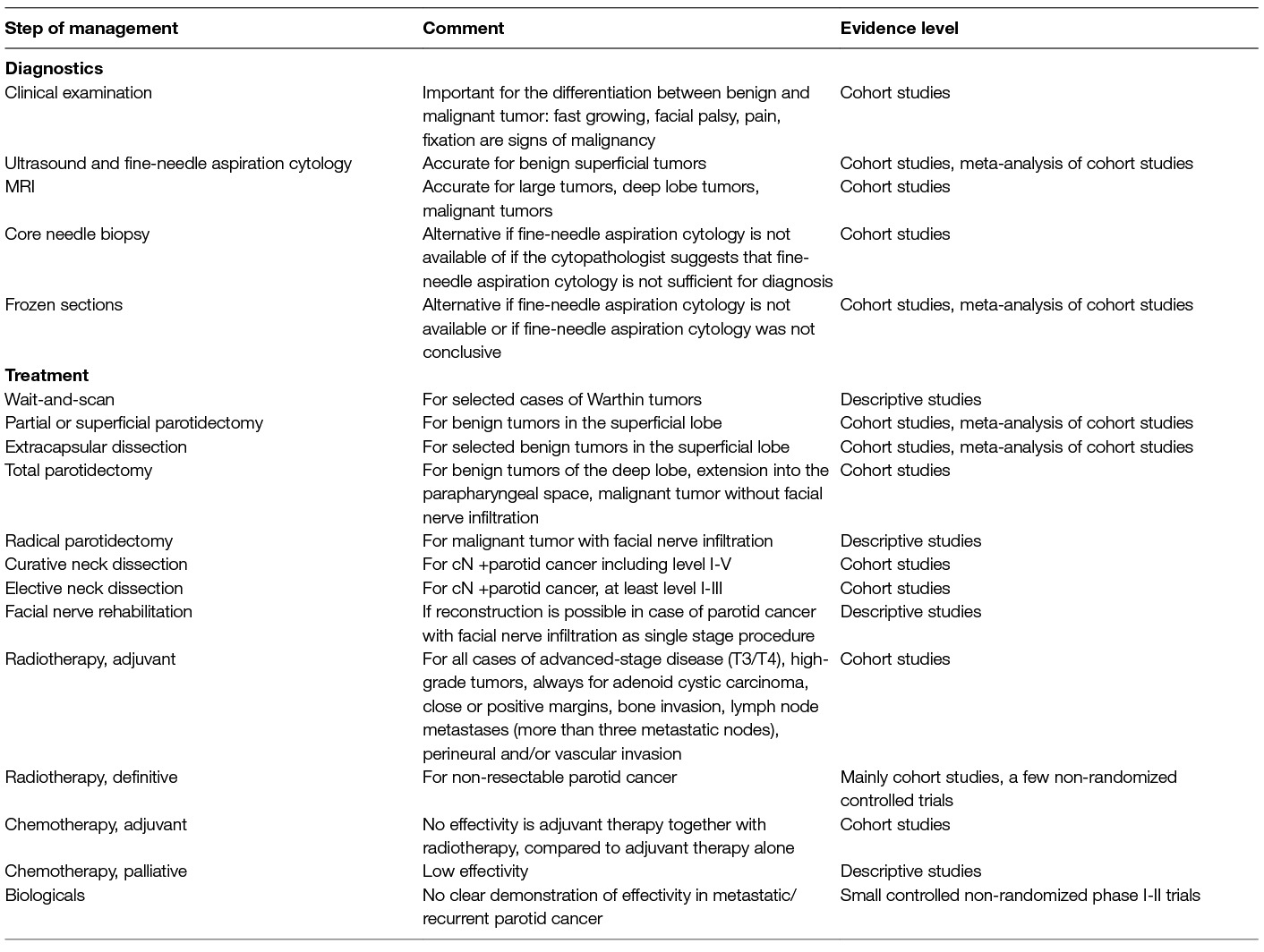
What is ICD-10 code for parotid tumor?
Benign neoplasm of parotid gland D11. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D11. 0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is benign neoplasm of parotid gland?
Tumors can occur in any of these glands, but the parotid glands are the most common location for salivary gland tumors. Most parotid tumors are noncancerous (benign), though some tumors can become cancerous.
What is the most common parotid neoplasm?
The most common tumor of the parotid gland is the pleomorphic adenoma, which represents about 60% of all parotid neoplasms, as seen in the table below.
What causes pleomorphic adenoma in parotid gland?
The causes of pleomorphic adenomas are still unknown and the risk factors have not been fully ascertained yet. In addition to age, risk factors may be related to smoking habits, alcohol abuse, a diet rich in cholesterol and previous radiation therapy treatments in the face and neck regions.
What are the 5 most common benign salivary gland tumors?
Types of noncancerous (benign) salivary gland tumors include:Pleomorphic adenoma.Basal cell adenoma.Canalicular adenoma.Oncocytoma.Warthin tumor.
How can you tell the difference between pleomorphic adenoma and Warthin tumor?
Conclusion: Ultrasound imaging characteristics, including multiple occurrences, shape, intrinsic cystic change, and the grade and distribution of tumor vessels, can be used to differentiate pleomorphic adenomas from Warthin's tumors.
Are most parotid tumors benign?
Approximately 80% of salivary gland tumours occur in the parotid gland. Of these, approximately 75- 80% are benign. There is no consistent correlation between the rate of tumour growth and whether a tumour is benign or malignant. The majority of benign tumours of the parotid gland are epithelial tumours.
What is the most common benign salivary gland tumor?
Pleomorphic adenoma (PA) is the most common benign tumor of major or minor salivary glands.
How often are parotid tumors cancerous?
Only about 20% of parotid gland tumors are malignant. Half of submandibular and sublingual tumors, and 20% of the minor salivary gland tumors are benign [7]. The five-year relative survival rate for salivary gland cancer depends on the stage the cancer.
What does pleomorphic adenoma mean?
Pleomorphic adenomas are benign salivary gland tumors, which predominantly affect the superficial lobe of the parotid gland. The “pleomorphic” nature of the tumor can be explained on the basis of its epithelial and connective tissue origin. The tumor has a female predilection between 30–50 years of age.
Can a pleomorphic adenoma become malignant?
Pleomorphic adenomas harbor a small risk of malignant transformation. The malignant potential is proportional to the time the lesion is in situ (1.5% in the first five years, 9.5% after 15 years). Therefore, excision is warranted in almost all cases.
Do benign parotid tumors have to be removed?
Although 80% of these lumps are benign, in most cases we recommend that they are removed since they generally continue to grow and can become unsightly. After many years a benign lump can turn malignant.
Do benign parotid tumors have to be removed?
Although 80% of these lumps are benign, in most cases we recommend that they are removed since they generally continue to grow and can become unsightly. After many years a benign lump can turn malignant.
What causes benign parotid gland tumor?
Causes of Salivary Gland Tumors The cause of most salivary gland tumors is currently unknown, but genetic research is being conducted to uncover it. In some cases, skin cancer can spread to the parotid gland. Smoking is also known to cause one type of benign tumor, Warthin's.
What is a benign neoplasm?
A benign tumor is an abnormal but noncancerous collection of cells also called a benign neoplasm. Benign tumors can form anywhere on or in your body, but many don't need treatment.
Should a parotid tumor be removed?
Treatment Surgery is recommended for almost all parotid gland tumors, whether cancerous or benign. Although most tumors grow slowly and are non-cancerous, they will often continue to grow and occasionally can become cancerous. Treatment of a parotid tumor generally requires removing the parotid gland (parotidectomy).
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 D37.039 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D37.039 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 D37.3 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D37.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
When will the ICd 10 D11.0 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D11.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 D44.6 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D44.6 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
When will the ICd 10 D40.11 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D40.11 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for mac infection
- 2. icd 10 code for pain with arm movement
- 3. icd 10 code for bone mineral density test medicare
- 4. icd 10 code for skin tag of ear
- 5. icd 10 cm code for paroxymal supraventricular tachycardia
- 6. icd 10 code for history of raynoud's phenomenon
- 7. icd 10 code for abscess pubic area
- 8. icd 10 code for acute subacute infarct
- 9. icd 10 code for 1st degree burn of right thigh
- 10. icd-10 dx code for vaginal itching