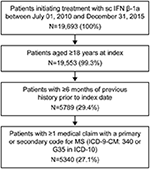
What is Pfeiffer syndrome type I?
Type I is considered mild compared to types II and III. In Pfeiffer syndrome type I, infants have craniosynostosis that causes the head to appear vertically elongated.
What are the treatment options for Pfeiffer syndrome?
Treatment is supportive and often involves surgery in the earliest years of life to correct skull deformities and respiratory function. Most individuals with Pfeiffer syndrome type 1 have a normal intelligence and life span, while types 2 and 3 typically result in neurodevelopmental disorders and early death.
What is the prognosis for children with Pfeiffer syndrome?
Children with Pfeiffer syndrome types 2 and 3 "have a higher risk for neurodevelopmental disorders and a reduced life expectancy" than children with Pfeiffer syndrome type 1, but if treated, favorable outcomes are possible. In severe cases, respiratory and neurological complications often lead to early death.
What is the ICD 10 code for patellofemoral syndrome?
Patellofemoral syndrome of bilateral knees Patellofemoral syndrome of left knee ICD-10-CM M22.2X2 is grouped within Diagnostic Related Group (s) (MS-DRG v38.0): 562 Fracture, sprain, strain and dislocation except femur, hip, pelvis and thigh with mcc
What is congenital malformation syndromes predominantly affecting facial appearance?
0 Congenital malformation syndromes predominantly affecting facial appearance. Syndrome: Goldenhar.
What is the ICD-10 code for vacterl syndrome?
EntryH01195 DiseaseOther DBsICD-11: LD2F.11 ICD-10: Q87.2 MeSH: C564752 OMIM: 276950 192350 314390 619227ReferencePMID:20849991AuthorsSchramm C, Draaken M, Bartels E, Boemers TM, Aretz S, Brockschmidt FF, Nothen MM, Ludwig M, Reutter HTitleDe novo microduplication at 22q11.21 in a patient with VACTERL association.33 more rows
What is the ICD-10 code for Pierre Robin sequence?
The ICD-10 code for “Pierre Robin sequence” is the ICD-10-RCPCH adaptation code Q87. 08.
What is the ICD-10 code for short stature?
ICD-10-CM Code for Short stature (child) R62. 52.
What is VACTERL syndrome?
VACTERL association is a disorder that affects many body systems. VACTERL stands for vertebral defects, anal atresia, cardiac defects, tracheo-esophageal fistula, renal anomalies, and limb abnormalities. People diagnosed with VACTERL association typically have at least three of these characteristic features.
What is Holt Oram Syndrome?
Holt-Oram syndrome is characterized by skeletal abnormalities of the hands and arms (upper limbs) and heart problems. People with Holt-Oram syndrome have abnormally developed bones in their upper limbs. At least one abnormality in the bones of the wrist (carpal bones) is present in affected individuals.
What is ICD 10 code for Charge Syndrome?
Other specified congenital malformations Q89. 8 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q89. 8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How common is Pierre Robin sequence?
Isolated Pierre Robin sequence affects an estimated 1 in 8,500 to 14,000 people.
Which of the following conditions would be reported with Code Q65 81?
Which of the following conditions would be reported with code Q65. 81? Imaging of the renal area reveals congenital left renal agenesis and right renal hypoplasia.
What is the definition of short stature?
Short stature is a term applied to a child whose height is 2 standard deviations (SD) or more below the mean for children of that sex and chronologic age (and ideally of the same racial-ethnic group). This corresponds to a height that is below the 2.3rd percentile.
Is idiopathic short stature?
Idiopathic short stature (ISS) is defined as a condition characterized by a height more than 2 standard deviations below the corresponding average height for a given age, sex and population, without findings of disease.
How do you evaluate short stature?
Anthropometric measurements: Short stature can be diagnosed by measuring the height vertex, body weight, trunk height, and limb length of an individual. These are assessed relative to age, sex, and population.
When will the ICD-10-CM Q87.0 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q87.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is autosomal recessive congenital malformation syndrome?
Rare autosomal recessive congenital malformation syndrome characterized by cryptophthalmos, syndactyly and urogenital abnormalities. Other anomalies of bone, ear, lung, and nose are common. Mutations on fras1 and frem2 are associated with the syndrome.
What is a rare congenital malformation characterized by micrognathia, posterior retraction of the?
A rare congenital malformation characterized by micrognathia, posterior retraction of the tongue, and cleft palate. A rare syndrome that is inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive pattern and caused by mutations in the myh3 gene. It is a severe form of arthrogryposis.
What is a complex syndrome?
A complex syndrome characterized mainly by aural, oral, and mandibular developmental anomalies which may vary from mild to severe and frequently involve one side of the body . Vertebral anomalies, epibulbar epidermoids, mental retardation, and numerous other anomalies are frequently associated.
What is a congenital malformation characterized by?
Congenital malformation characterized by micrognathia, glossoptosis and cleft palate.
What is Pfeiffer syndrome?
Listen. Pfeiffer syndrome is a disorder that affects the development of the bones in the skull, hands and feet. Signs and symptoms can include craniosynostosis, which prevents normal skull growth and affects the shape of the head and face; distinctive facial features including bulging and wide-set eyes, a high forehead, an underdeveloped upper jaw, ...
What is the difference between Pfeiffer syndrome type 1 and type 2?
People with type I usually have normal intelligence and a good prognosis with a normal life span. In Pfeiffer syndrome type II, people typically have more severe craniosynostosis, more severe hand and foot abnormalities, and additional malformations of the limbs. Infants with type II have a form of craniosynostosis that causes ...
What is the name of the deformity in the skull of a type II infant?
Infants with type II have a form of craniosynostosis that causes the skull to have a "tri-lobed" appearance (called a "cloverleaf skull" deformity). This is often associated with hydrocephalus, which causes increased pressure on the brain.
What are the physical problems of a type 2 infant?
Infants with type II often have intellectual disabilities and neurological problems due to severe brain involvement.
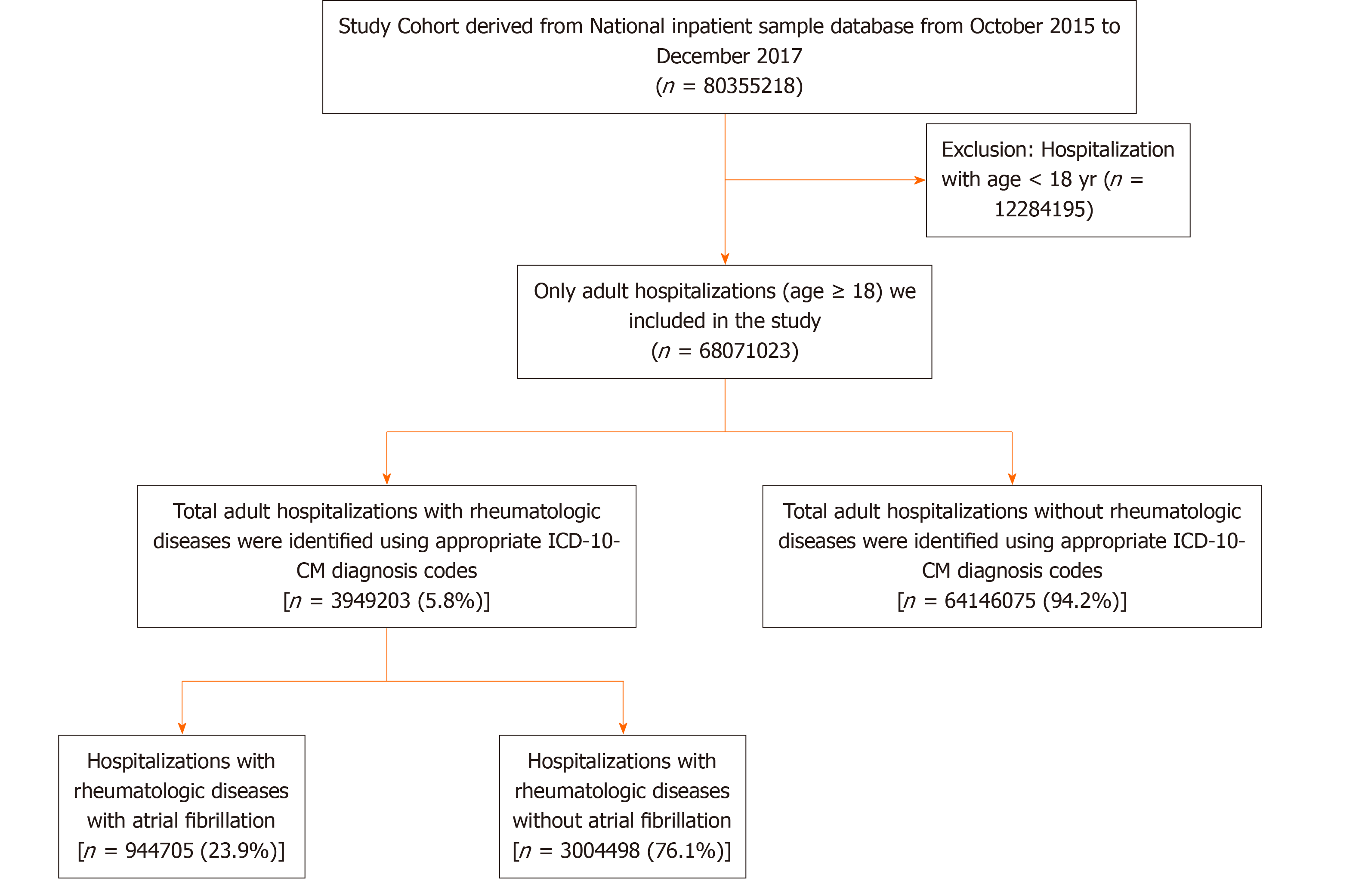
Overview
Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull (craniosynostosis) which affects the shape of the head and face. In addition, the syndrome includes abnormalities of the hands (such as wide and deviated thumbs) and feet (such as wide and deviated big toes).
Pfeiffer syndrome is caused by mutations in the fibroblast growth factor receptors FGFR1 and FG…
Signs and symptoms
Many of the characteristic facial features result from the premature fusion of the skull bones (craniosynostosis). The head is unable to grow normally, which leads to a high prominent forehead (turribrachycephaly), and eyes that appear to bulge (proptosis) and are wide-set (hypertelorism). In addition, there is an underdeveloped upper jaw (maxillary hypoplasia). More than 50 percent of chil…
Cause
Pfeiffer syndrome is strongly associated with mutations of the fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) on chromosome 8 or the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) gene on chromosome 10. These genes code for fibroblast growth factor receptors, which are important for normal bone development. Advanced paternal age is thought to be a risk factor for sporadic cases of Pfeiffer syndrome due to an increase in mutations in sperm as men become older.
Diagnosis
The most widely accepted clinical classification of Pfeiffer syndrome was published by M. Michael Cohen in 1993. Cohen divided the syndrome into three possibly overlapping types, all of which are characterized by broad thumbs, broad great toes, brachydactyly and possibly syndactyly:
• Type 1, also known as classic Pfeiffer syndrome, includes craniosynostosis and "midface deficiency". This type is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Most individuals with type 1 …
Management
The key problem is the early fusion of the skull, which can be corrected by a series of surgical procedures, often within the first three months after birth. Later surgeries are necessary to correct respiratory and facial deformities.
Outcomes
Children with Pfeiffer syndrome types 2 and 3 "have a higher risk for neurodevelopmental disorders and a reduced life expectancy" than children with Pfeiffer syndrome type 1, but if treated, favorable outcomes are possible. In severe cases, respiratory and neurological complications often lead to early death.
History
The syndrome is named after German geneticist Rudolf Arthur Pfeiffer (1931–2012). In 1964, Pfeiffer described eight individuals in three generations of a family who had abnormalities of the head, hands and feet (acrocephalosyndactylia) that were inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
Notable cases
• In 1996, a son was born to American musician Prince and his wife Mayte Garcia. The highly anticipated child, Amiir ("prince" in Arabic), was diagnosed at birth with Pfeiffer syndrome type 2 and died several days later. In 1997, after Garcia's former personal assistants raised concerns about the manner of death, the medical examiner performed an investigation and declared that the death was due to natural causes (meaning it was not a homicide).
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for acl sprain
- 2. icd 10 code for fracture of base of right fifth metatarsal
- 3. icd-10 code for cpap use
- 4. what is icd-10 code for cyst on ovary
- 5. icd code for stitches
- 6. what is the icd 10 code for insomnia
- 7. icd 10 code for ligamentous injury
- 8. icd 10 code for tubal ligation evaluation
- 9. icd 9 code for acute systolic diastolic rigth heart failure
- 10. icd 10 cm code for intermediate coronary syndrome