What is the ICD-11 code for persistent truncus arteriosus?
For the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-11), the International Paediatric and Congenital Cardiac Code (IPCCC) was developed to standardize the nomenclature of congenital heart disease. Under this system, English is now the official language, and persistent truncus arteriosus should properly be termed Common arterial trunk.
What is the ICD 10 code for patent ductus arteriosus?
Patent ductus arteriosus. Q25.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM Q25.0 became effective on October 1, 2019. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q25.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 Q25.0 may differ.
What is persistent truncus arteriosus?
Persistent truncus arteriosus. Persistent truncus arteriosus (or patent truncus arteriosus or common arterial trunk ), is a rare form of congenital heart disease that presents at birth. In this condition, the embryological structure known as the truncus arteriosus fails to properly divide into the pulmonary trunk and aorta.
What is a truncus arteriosus a congenital anomaly?
A congenital anomaly caused by the failed development of truncus arteriosus into separate aorta and pulmonary artery. It is characterized by a single arterial trunk that forms the outlet for both heart ventricles and gives rise to the systemic, pulmonary, and coronary arteries.
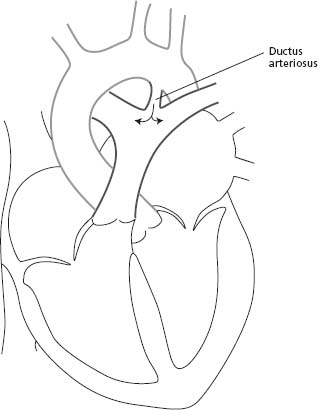
What does truncus arteriosus mean?
Truncus arteriosus pronounced TRUNG-kus ahr-teer-e-O-sus), also known as common truncus, is a rare defect of the heart in which a single common blood vessel comes out of the heart, instead of the usual two vessels (the main pulmonary artery and aorta).
What is the ICD-10 code for ductus arteriosus?
Q25.0ICD-10 code Q25. 0 for Patent ductus arteriosus is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities .
What is an arterial trunk?
Common arterial trunk (CAT) is characterised by a single great artery arising from the base of the heart, which supplies the systemic, coronary, and pulmonary blood flow, and by a ventricular septal defect (VSD).
What is ICD-10 code for History of ASD repair?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z87. 79: Personal history of other (corrected) congenital malformations.
What is the ICD 10 code for VSD?
Ventricular Septal Defect – VSD (ICD-10: Q21)
What is PDA ligation?
When the condition is present, a vein that normally closes at birth (the ductus arteriosus) stays open. The result is that oxygen-rich blood that should be circulating into the body instead goes back to the lungs. PDA ligation is a procedure to repair this problem.
What is persistent truncus arteriosus?
Persistent truncus arteriosus (TA) is a rare, congenital, cyanotic heart defect characterized by a ventricular septal defect (VSD), a single truncal valve, and a common ventricular outflow tract (OT).
What is truncus arteriosus Wikipedia?
The truncus arteriosus is a structure that is present during embryonic development. It is an arterial trunk that originates from both ventricles of the heart that later divides into the aorta and the pulmonary trunk.
What is pulmonary trunk?
The pulmonary trunk is a major vessel of the human heart that originates from the right ventricle. It branches into the right and left pulmonary arteries, which lead to the lungs.
What are the 3 types of ASD?
There are three types of autism spectrum disorders:Autistic Disorder. This is sometimes called “classic” autism. ... Asperger Syndrome. People with Asperger syndrome usually have milder symptoms of autistic disorder. ... Pervasive Developmental Disorder – Not Otherwise Specified.
What does the code I25 10 mean?
Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery withoutICD-10 Code for Atherosclerotic heart disease of native coronary artery without angina pectoris- I25. 10- Codify by AAPC. Diseases of the circulatory system.
What is the ICD-10 code Q21 1?
ICD-10 code: Q21. 1 Atrial septal defect | gesund.bund.de.
What is the main trunk of the arterial system?
Definition of aorta the main trunk of the arterial system, conveying blood from the left ventricle of the heart to all of the body except the lungs.
What is the main artery of the trunk?
Pulmonary arteryPrecursortruncus arteriosusSystemCardiovascular, RespiratorySourceright ventricleIdentifiers8 more rows
What is the common trunk?
Common arterial trunk is a defect in which a single great artery, or "trunk," comes out of the ventricles instead of the usual pulmonary artery and aorta. This big artery sits on top of the left and right ventricle and is usually accompanied by a ventricular septal defect.
What are the 4 major arteries?
The aorta is the largest artery in the body that exits the left ventricle of the heart. Main branches from the aorta include the brachiocephalic artery, left carotid artery, and the left subclavian artery.
What is abnormal persistence of an open lumen in the ductus arteriosus after birth?
Abnormal persistence of an open lumen in the ductus arteriosus after birth, the direction of flow being from the aorta to the pulmonary artery, resulting in recirculation of arterial blood through the lungs. Present On Admission. POA Help.
What is the descending aorta?
A congenital heart defect characterized by the persistent opening of fetal ductus arteriosus that connect s the pulmonar y artery to the descending aorta (aorta, descending) allowing unoxygenated blood to bypass the lung and flow to the placenta. Normally, the ductus is closed shortly after birth.
What is patent ductus arteriosus?
Clinical Information. A congenital defect characterized by the failure of the ductus arteriosus to close soon after birth. As a consequence, blood from the aorta mixes with blood from the pulmonary artery. If untreated, it may lead to congestive heart failure.
What is a common trunk?
Common truncus or common arterial trunk is a structural heart defect characterized anatomically by having a single common arterial trunk, rather than a separate aorta and main pulmonary artery (see Fig. 4.15 ). This common trunk carries blood from the heart to the body, lungs and the heart itself – that is, the common trunk gives rise to the systemic, pulmonary and coronary circulation. A ventricular septal defect is present. Other terms for the condition are (persistent) truncus arteriosus.
What is a common arterial trunk?
Related Pages. Common truncus or common arterial trunk is a structural heart defect characterized anatomically by having a single common arterial trunk, rather than a separate aorta and main pulmonary artery (see Fig. 4.15 ). This common trunk carries blood from the heart to the body, lungs and the heart itself – that is, ...
Can truncus be missed?
pulmonary atresia with ventricular septal defect or aortic atresia with ventricular septal defect). Common truncus can be missed prenatally if the outflow tract is not fully examined. Prenatal diagnoses should be confirmed postnatally, typically by echocardiography.
What is a PTA?
Persistent truncus arteriosus ( PTA ), often referred to simply as Truncus Arteriosus, is a rare form of congenital heart disease that presents at birth. In this condition, the embryological structure known as the truncus arteriosus fails to properly divide into the pulmonary trunk and aorta.
What is persistent truncus arteriosus?
Persistent truncus arteriosus ( PTA ), often referred to simply as Truncus Arteriosus, is a rare form of congenital heart disease that presents at birth. In this condition, the embryological structure known as the truncus arteriosus fails to properly divide into the pulmonary trunk and aorta.
What is the neural crest?
The neural crest, specifically a population known as the cardiac neural crest, directly contributes to the aorticopulmonary septum. Microablation of the cardiac neural crest in developing chick embryos and genetic anomalies affecting this population of cells in rodents results in persistent truncus arteriosus.
What is the difference between type III and IV pulmonary arteries?
Type III: The branch pulmonary arteries arise separately and far apart off the common trunk. Type IV: The branch pulmonary arteries arise distally off the aorta, or the lungs are supplied by multiple aortopulmonary collaterals . Type IV is now considered a form of Tetralogy of Fallot and not Common Arterial Trunk.
What is the difference between A3 and A4?
Type A3: One branch pulmonary artery arises off the common trunk, and one branch pulmonary artery is isolated, arising from a patent ductus arteriosus. Type A4: Common arterial trunk in association with interrupted aortic arch.
What is Type IV?
Type IV is now considered a form of Tetralogy of Fallot and not Common Arterial Trunk. Another well-known classification was defined by Stella and Richard Van Praagh in 1965. In this classification scheme, the preceding letter ("A" or "B") refers to the presence or absence, respectively, of a ventricular septal defect.
What is neonatal surgery?
Treatment is with neonatal surgical repair, with the objective of restoring a normal pattern of blood flow. The surgery is open heart, and the patient will be placed on cardiopulmonary bypass to allow the surgeon to work on a still heart. The heart is opened and the ventricular septal defect is closed with a patch.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for portal hypertensive gastropathy
- 2. icd 10 code for self bite
- 3. icd 10 code for icd pocket infection
- 4. icd 10 cpt code for bradycardia
- 5. 2017 icd 10 for pediatric code for anterior temporal lobes
- 6. icd 10 code for bilateral foot deformities
- 7. icd 10 code for impingement syndrome right shoulder
- 8. icd 10 code for swan-neck deformities
- 9. icd 10 code for ketoacidosis
- 10. 2021 icd 10 code for lower back pain