Full Answer
What is the ICD 10 code for peripheral vascular disease?
Peripheral vascular disease, unspecified 1 I73.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM I73.9 became effective on October 1, 2019. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I73.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 I73.9 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for paresthesia of skin?
Paresthesia of skin 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Billable/Specific Code R20.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM R20.2 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What is the ICD 10 code for spondylosis?
G54.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G54.0 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of G54.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 G54.0 may differ. spondylosis ( M47.-)
What is the ICD 10 code for paroxysmal anxiety?
Panic disorder [episodic paroxysmal anxiety] F41.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM F41.0 became effective on October 1, 2018.
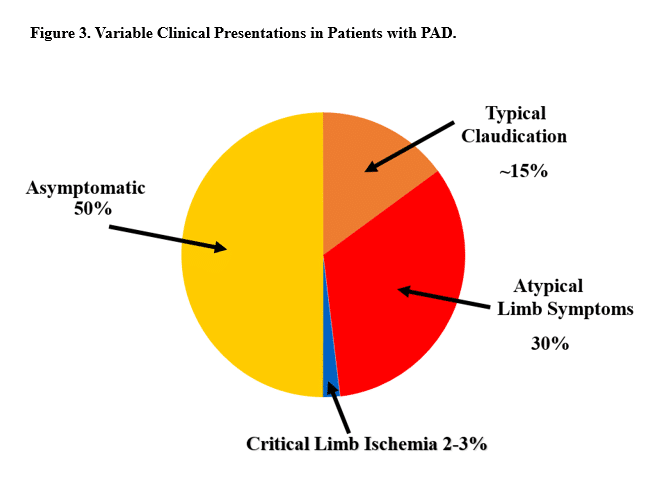
Is Diabetic peripheral angiopathy the same as PVD?
PVD is also synonymous with peripheral angiopathy. If the patient has atherosclerosis of native arteries of extremities, use an additional code to provide other details, such as laterality and manifestations.
Is peripheral vascular disease the same as peripheral artery disease?
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is often used interchangeably with the term “peripheral vascular disease (PVD).” The term “PAD” is recommended to describe this condition because it includes venous in addition to arterial disorders.
What is ICD-10 code for peripheral vascular disease?
ICD-10 code I73. 9 for Peripheral vascular disease, unspecified is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the circulatory system .
What ICD-10 code for peripheral sensory neuropathy?
Other idiopathic peripheral autonomic neuropathy G90. 09 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM G90. 09 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are the types of peripheral vascular disease?
Types of Peripheral Vascular Disease The two major categories of PVD are occlusive and functional. The types of PVD that stem from a blockage of the vessels are called occlusive. Atherosclerosis: Thickening or hardening of the arteries over time can also lead to heart attack or stroke if not treated.
What are the 6 P's of peripheral vascular disease?
The six Ps (pain, pallor, poikilothermia, pulselessness, paresthesia, paralysis) are the classic presentation of acute arterial occlusion in patients without underlying occlusive vascular disease.
What does peripheral vascular disease unspecified mean?
What is peripheral vascular disease? Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) is a slow and progressive circulation disorder. Narrowing, blockage, or spasms in a blood vessel can cause PVD. PVD may affect any blood vessel outside of the heart including the arteries, veins, or lymphatic vessels.
What is the cause of peripheral vascular disease?
Causes of Peripheral Vascular Disease. The most common cause of PVD is peripheral artery disease, which is due to atherosclerosis. Fatty material builds up inside the arteries and mixes with calcium, scar tissue, and other substances. The mixture hardens slightly, forming plaques.
How do you code PVD?
1,2 “Peripheral arterial disease (PAD),” “peripheral vascular disease (PVD)”, “spasm of artery” and “intermittent claudication” are coded as I73. 9. It is important to note that this code excludes atherosclerosis of the extremities (I70. 2- – I70.
How do you code peripheral neuropathy?
Peripheral neuropathy that is not further specified as being caused by an underlying condition is assigned to code 356.9.
Is polyneuropathy the same as peripheral neuropathy?
Polyneuropathy is when multiple peripheral nerves become damaged, which is also commonly called peripheral neuropathy. Peripheral nerves are the nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord. They relay information between the central nervous system (CNS), and all other parts of the body.
What is peripheral autonomic neuropathy?
Autonomic neuropathy occurs when there is damage to the nerves that control automatic body functions. It can affect blood pressure, temperature control, digestion, bladder function and even sexual function.
What is the difference between arterial and venous vascular disease?
As the name implies, arterial disorders affect your arteries — the blood vessels that deliver oxygen-rich blood from your heart to your body. Venous disorders involve your veins — the blood vessels that return blood to your heart for more oxygen.
What is the most common type of peripheral vascular disease?
The most common cause of PVD is atherosclerosis, the buildup of plaque inside the artery wall. Plaque reduces the amount of blood flow to the limbs.
What is another name for PVD?
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) or peripheral vascular occlusive disease (PVOD) is another name for peripheral arterial disease (or peripheral artery disease), often called PAD.
What is carpal tunnel?
The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway of ligament and bones at the base of your hand. It contains nerve and tendons. Sometimes, thickening from irritated tendons or other swelling narrows the tunnel and causes the nerve to be compressed. Symptoms usually start gradually.
How do I treat carpal tunnel syndrome?
Treatment includes resting your hand, splints, pain and anti-inflammatory medicines, and surgery. Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
Is lower cross a diagnosis?
But Lower Cross is not a diagnosis. However, it’s a posture observation and can be a contributing component of a more definitive diagnosis. Even though it’s not coded, it should be documented properly so that when necessary you can try to justify longer term treatment.
Is posture a good ICD-10?
These are real bio-mechanic issues that respond well to care, but for all ICD-10’s specificity, there aren’t good ICD-10 diagnosis for posture conditions.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for numbness and tingling in upper extremities
- 2. icd 10 code for avian influenza a virus with pneumonia
- 3. icd 10 code for bilateral le edema
- 4. 2019 icd 10 code for pseudoaneurysm in the left groin
- 5. icd-10 code for borderline glaucoma
- 6. icd 10 code for rotator cuff dysfunction
- 7. icd 10 code for mass on back
- 8. icd 10 code for cellulitis right lower extremities
- 9. icd-9-cm code for constipation, unspecified
- 10. icd-10 code for family history of melanoma