What is the ICD 10 code for lung abscess?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code J85.2. Abscess of lung without pneumonia. J85.2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for pneumonia?
Pneumonia, unspecified organism. J18.9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM J18.9 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of J18.9 - other international versions of ICD-10 J18.9 may differ.
What is the medical term for pneumonia?
Pneumonia, unspecified organism. A severe inflammation of the lungs in which the alveoli (tiny air sacs) are filled with fluid. This may cause a decrease in the amount of oxygen that blood can absorb from air breathed into the lung. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection but may also be caused by radiation therapy, allergy,...
What is the pathophysiology of pneumonia?
Pneumonia, unspecified organism. A disorder characterized by inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma. A severe inflammation of the lungs in which the alveoli (tiny air sacs) are filled with fluid. This may cause a decrease in the amount of oxygen that blood can absorb from air breathed into the lung.

Is lung abscess a complication of pneumonia?
Most frequently, the lung abscess arises as a complication of aspiration pneumonia caused by mouth anaerobes. The patients who develop lung abscess are predisposed to aspiration and commonly have periodontal disease.
What is the ICD-10 code for pulmonary abscess?
Abscess of lung without pneumonia J85. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J85. 2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is lung abscess common in pneumonia?
Pneumonia, including a type known as aspiration pneumonia, can also cause a primary lung abscess. Aspiration pneumonia is an infection that develops after food or secretions from the mouth, stomach, or sinuses are inhaled into the lungs instead of going into the esophagus. It's a very common cause of primary abscesses.
How can you tell the difference between pneumonia and lung abscess?
Early signs and symptoms of lung abscess cannot be differentiate from pneumonia and include fever with shivering, cough, night sweats, dispnea, weight loss and fatigue, chest pain and sometimes anemia.
What is Cavitary pneumonia?
Cavitary pneumonia is a rare complication of severe pneumonia in which normal lung tissue is replaced by a cavity. Most notably, it is associated with Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
What is the ICD 10 code for bilateral pleural effusions?
ICD-10 code J91. 8 for Pleural effusion in other conditions classified elsewhere is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the respiratory system .
What is the most common localization of abscessed pneumonia?
In 75% of all lung abscesses, they are located in posterior segment of right upper lobe or in apical segment of lower lobe of both lungs (5).
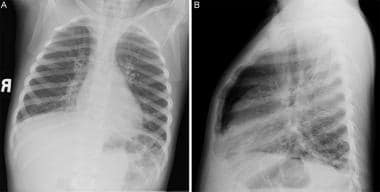
What is the lung abscess?
A lung abscess is a pus-filled cavity in your lung surrounded by inflamed tissue. It usually results from breathing bacteria that normally live in your mouth or throat into the lungs, leading to an infection.
What is the difference between lung abscess and empyema?
Empyema is defined by purulent fluid collection in the pleural space, which is most commonly caused by pneumonia. A lung abscess, on the other hand, is a parenchymal necrosis with confined cavitation that results from a pulmonary infection.
What causes lung abscesses?
A lung abscess is usually caused by bacteria that normally live in the mouth and are inhaled into the lungs. Symptoms include fatigue, loss of appetite, night sweats, fever, weight loss, and a cough that brings up sputum. Diagnosis is usually determined with a chest x-ray.
How is a lung abscess diagnosis?
Lung abscess is a necrotizing lung infection characterized by a pus-filled cavitary lesion. It is most commonly caused by aspiration of oral secretions by patients who have impaired consciousness. Symptoms are persistent cough, fever, sweats, and weight loss. Diagnosis is based primarily on chest x-ray.
Can a lung abscess cause a pleural effusion?
Parapneumonic effusion is referring to a pleural fluid collection resulting from bacterial pneumonia, lung abscess, and bronchiectasis. The most common source of exudative effusion is parapneumonic effusion. Parapneumonic effusions are usually resolved with appropriate treatment.
What causes an abscess on the lung?
A lung abscess is usually caused by bacteria that normally live in the mouth and are inhaled into the lungs. Symptoms include fatigue, loss of appetite, night sweats, fever, weight loss, and a cough that brings up sputum. Diagnosis is usually determined with a chest x-ray.
What are the risk factors for lung abscess?
Some of the most common factors that predispose a patient to develop lung abscess are:Immunocompromised hosts (HIV-AIDS, post-transplantation, or those receiving prolonged immune suppressive therapy). ... Patients with high risk for aspiration: seizures, bulbar dysfunction, alcohol intoxication, and cognitive impairment.
Can Covid cause a lung abscess?
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 epidemic was first described in China [2], bacterial and fungal superinfections after COVID-19 pneumonia have been described on multiple occasions [3], [4]. However, to our knowledge, this is the first case of a post-COVID-19 infection pulmonary abscess.
What can cause pus in the lungs?
A lung abscess, also called a pulmonary abscess, is a pus-filled cavity in the lungs caused by an infection. It's usually caused by a bacterial infection, and sometimes by fungi or parasites. A lung abscess may be diagnosed with imaging studies of the chest.
What is the B95 code?
code ( B95-B97) to identify infectious agent. A bacterial, fungal or parasitic abscess that develops in the lung parenchyma. Causes include aspiration pneumonia, necrotizing pneumonia, necrotizing malignant tumors, and wegener's granulomatosis. Solitary or multiple collections of pus within the lung parenchyma as a result of infection by bacteria, ...
What causes a solitary collection of pus in the lung?
Solitary or multiple collections of pus within the lung parenchyma as a result of infection by bacteria, protozoa, or other agents.
When will the ICD-10 J85.2 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J85.2 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is a code also note?
A “code also” note instructs that two codes may be required to fully describe a condition, but this note does not provide sequencing direction. The sequencing depends on the circumstances of the encounter.
What is a type 1 exclude note?
A type 1 Excludes note is a pure excludes. It means 'NOT CODED HERE!' An Excludes1 note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as the code above the Excludes1 note. An Excludes1 is used when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition.
What are the symptoms of pneumonia?
Symptoms include cough, shortness of breath, fevers, chills, chest pain, headache, sweating, and weakness. Inflammation of any part, segment or lobe, of the lung parenchyma. Inflammation of the lungs with consolidation and exudation. Pneumonia is an inflammation of the lung, usually caused by an infection.
How do you know if you have pneumonia?
You can also get pneumonia by accidentally inhaling a liquid or chemical. People most at risk are older than 65 or younger than 2 years of age, or already have health problems. If you have pneumonia, you may have difficulty breathing and have a cough and a fever. A physical exam and history can help determine if you have pneumonia. Chest x-rays and blood tests can help determine what is wrong. Treatment depends on what made you sick. If bacteria are the cause, antibiotics should help. Viral pneumonia may get better with rest and drinking liquids.preventing pneumonia is always better than treating it. The best preventive measures include washing your hands frequently, not smoking, and wearing a mask when cleaning dusty or moldy areas. There is a vaccine for pneumococcal pneumonia, a bacterial infection which accounts for up to a quarter of all pneumonias.
What is pneumonia due to solids and liquids?
pneumonia due to solids and liquids ( J69.-) aspiration pneumonia due to solids and liquids ( J69.-) neonatal aspiration pneumonia ( P24.-) (noo-mone-ya) an inflammatory infection that occurs in the lung. A disorder characterized by inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma.
What causes inflammation of the lung parenchyma?
An acute, acute and chronic, or chronic inflammation focally or diffusely affecting the lung parenchyma, due to infections (viruses, fungi, mycoplasma, or bacteria), treatment (e.g. Radiation), or exposure (inhalation) to chemicals.
What causes a decrease in oxygen in the lungs?
This may cause a decrease in the amount of oxygen that blood can absorb from air breathed into the lung. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection but may also be caused by radiation therapy, allergy, or irritation of lung tissue by inhaled substances. It may involve part or all of the lungs.
When will the ICD-10 J18.9 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J18.9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
When will the ICD-10 J15 be released?
The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM J15 became effective on October 1, 2021.
Is J15 a reimbursement code?
Bacterial pneumonia, not elsewhere classified. J15 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM J15 became effective on October 1, 2020.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for tonsillar hypertrophy
- 2. icd 10 code for pvd test
- 3. icd 9 code for thoracic facet arthropathy
- 4. icd 10 cm code for congenital malformation of the trachea
- 5. icd 10 code for history of spider bite
- 6. icd code for lower abdominal pain
- 7. icd-10 code for condyloma groin
- 8. icd 10 code for elevated lipids
- 9. icd 9 code for asthmatic croup with acute exacerbation
- 10. icd 10 code for eyelid bruising