What is the ICD 10 code for pneumocystosis?
Pneumocystosis. B59 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM B59 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B59 - other international versions of ICD-10 B59 may differ.
What is Pneumocystis jirovecii?
Pneumocystis pneumonia is a frequently seen opportunistic infection in aids. It is caused by the fungus pneumocystis jirovecii. The disease is also found in other mammals where it is caused by related species of pneumocystis.
What is the ICD 10 code for viral pneumonia?
Other viral pneumonia 1 J12.8 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. 2 The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM J12.8 became effective on October 1, 2020. 3 This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J12.8 - other international versions of ICD-10 J12.8 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for interstitial pneumonitis?
Acute interstitial pneumonitis. J84.114 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM J84.114 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J84.114 - other international versions of ICD-10 J84.114 may differ.
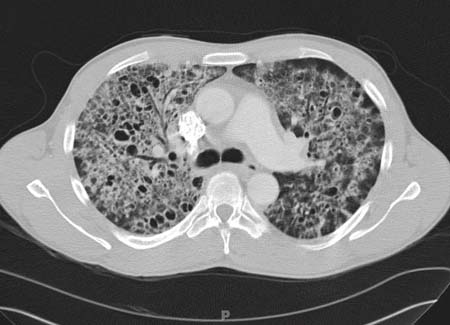
What is Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia?
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is a serious infection caused by the fungus Pneumocystis jirovecii. Most people who get PCP have a medical condition that weakens their immune system, like HIV/AIDS, or take medicines (such as corticosteroids) that lower the body's ability to fight germs and sickness.
Is Pneumocystis jiroveci atypical pneumonia?
Pulmonary Pneumocystis jiroveci infection, also known as Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP) or Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP), is an atypical pulmonary infection and the most common opportunistic infection in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
What was Pneumocystis jirovecii formerly known as?
Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia is a fungal infection of the lungs. The disease used to be called Pneumocystis carini or PCP pneumonia.
Is Pneumocystis the same as pneumonia?
Pneumocystis pneumonia is a type of infection of the lungs (pneumonia) in people with a weak immune system. It is caused by a yeast-like fungus called Pneumocystis jirovecii (PJP). People with a healthy immune system don't usually get infected with PCP.
What is the ICD 10 code for pneumocystis pneumonia?
B59 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B59 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of B59 - other international versions of ICD-10 B59 may differ.
How do you get Pneumocystis jirovecii?
Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP) is a serious infection that causes inflammation and fluid buildup in your lungs. It's brought on by a fungus called Pneumocystis jirovecii that spreads through the air. This fungus is very common. Most people's immune systems have fought it off by the time they're 3 or 4 years old.
What are the signs of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia?
What are the symptoms of PCP?Fever that comes on suddenly.Cough.Trouble breathing. It often gets worse with activity.A dry cough, with little or no mucus.Chest tightness.Weight loss.Night sweats.
Why is Pneumocystis classified as a fungus?
Pneumocystis jirovecii (previously classified as Pneumocystis carinii) was previously classified as a protozoa. Currently, it is considered a fungus based on nucleic acid and biochemical analysis. Reference: Frenkel JK.
Is Pneumocystis Jiroveci Gram positive or negative?
The cysts appeared as 5- to 7-microns unstained spheres, each containing six to eight intracystic gram-negative bodies (sporozoites).
What is the fungus that causes pneumocystis?
Pneumocystis pneumonia is a frequently seen opportunistic infection in aids. It is caused by the fungus pneumocystis jirovecii. The disease is also found in other mammals where it is caused by related species of pneumocystis. Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (pcp).
What is PCP in medical terms?
Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (pcp). Pneumonia resulting from infection with pneumocystis carinii, frequently seen in the immunologically compromised, such as persons with aids, or steroid-treated individuals, the elderly, or premature or debilitated babies during their first three months.
When will the ICd 10 B59 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM B59 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the synonym for protozoal intestinal disease?
other protozoal intestinal diseases ( A07.-) Protozoal diseases. Approximate Synonyms. Pneumocystis pneumonia. Pneumocystosis pneumonia. Clinical Information. A pulmonary disease in humans occurring in immunodeficient or malnourished patients or infants, characterized by dyspnea, tachypnea, and hypoxemia.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, fevers, chills, chest pain, headache, sweating, and weakness. Inflammation of any part, segment or lobe, of the lung parenchyma. Inflammation of the lungs with consolidation and exudation. Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection.
When will the ICD-10 J18.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J18.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is pneumonia due to solids and liquids?
pneumonia due to solids and liquids ( J69.-) aspiration pneumonia due to solids and liquids ( J69.-) neonatal aspiration pneumonia ( P24.-) (noo-mone-ya) an inflammatory infection that occurs in the lung. A disorder characterized by inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma.
How do you know if you have pneumonia?
You can also get pneumonia by accidentally inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems. If you have pneumonia, you may have difficulty breathing and have a cough and a fever. A physical exam and history can help determine if you have pneumonia. Chest x-rays and blood tests can help determine what is wrong. Treatment depends on what made you sick. If bacteria are the cause, antibiotics should help. Viral pneumonia may get better with rest and drinking liquids.preventing pneumonia is always better than treating it. The best preventive measures include washing your hands frequently, not smoking, and wearing a mask when cleaning dusty or moldy areas. There is a vaccine for pneumococcal pneumonia, a bacterial infection which accounts for up to a quarter of all pneumonias.
What causes inflammation of the lung parenchyma?
An acute, acute and chronic, or chronic inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma, due to infections (viruses, fungi, mycoplasma, or bacteria), treatment (e.g. Radiation), or exposure (inhalation) to chemicals.
When will the ICD-10 J12.8 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J12.8 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the J11.82?
J11.82 Influenza due to unidentified influenza virus with myocarditis. J11.83 Influenza due to unidentified influenza virus with otitis media. J11.89 Influenza due to unidentified influenza virus with other manifestations. J12 Viral pneumonia, not elsewhere classified.
When will the ICd 10 J84.114 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J84.114 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as J84.114. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for displaced left midshaft clavicle fracture
- 2. icd 10 code for traumatic injury to left leg
- 3. icd 20 code for head injury
- 4. icd 10 code for exacerbation of congestive heart failure
- 5. icd-9-cm code for history of cardiac arrest
- 6. icd 10 code for ekg screening
- 7. icd 10 code for complex migraine headaches
- 8. icd 10 code for medicare reimbursement
- 9. icd 9 code for urinary retention due to foley
- 10. icd 9 code for hypertransaminasemia