What is the ICD 10 code for pituitary macroadenoma?
Oct 01, 2019 · What is the ICD 10 code for pituitary adenoma? Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland D35. 2 is a billable/specific ICD - 10 -CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
How to pronounce pituitary adenoma?
Apr 05, 2020 · What is the ICD-10 code for pituitary adenoma? D35.2. Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland D35. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the diagnosis code for pituitary tumor?
Oct 01, 2021 · Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. D35.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM D35.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the prognosis for a pituitary tumor?
Sep 25, 2021 · September 25, 2021 alsoadmin. Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland. D35. 2 is a billable/specific ICD–10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD–10-CM D35. 2 became effective on October 1, 2019.
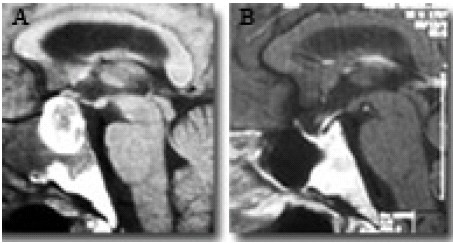
How do you code a pituitary adenoma?
Acromegaly – Pituitary tumor – Pituitary Adenoma (ICD-10 : E22)
What is a benign pituitary adenoma?
A pituitary adenoma is a growth or tumor on the pituitary. Most pituitary adenomas are slow-growing and benign, which means they are not cancer and do not spread to other parts of the body.Mar 22, 2017
What are the types of pituitary adenomas?
Types of Pituitary TumorsNonfunctional Adenomas. At least half of pituitary adenomas are nonfunctional, meaning they do not cause levels of pituitary hormones in your body to rise. ... Functional Adenomas. ... Pituitary Carcinoma or Cancer. ... Hyperprolactinemia. ... Cushing's Disease. ... Acromegaly. ... Hypopituitarism. ... Secondary Hyperthyroidism.
What is diagnosis code D35 2?
2: Benign neoplasm: Pituitary gland.
What is an adenoma tumor?
Listen to pronunciation. (A-deh-NOH-muh) A tumor that is not cancer. It starts in gland-like cells of the epithelial tissue (thin layer of tissue that covers organs, glands, and other structures within the body).
What causes pituitary adenoma?
Pituitary microadenomas develop when DNA mutations cause cells in the pituitary gland grow and divide uncontrollably. Experts are not entirely sure what causes these genetic mutations to happen. A small percentage of pituitary tumors run in families, but most cases do not have any obvious hereditary factor.
What is the most common pituitary adenoma?
Prolactin-secreting pituitary adenomas are the most common type of pituitary tumor, accounting for approximately 30 percent of all pituitary tumors.
What are the two types of pituitary tumors?
Below are the main types of pituitary tumors.Nonfunctional adenomas (null cell adenomas) These tumors are the most common type. ... Prolactin-producing tumors (prolactinomas) These benign tumors are also common. ... ACTH-producing tumors. ... Growth hormone-producing tumors.
How can you tell if a pituitary tumor is benign or malignant?
MRI or CT scans can detect tumors in the pituitary gland. And blood and urine tests can determine hormone levels. Even under a microscope, it's difficult to recognize the difference between a cancerous and a noncancerous pituitary tumor.
What is Gonadotroph adenoma?
Functioning gonadotroph adenomas (FGAs) are adenomas expressing and secreting biologically active gonadotropins and causing distinct clinical manifestations (mainly menstrual irregularity and the ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome in premenopausal females and adolescent girls, testicular enlargement in males, and ...Dec 1, 2014
What is R79 89?
Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistryICD-10 code R79. 89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is a Macroadenoma?
A macroadenoma is a tumor that typically develops in the pituitary gland, a pea-sized organ behind the eyes. They are almost always noncancerous.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What does "type 1 excludes" mean?
A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What chapter is functional activity?
Functional activity. All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology]

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for pregnancy first trimester initial visit
- 2. icd 10 code for history of sdh
- 3. icd 9 code for food intolerance
- 4. icd 10 code for postoperative intestinal obstruction
- 5. icd 10 cm code for nonsustained ventricular tachyucardia
- 6. icd 10 cm code for pulmonary htn
- 7. icd 10 code for ibs unspecified
- 8. icd 10 code for rupture of pectoralis muscle
- 9. icd 10 code for pancreatic tail cancer
- 10. icd-10 code for carpal tunnel syndrome bilateral