How to confirm PCOS diagnosis?
Oct 01, 2021 · Polycystic ovarian syndrome 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code E28.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E28.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Are there any specific diet for PCOS?
ICD-10-CM Code E28.2 Polycystic ovarian syndrome BILLABLE Female Only | ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 E28.2 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis. The ICD code E282 is used to code Polycystic ovary syndrome
Should I be tested for PCOS?
Oct 01, 2021 · Polycystic ovarian syndrome Billable Code E28.2 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Polycystic ovarian syndrome . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 . ↓ See below for any exclusions, inclusions or special notations
How can PCOS be diagnosed?
The ICD-10-CM code E28.2 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like androgenetic alopecia in association with polycystic ovaries, cyst of bilateral ovaries, diffuse alopecia, endocrine alopecia, hyperandrogenization syndrome , isosexual virilization, etc. The code E28.2 is applicable to female patients only.
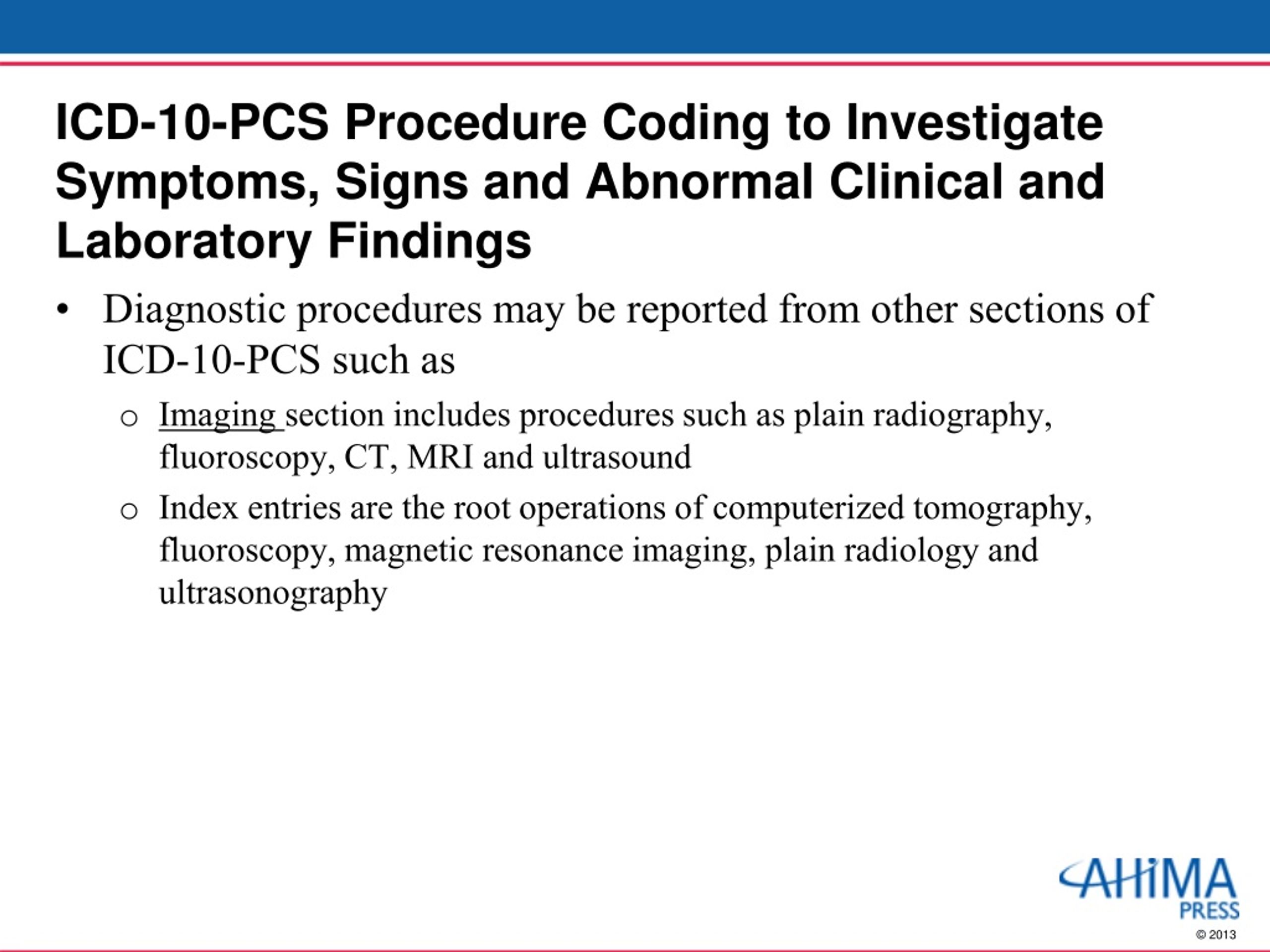
How do you code PCOS?
PCOS, which was once called Stein-Leventhal syndrome, is assigned to ICD-9-CM code 256.4. The term isosexual virilization is also included under code 256.4.Mar 2, 2009
What is the ICD-10 code for PCOS in pregnancy?
Maternal care for other abnormalities of pelvic organs, unspecified trimester. O34. 80 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is PCOS type?
There are four types of PCOS: Insulin-resistant PCOS, Inflammatory PCOS, Hidden-cause PCOS, and Pill-induced PCOS.
Is PCOS an endocrine disease?
Polycystic ovary syndrome: a common endocrine disorder and risk factor for vascular disease.
Is PCOS a hormonal disorder?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods or excess male hormone (androgen) levels. The ovaries may develop numerous small collections of fluid (follicles) and fail to regularly release eggs.Oct 3, 2020
What are the 4 types of PCOS?
The 4 types of PCOS include:Insulin resistant PCOS. This is the most common type of PCOS, affecting around 70% of people. ... Post-pill PCOS. Post-pill PCOS occurs in some people after they stop taking the oral contraceptive pill. ... Adrenal PCOS. ... Inflammatory PCOS.Apr 26, 2021
Is PCOS an autoimmune disease?
Technically, PCOS (or polycystic ovary syndrome) is classified as an endocrine disorder, not an autoimmune disease. In fact, it's the most common endocrine disorder to affect women. Endocrine diseases are related to your hormones.
Is PCOD and PCOS same?
Difference between PCOD and PCOS PCOD is a condition in which ovaries produce many immature or partially mature eggs, this happen due to poor lifestyle, obesity, stress and hormonal imbalance. PCOS is a metabolic disorder and more severe form of PCOD can lead to anovulation where ovaries stop releasing eggs.
What is the ICd code for PCOS?
The ICD code E282 is used to code Polycystic ovary syndrome. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), also called hyperandrogenic anovulation (HA), or Stein–Leventhal syndrome, is a set of symptoms due to elevated male hormone in women.
What is the ICD code for polycystic ovarian syndrome?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Code is only used for female patients. E28.2 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome.
How do you know if you have PCOs?
Signs and symptoms of PCOS include irregular or no menstrual periods, heavy periods, excess body and facial hair, acne, pelvic pain, trouble getting pregnant, and patches of thick, darker, velvety skin.
What is the ICd 10 code for polycystic ovarian syndrome?
E28.2 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of polycystic ovarian syndrome. The code E28.2 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code E28.2 might also be used to specify conditions or terms like androgenetic alopecia in association with polycystic ovaries, diffuse alopecia, endocrine alopecia, hyperandrogenization syndrome, isosexual virilization , male pattern alopecia, etc.#N#The code E28.2 is applicable to female patients only. It is clinically and virtually impossible to use this code on a non-female patient.
How to diagnose PCOs?
To diagnose PCOS, your health care provider may do a physical exam, pelvic exam, blood tests, and an ultrasound. There is no cure, but diet, exercise, and medicines can help control the symptoms. Birth control pills help women have normal periods, reduce male hormone levels, and clear acne.
What is the name of the condition where a woman's ovaries produce more male hormones than normal?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) happens when a woman's ovaries or adrenal glands produce more male hormones than normal. PCOS causes cysts (fluid-filled sacs) to grow on the ovaries. Symptoms include
What is polycystic ovary syndrome?
POLYCYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME-. a complex disorder characterized by infertility hirsutism; obesity; and various menstrual disturbances such as oligomenorrhea; amenorrhea; anovulation. polycystic ovary syndrome is usually associated with bilateral enlarged ovaries studded with atretic follicles not with cysts. the term polycystic ovary is misleading.
What are the risks of PCOs?
Weight gain. Acne or oily skin. Patches of thickened skin. Women with PCOS are at higher risk of diabetes, metabolic syndrome, heart disease, and high blood pressure. PCOS is more common in women who have obesity, or have a mother or sister with PCOS.
What happens to ovarian follicles during ovulation?
Normally, ovarian follicles contain egg cells, which are released during ovulation. In polycystic ovary syndrome, abnormal hormone levels prevent follicles from growing and maturing to release egg cells. Instead, these immature follicles accumulate in the ovaries. Affected women can have 12 or more of these follicles.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for infection of screw in leg
- 2. icd 10 cm code for fu on car accident
- 3. what is the icd 10 code for elevated hemoglobin
- 4. icd 10 code for abnormal finding brain mri
- 5. icd-10-pcs code for mastectomy of the left breast
- 6. icd 10 code for nursemaids elbow left
- 7. icd 10 code for adverse effect of statin
- 8. icd 10 code for thin prep
- 9. icd 10 code for k30
- 10. icd 10 code for status post fusion