How to identify penicillin allergy?
penicillin allergy. Penicillin skin testing and challenge doses are reliable and useful methods for evaluating for IgE-mediated penicillin allergy.5 Penicillin Skin Testing A positive result means the patient is likely to have a penicillin allergy. If negative, the skin test is usually followed by an oral penicillin class challenge (e.g., with ...
How can you know if you are allergic to penicillin?
Symptoms
- Anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis is a rare, life-threatening allergic reaction that causes the widespread dysfunction of body systems.
- Delayed reactions resulting from penicillin allergy. ...
- Adverse events that are not allergic reactions. ...
- When to see a doctor. ...
Are you really allergic to penicillin?
“Even though you might have a penicillin allergy on your record, you may not actually be allergic to penicillin. Over 90 percent of people who have a listed penicillin allergy, when tested and challenged, do not have that allergy,” says Dr. Paige G. Wickner, MD, MPH, of the Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Can you be allergic to penicillin and not amoxicillin?
The reverse is also true: If you’re allergic to amoxicillin, you shouldn’t take penicillin or other penicillin antibiotics. In addition, if you’re allergic to cephalosporin antibiotics, you’re at risk for an allergic reaction to penicillin antibiotics.
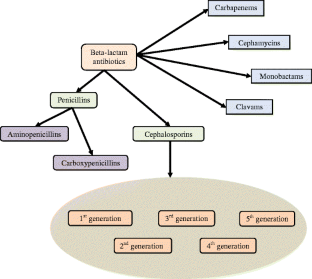
What is the ICD-10 code for penicillin allergy?
ICD-10 code: Z88. 0 Personal history of allergy to penicillin.
How do you code allergy to penicillin?
Z88. 0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
Is penicillin allergy A Type 1 hypersensitivity?
The incidence of anaphylaxis to penicillin is 0.02% to 0.04% and is mediated by a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction.
What is the ICD-10 code for allergy to antibiotics?
ICD-10 Code for Allergy status to other antibiotic agents- Z88. 1- Codify by AAPC.
How do you code an allergic reaction in ICD-10?
ICD-10-CM Code for Allergy, unspecified, initial encounter T78. 40XA.
What is the diagnosis for ICD-10 code r50 9?
9: Fever, unspecified.
Is penicillin allergy type 2 hypersensitivity?
The most common cause of type II reactions are medications including penicillins, cephalosporins, hydrochlorothiazide, and methyldopa, which become associated with red blood cells or platelets leading to anemia and thrombocytopenia.
What type of allergy is penicillin?
Penicillin allergy is an abnormal reaction of your immune system to the antibiotic drug penicillin. Penicillin is prescribed for treating various bacterial infections. Common signs and symptoms of penicillin allergy include hives, rash and itching.
What is type II hypersensitivity?
Type II hypersensitivity reaction is a form of immune-mediated reaction in which antibodies are directed against cellular or extracellular matrix antigens. This antibody-mediated response leads to cellular destruction, functional loss, or damage to tissues.
Is amoxicillin and penicillin the same thing?
Official answer. The main difference between amoxicillin and penicillin is that amoxicillin is effective against a wider spectrum of bacteria compared with penicillin. Both amoxicillin and penicillin belong to the class of antibiotics called penicillins.
What is the ICD-10 code for Allergy to sulfa drugs?
ICD-10-CM Code for Allergy status to sulfonamides Z88. 2.
How do you bill for drug challenge?
CPT 95076 and 95079 are the codes to use for any additional oral drug challenge. 95076 is billed for the first 61-120 minutes of the challenge. “Time” begins as soon as work begins on the challenge (including explaining the test to the patient) and ends with a negative result or with reactions that need to be treated.
What is the T code for cephalosporin?
Adverse effect of Cephalosporins & other beta-lactam antibiotics T36.1X5A (or D) ( Be sure to document why penicillin testing is required if the reaction was to a Cephalosporin.) T codes require a seventh character of A, D, or S (“S” is rarely used by allergists).
What is CPT 95076?
CPT 95076 and 95079 are the codes to use for any additional oral drug challenge. 95076 is billed for the first 61-120 minutes of the challenge.
Is penicillin allergy testing a CPT?
Penicillin allergy testing can help extend the scope of your practice and provide a valuable service to your patients. But ICD-10 and CPT coding for penicillin allergy testing can be confusing. Here’s what you need to know to get reimbursed for this important service.
What is T36.1?
T36.1 Poisoning by , adverse effect of and underdosing of cephalosporins and other beta-lactam antibiotics. T36.1X Poisoning by, adverse effect of and underdosing of cephalosporins and other beta-lactam antibiotics.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.
What is T37 poisoning?
T37 Poisoning by, adverse effect of and underdosing of other systemic anti-infectives and antiparasitics. T37.0 Poisoning by, adverse effect of and underdosing of sulfonamides. T37.0X Poisoning by, adverse effect of and underdosing of sulfonamides.
What is the secondary code for Chapter 20?
Use secondary code (s) from Chapter 20, External causes of morbidity, to indicate cause of injury. Codes within the T section that include the external cause do not require an additional external cause code. Type 1 Excludes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for essential primary hypertension
- 2. icd 10 code for post hospital visit
- 3. icd 10 code for primary liver cancer
- 4. icd-10 code for iga vasculitis
- 5. icd 10 code for tingling
- 6. icd-10 code for vit b complex
- 7. icd 10 code for r leg injury
- 8. icd 10 code for prerenal azotemia
- 9. icd 10 code for intermittent claudication of leg
- 10. icd 10 code for bipolar disorder hypomanic