What is the best treatment for a diabetic ulcer?
The Best Diabetic Foot Ulcer Treatments
- Assess Wound With a Full Exam. The best treatments begin with a comprehensive exam with a full evaluation. ...
- Proper Dressing, Infection Control, and Offloading. ...
- Hyperbaric Wound Care for Diabetic Ulcers. ...
How do you treat a diabetic foot ulcer?
What can I do to prevent diabetic foot ulcers?
- Keep your blood sugar levels under control. Continue the plan for your diabetes that you and your healthcare provider have discussed. ...
- Protect your feet. Do not walk barefoot or wear your shoes without socks. ...
- Do not smoke. Nicotine can damage your blood vessels and increase your risk for foot ulcers. ...
- Maintain a healthy weight. ...
What is a diabetic ulcer?
Diabetic ulcers are open wounds or sores usually found on the bottom of feet. These ulcers affect many people with diabetes and experts suggest that about 15 percent of diabetics will develop one or more at some point in their lifetime. Many of those with diabetic ulcers are hospitalized due to infections or other complications.
What is diabetic leg ulcers?
The three most common types of leg and foot ulcers include:
- Venous stasis ulcers
- Neurotrophic (diabetic)
- Arterial (ischemic ulcers)
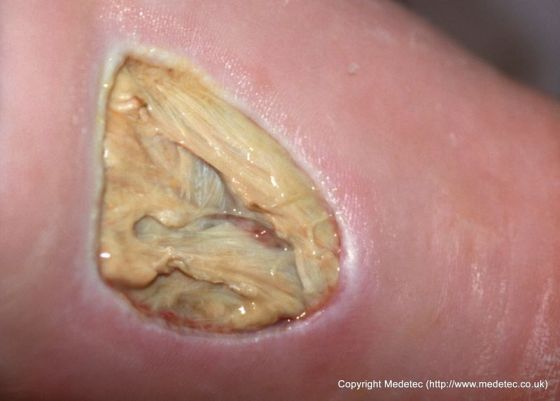
What is the ICD-10 code for foot ulcer?
ICD-10 code L97. 509 for Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of unspecified foot with unspecified severity is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue .
What is the ICD-10 diagnosis code for right foot ulcer?
Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of right foot with unspecified severity. L97. 519 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L97.
What is the ICD-10 for diabetic foot ulcer?
ICD-10 code E11. 621 for Type 2 diabetes mellitus with foot ulcer is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is the ICD-10 code for left foot ulcer?
ICD-10-CM Code for Non-pressure chronic ulcer of other part of left foot with unspecified severity L97. 529.
What is an ulcer on the foot?
Foot ulcers are open sores or lesions that will not heal or that return over a long period of time. These sores result from the breakdown of the skin and tissues of the feet and ankles and can get infected. Symptoms of foot ulcers can include swelling, burning, and pain.
What is the ICD-10 code for foot infection?
X7 for Direct infection of ankle and foot in infectious and parasitic diseases classified elsewhere is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Arthropathies .
What is ICD-10 code for diabetic wound infection?
Type 2 diabetes mellitus with other skin ulcer The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E11. 622 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Whats the difference between a pressure ulcer and a diabetic ulcer?
While diabetic patients can get pressure ulcers due to abuse or neglect in a nursing home, diabetic ulcers may appear in areas that are not typically subject to extended pressure—such as the bottoms of the feet when a resident has been lying down. In these cases, a diagnosis of a diabetic ulcer is more apt.
Is a diabetic foot ulcer a pressure ulcer?
Skin necrosis and gangrene are also included in the current system as ulcers.” This definition is similar to that of the EPUAP, all-inclusive and, as such, any pressure ulcer on the foot of a person with diabetes is a diabetic foot ulcer — as is any traumatic wound, including a thermal or chemical injury.
What is the ICD 10 code for venous stasis ulcer?
The stasis ulcer caused by venous insufficiency is captured first with the code for underlying disease (459.81) followed by the code for the location of the ulcer (707.13).
What is the ICD 10 code for peripheral arterial disease?
Provider's guide to diagnose and code PAD Peripheral Artery Disease (ICD-10 code I73. 9) is estimated to affect 12 to 20% of Americans age 65 and older with as many as 75% of that group being asymptomatic (Rogers et al, 2011).
How do you code an arterial ulcer?
Pressure ulcer codes begin with L89-. Stasis ulcer codes begin with I83- and codes for arterial ulcers are in the I70- section.
What is a L97.91 ulcer?
L97.91 -Non-pressure chronic ulcer of unspecified part of right lower leg. L97.92 – Non-pressure chronic ulcer of unspecified part of left lower leg. According to the American Podiatric Medical Association, about 14 to 24 percent of Americans with diabetic foot ulcers have amputations.
What is a diabetic foot ulcer?
Regarded as the most common reason for hospital stays among people with diabetes, a diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) is an open sore caused by neuropathic (nerve) and vascular (blood vessel) complications of the disease. Typically located on the plantar surface, or bottom/top of toes, pad of foot, or heel of foot, these complex, ...
What are the risk factors for ulcers?
The most common risk factors for ulcer formation include – diabetic neuropathy, structural foot deformity, kidney disease, obesity and peripheral arterial occlusive disease. The condition can be effectively prevented if the underlying conditions causing it are diagnosed early and treated correctly.
What is the best way to offload wounds on the forefoot?
Half shoes, therapeutic shoes, custom insoles, and the use of felted foam are other alternative methods to off-load wounds located on the forefoot. Dressings– Wounds and ulcers heal faster and have a lower risk of infection if they are kept covered and moist, using dressings and topically-applied medications.
How many people with diabetes have foot ulcers?
According to the American Podiatric Medical Association (APMA), approximately 15 percent of people with diabetes suffer from foot ulcers. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, about 6 percent will be hospitalized due to serious infections or other ulcer-related complications.
Where does neuropathic ulcer occur?
Neuropathic ulcers– occur where there is peripheral diabetic neuropathy, but no ischemia caused by peripheral artery disease. This type of foot infection generally occurs on the plantar aspect of the foot under the metatarsal heads or on the plantar aspects of the toes.
Where are diabetic ulcers located?
Typically located on the plantar surface, or bottom/top of toes, pad of foot, or heel of foot , these complex, chronic wounds can affect people with both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. If left untreated, diabetic foot ulcers can have a permanent, long-term impact on the morbidity, mortality and quality of a patients’ life.
What is the L89 code for a pressure ulcer?
Pressure injuries with skin breakdown are considered pressure ulcers. An additional L89 code specifies the stage (depth of tissue injury) and the anatomical site. Pressure ulcers form in sites that experience shear or pressure, typically in tissue overlying bony prominences such as elbows, the sacrum, hips, or heels.
Why are pressure ulcers considered a patient safety indicator?
Pressure ulcers are deemed patient safety indicators and hospital acquired conditions because a concerted program for prevention and treatment can prevent them and protect our patients from iatrogenic harm. The diagnosis of a “pressure ulcer” may trigger prevalence and incident reporting.
What causes diabetic foot ulcers?
A “diabetic foot ulcer,” which is caused exclusively by hyperglycemia, in the absence of neuropathy or ischemia, is a rarity. That term almost always refers to an ulcer on the foot of a diabetic that derives from neuro/ischemic etiology, as opposed to being strictly and principally due to pressure injury.
Why do diabetics get ulcers?
The American Podiatric Medical Association adds that “ (diabetic foot) ulcers form due to a combination of factors , such as lack of feeling in the foot, poor circulation, foot deformities, irritation (such as friction or pressure), and trauma, as well as duration of diabetes .”. They go on to note that “vascular disease can complicate a foot ulcer, ...
What is the most common site of ulceration?
The plantar surface is the most common site of ulceration, especially at areas of bony prominence.”.
Can diabetes cause heel ulcers?
Heel ulcers, however, are usually a consequence of a pressure injury, although it is also possible to have another mechanism cause a non-pressure injury involving the heel. Diabetes may accelerate or complicate the injury. Neuropathy results in malum perforans pedis (a.k.a. bad perforating foot) ulcers.
Can vascular disease cause ulcers on the foot?
They go on to note that “vascular disease can complicate a foot ulcer, reducing the body’s ability to heal and increasing the risk for an infection.”. In the podiatric literature, NPUAP is often referenced as having given guidance to use “diabetic foot ulcer” for “any ulcer on the foot of a diabetic, even if arterial disease and/or pressure played ...

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for chronic uti
- 2. icd-10-cm code for lower leg pain
- 3. icd 10 code for inflamation in the neck
- 4. icd 10 code for injury to left thumb
- 5. icd-10 code for mass in colon
- 6. icd 10 code for atrial septal defect
- 7. icd 10 code for threatened premature labor
- 8. icd 10 code for right upper lid neoplasm
- 9. icd 10 code for hypothyroid in neoplastic disease
- 10. what icd-10-cm code is reported for vin iii