What is Pat in heart rhythm?
Is Pat the same as PSVT?
Is Pat a SVT?
What is diagnosis code I47 2?
What does PAT mean in medical terms?
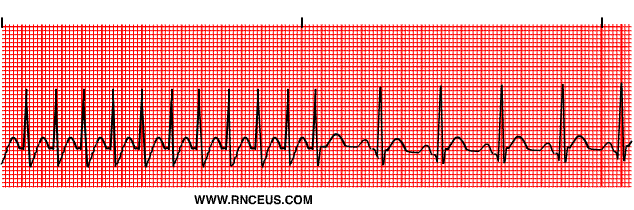
Does PAT have P waves?
What does PAT stand for in NFL?
It is an untimed scrimmage down, also called the try, where a team can kick the ball into the goal post for one point or run it into the end zone for two points. Extra Point (PAT) - 1 point. Two Point Conversion (Conversion) - 2 points.
What is PAT School?
How can you tell the difference between PAT and SVT?
What is the ICD-10 code for PSVT?
What is the ICD-10 code for V tach?
What is the ICD-10 code for rapid ventricular response?
What is a disease of multiple peripheral nerves?
Diseases of multiple peripheral nerves simultaneously. Polyneuropathies usually are characterized by symmetrical, bilateral distal motor and sensory impairment with a graded increase in severity distally. The pathological processes affecting peripheral nerves include degeneration of the axon, myelin or both. The various forms of polyneuropathy are categorized by the type of nerve affected (e.g., sensory, motor, or autonomic), by the distribution of nerve injury (e.g., distal vs. Proximal), by nerve component primarily affected (e.g., demyelinating vs. Axonal), by etiology, or by pattern of inheritance.
What is a cranial nerve disorder?
Clinical Information. A disorder affecting the cranial nerves or the peripheral nervous system. It is manifested with pain, tingling, numbness, and muscle weakness. It may be the result of physical injury, toxic substances, viral diseases, diabetes, renal failure, cancer, and drugs.
When will the ICD-10 G62.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G62.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How to determine unspecified diagnosis code?
The unspecified diagnosis code rate is calculated by dividing the number of unspecified diagnosis codes by the total number of diagnosis codes assigned. Health information management professionals should be tracking and trending unspecified diagnosis code rates across the continuum of care. This can also be drilled down to unspecified laterality codes. Keep in mind that this is not really an error rate per se, but is an indicator of the quality of medical record documentation. Early on in FY2016 when ICD-10 was implemented, HIA conducted numerous medical record reviews to determine the level of unspecified code use and made recommendations as to how our clients could improve specified code use through provider education. Hospitals and other providers may want to perform similar audits before the April 1, 2022 implementation date. A review of the clinical documentation associated with these codes may reveal clinical details needed to assign a more specific diagnosis code.
How long to delay CMS code change?
In response to the FY2022 Proposed Rule comment period, “ A number of commenters recommended (or urged) CMS to delay any possible change to the designation of these codes for at least two years to give hospitals and their physicians time to prepare.”
Why are ICD-10 codes unspecified?
This is because many times there is not sufficient information in the patient record or clinical information for the physician to make specific diagnoses. An ICD-10-CM code is considered unspecified if either of the terms “unspecified” or “NOS” are used in the code description. Coders are forced to use unspecified codes when further information is not documented. Way back in 2015, right around the time ICD-10 was implemented, there was talk of the elimination or the denial of the use of unspecified diagnosis codes on claims. There was quite a bit of uproar as requiring specific diagnosis codes and the querying that would be needed to accomplish this would have been overly burdensome for hospitals and providers right at the time of ICD-10 implementation. While diagnosis code specificity has always been the goal, providers were granted a reprieve in order to facilitate implementation of ICD-10. For the first 12 months of ICD-10-CM use, the CMS promised that Medicare review contractors would not deny claims “based solely on the specificity of the ICD-10-CM diagnosis code, as long as the physician/practitioner used a valid code from the right family.” Referred to as the “grace period,” this flexibility was intended to help providers implement the ICD-10-CM code set and was never intended to be permanent. In fact, this CMS-granted grace period expired on October 1, 2016. Some third party payors started denying unspecified codes, but this has been intermittent depending on the payor.
What is an unspecified code?
Codes titled “unspecified” are for use when the information in the medical record is insufficient to assign a more specific code. For those categories for which an unspecified code is not provided, the “other specified” code may represent both other and unspecified.
Is CMS changing severity levels?
So in the FY2022 Final Rule, CMS stated it is not changing severity levels, at least not yet. However what they DID finalize was this:
Is the information contained in this post valid?
The information contained in this post is valid at the time of posting. Viewers are encouraged to research subsequent official guidance in the areas associated with the topic as they can change rapidly.
What is the code for acute exacerbation of CHF?
Assign the acute exacerbation of CHF (HFpEF) code I50.33, Acute on chronic diastolic (congestive) heart failure as the principal diagnosis in this case. The surgery date was already set and not performed on this admission. The patient ran out of Lasix and did not go to the pharmacy to get it (noncompliance). That is the reason she went into CHF (HFpEF) exacerbation and presented with SOB and elevated BNP on admission. She later went home AMA to come back for original surgery. In addition, assign T82.03XA, Leakage of heart valve prosthesis, initial encounter; T50.1X6A, Underdosing of loop [high-ceiling] (Lasix) diuretics, initial encounter; Z91.128, Patient’s intentional underdosing of medication regimen for other reason; and any other secondary diagnoses on the case.
Is shortness of breath improved with Lasix?
Subjective: Shortness of breath is improved since she has been on Lasix. Patient is happy to be getting her valve replacement on 6/7.
Is every case unique?
We know that every case is unique. The above post is simply our opinion based on the information we have received. We encourage readers to research subsequent official guidance in the areas associated with this topic as they can change rapidly.
Is a PA employed by a physician?
The PA is not employed by physician, however,they are both (physician performing surgery and PA) are employed by the hospital. In all cases the reason for performing the PAT is due an impending surgery.
Do hospitals require pre-operative evaluations?
Hospitals frequently require some sort of pre-operative evaluation/report. Doesn't mean the physician can bill for and be paid for it.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for intractible ha
- 2. icd 10 code for malignant melanoma of lip
- 3. icd 10 code for concussion
- 4. icd 10 code for tenosynovitis wrist
- 5. icd 10 code for moderate depressive episode
- 6. icd 10 cm code for cva with left hemiplegia
- 7. icd 10 code for colangel carcinoma
- 8. icd 9 code for suture abscess
- 9. icd 10 code for 2 vessle coronary stent
- 10. icd 10 code for calcified lymph nodes