How do I treat plasmablastic lymphoma?
Follicular lymphoma. mature T/NK-cell lymphomas (C84.-); personal history of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (Z85.72); follicular lymphoma with or without diffuse areas. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C82. C82 Follicular lymphoma. C82.0 Follicular lymphoma grade I. C82.00 Follicular lymphoma grade I, unspecified site...
What type of lymphoma is curable?
Oct 01, 2021 · The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM C83.3 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of C83.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 C83.3 may differ. Applicable To. Anaplastic diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. CD30-positive diffuse large B …
Can small lymphocytic lymphoma be cured?
mediastinal (thymic) large B-cell lymphoma (C85.2-); T-cell rich B-cell lymphoma (C83.3-); Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma; Lymphoid granulomatosis; Primary effusion B-cell lymphoma ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C83.8
What is the ICD 10 code for small lymphocytic lymphoma?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code C88.4 Extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue [MALT-lymphoma] 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code
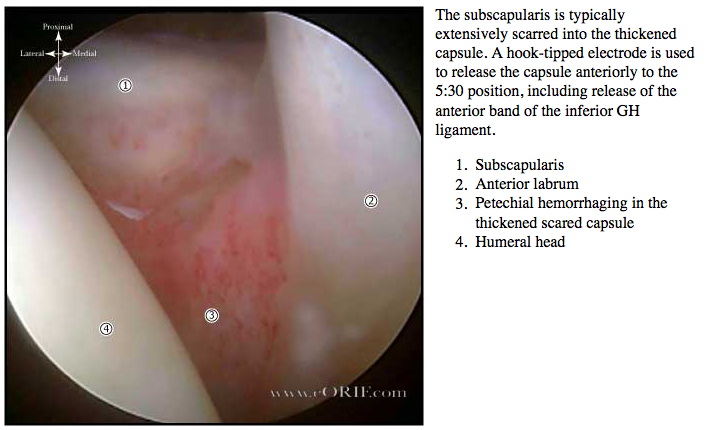
What is cutaneous B cell lymphoma?
Is Plasmablastic lymphoma Dlbcl?
Is Plasmablastic lymphoma non-Hodgkin?
What is double hit lymphoma?
How do you get Plasmablastic lymphoma?
What causes Plasmablastic lymphoma?
Is Plasmablastic lymphoma cancerous?
What is plasmablastic myeloma?
What is the survival rate of Plasmablastic lymphoma?
What is double triple hit lymphoma?
What type is double hit?
What is the prognosis of double hit lymphoma?
Primary Site (s)
Most common sites of involvement: oral cavity mass, mucosal sites, sinonasal cavity, orbit, skin, bone, soft tissues and GI tract. For HIV negative patients-lymph nodes
Diagnostic Confirmation
This histology can be determined by positive histology (including peripheral blood) with or without genetics and/or immunophenotyping. Review the Definitive Diagnostic Methods, Immunophenotyping and Genetics Data sections below, and the instructions in the Hematopoietic Manual for further guidance on assigning Diagnostic confirmation.
Definition
Plasma blastic lymphoma (PBL) is a very aggressive lymphoma with a diffuse proliferation of large neoplastic cell s, most of which resemble B immunoblasts or plasma blasts, that have a CD20-negative plasmacytic phenotype.
Sources
International Classification of Diseases for Oncology, Third Edition, Second Revision. Geneva: World Health Organization, 2020.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 9 code for nystagmus
- 2. icd 10 code for degenerative disc disease lumbosacral
- 3. icd 10 code for leaking catheter
- 4. icd 10 code for suspect accreta in pregnancy
- 5. medical icd-10 code for pneum8nia due to sars
- 6. icd 10 code for screening pregnancy test
- 7. icd 10 code for leg ulcer, left, with unspecified severity
- 8. icd 10 code for tendonitis left lower leg
- 9. icd-10 code for dyslipidemia unspecified
- 10. icd 10 code for newborn lung infiltrate