What is the prognosis for a pituitary tumor?
The 5-year survival rate tells you what percent of people live at least 5 years after the tumor is found. Percent means how many out of 100. The 5-year survival rate for people with a pituitary gland tumor is 97%. Survival rates depend on the type of tumor, the person’s age, and other factors. It is important to remember that statistics on survival rates for people with a pituitary gland tumor are an estimate. Experts generally measure the survival statistics every 5 years.
What is the diagnosis code for pituitary tumor?
The following are the ICD-9-CM code assignments for pituitary tumors, depending on their behavior classification: • Unspecified—239.7. Pituitary tumors can be considered either functioning or nonfunctioning tumors. Functioning tumors are tumors that produce one or more pituitary hormones.
How is a pituitary tumor detected?
This can cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), such as:
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Tremors (shaking)
- Weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Feeling warm or hot
- Sweating
- Trouble falling asleep
- Anxiety
- Frequent bowel movements
- A lump in the front of the neck (enlarged thyroid)
What are the causes of a pituitary tumor?
What is a pituitary tumor?
- Nonfunctional adenomas (null cell adenomas) These tumors are the most common type. They don't make extra hormones. ...
- Prolactin-producing tumors (prolactinomas) These benign tumors are also common. They make too much prolactin. ...
- ACTH-producing tumors. ...
- Growth hormone-producing tumors. ...
- Other hormone-producing tumors. ...

What is the ICD-10-CM code for pituitary adenoma?
D35. 2 - Benign neoplasm of pituitary gland | ICD-10-CM.
What are the two types of pituitary tumors?
Below are the main types of pituitary tumors.Nonfunctional adenomas (null cell adenomas) These tumors are the most common type. ... Prolactin-producing tumors (prolactinomas) These benign tumors are also common. ... ACTH-producing tumors. ... Growth hormone-producing tumors.
What is the pituitary tumor?
Pituitary tumor Pituitary tumors are abnormal growths that develop in your pituitary gland. Some pituitary tumors result in too much of the hormones that regulate important functions of your body. Some pituitary tumors can cause your pituitary gland to produce lower levels of hormones.
What is diagnosis code D35 2?
2: Benign neoplasm: Pituitary gland.
What is the most common pituitary tumor called?
Prolactinoma: A prolactinoma is the most common secretory tumor. This tumor produces too much prolactin, the hormone that causes milk production. It can be treated with a medication. Non-secreting tumors: Non-secreting tumors do not secrete hormones but can cause health problems because of their size and location.
Is pituitary tumor considered a brain tumor?
A tumor that develops in the pituitary gland is typically considered to be a type of brain cancer. The pituitary gland, which is responsible for producing and releasing hormones into the body, is located inside the skull, just beneath the brain and above the nasal passages.
How is a pituitary tumor diagnosed?
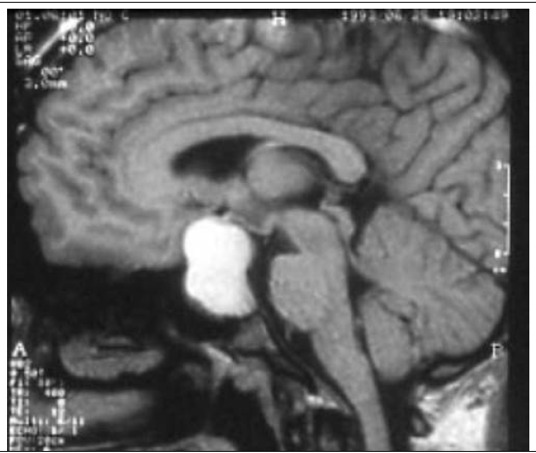
AdvertisementBlood and urine tests. These tests can determine whether you have an overproduction or deficiency of hormones.Brain imaging. A CT scan or MRI scan of your brain can help your doctor judge the location and size of a pituitary tumor.Vision testing.
Why does pituitary tumors occur?
The causes of pituitary tumors are unknown. Some tumors are caused by hereditary disorders such as multiple endocrine neoplasia I (MEN I). The pituitary gland can be affected by other brain tumors that develop in the same part of the brain (skull base), resulting in similar symptoms.
Is the pituitary gland part of the brain?
Your pituitary gland is located at the base of your brain, behind the bridge of your nose and directly below your hypothalamus. It sits in an indent in the sphenoid bone called the sella turcica.
What is R79 89?
ICD-10 code R79. 89 for Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD 10 code for brain tumor?
ICD-10-CM Code for Malignant neoplasm of brain, unspecified C71. 9.
Where is the pituitary gland located?
the brainThe pituitary gland is no larger than a pea, and is located at the base of the brain. The gland is attached to the hypothalamus (a part of the brain that affects the pituitary gland) by nerve fibers and blood vessels.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
What chapter is neoplasms classified in?
All neoplasms are classified in this chapter, whether they are functionally active or not. An additional code from Chapter 4 may be used, to identify functional activity associated with any neoplasm. Morphology [Histology] Chapter 2 classifies neoplasms primarily by site (topography), with broad groupings for behavior, malignant, in situ, benign, ...
What is the ICd 10 code for neoplasm of uncertain behavior?
Neoplasm of uncertain behavior of pituitary gland 1 D44.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM D44.3 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of D44.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 D44.3 may differ.
What is the code for a primary malignant neoplasm?
A primary malignant neoplasm that overlaps two or more contiguous (next to each other) sites should be classified to the subcategory/code .8 ('overlapping lesion'), unless the combination is specifically indexed elsewhere.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for htn complicating dm
- 2. icd 10 code for stage 1 pressure ulcer right buttock
- 3. icd-10 code for chronic dvt right leg
- 4. icd code for fungus on feet
- 5. icd 10 code for pain crisis
- 6. icd 9 code for coronary artery disease unspecified
- 7. icd 10 code for neutropenic splenomegaly
- 8. icd 10 cm code for history of multiple bouts with cystitis
- 9. icd 10 code for respiratory secretions
- 10. icd 10 code for presence of cardiac loop recorder