Polycystic kidney, unspecified
- Q61.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM Q61.3 became effective on October 1, 2020.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q61.3 - other international versions of ICD-10 Q61.3 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 diagnosis code for?
Oct 01, 2021 · 2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Q61.3 Polycystic kidney, unspecified 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code POA Exempt Q61.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q61.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 for end stage renal disease?
753.13. Polycystic kidney, autosomal dominant (exact match) This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 753.13 was previously used, Q61.2 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
Is chronic kidney disease stage 5 ICD 10 curable?
Polycystic kidney, adult type (Q61.2) Q61.19 Q61.2 Q61.3 ICD-10-CM Code for Polycystic kidney, adult type Q61.2 ICD-10 code Q61.2 for Polycystic kidney, adult type is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and …
What is code 1cd-10 code for end-stage renal disease?
Oct 01, 2021 · Q61.2 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Polycystic kidney, adult type . It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 . POA Exempt Q61.2 is exempt from POA reporting ( Present On Admission).
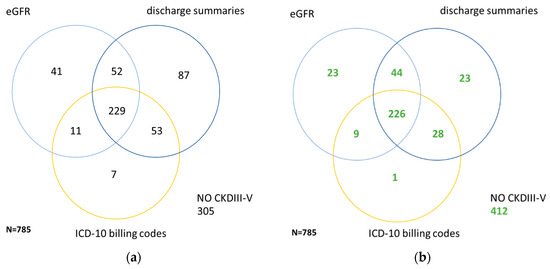
How do you code polycystic kidney disease?
ICD-10 code Q61. 2 for Polycystic kidney, adult type is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Congenital malformations, deformations and chromosomal abnormalities .
What is the ICD 10 code for family history of polycystic kidney disease?
2022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code Z82. 71: Family history of polycystic kidney.
Is polycystic kidney disease acute or chronic?
PKD is a form of chronic kidney disease (CKD) that reduces kidney function and may lead to kidney failure. PKD also can cause other complications, or problems, such as high blood pressure, cysts in the liver, and problems with blood vessels in your brain and heart.
What is polycystic kidney disease Type 2?
ADPKD-2 represents a mild variant of polycystic kidney disease with a low prevalence of symptoms and a late onset of end-stage renal failure.
What is the history of polycystic kidney disease?
In 1888, Flix Lejars used the term of "polycystic kidney" for the first time, and stressed that these cysts were bilateral, and causing clinically identifiable symptoms. At the end of 19th century, the basic clinical signs, and genetic basis of the disease have been better defined.
What is ICD-10 code for congenital Chordee?
ICD-10 | Congenital chordee (Q54. 4)
What is the difference between simple cysts and polycystic kidney disease?
Simple kidney cysts are usually harmless. Simple kidney cysts don't enlarge the kidneys, replace their normal structure, or cause reduced kidney function like cysts do in people with polycystic kidney disease (PKD). PKD is a genetic disorder that can cause chronic kidney disease.
Is polycystic kidney disease an autoimmune disease?
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is one of the most prevalent inheritable kidney disorders globally. The coexistence of ADPKD and autoimmune diseases is unusual and is rarely reported in literature....Article Access StatisticsComments[Add]11 more rows•Mar 23, 2017
Is PKD dominant or recessive?
Inheritance. Most cases of polycystic kidney disease have an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. People with this condition are born with one mutated copy of the PKD1 or PKD2 gene in each cell. In about 90 percent of these cases, an affected person inherits the mutation from one affected parent .
What are the types of polycystic kidney disease?
The two main types of polycystic kidney disease, caused by different genetic flaws, are:Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Signs and symptoms of ADPKD often develop between the ages of 30 and 40. ... Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD). This type is far less common than is ADPKD .Oct 14, 2020
What is the difference between PKD1 and PKD2?
Interpretation Although PKD2 is clinically milder than PKD1, it has a deleterious impact on overall life expectancy and cannot be regarded as a benign disorder. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is one of the most common dominantly inherited conditions, with an estimated prevalence of 1 in 1000.
What causes polycystic kidneys?
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) causes cysts (fluid-filled growths) to develop in the kidneys. PKD is a genetic disorder, meaning you have to have a mutated (changed) gene to get the disorder. PKD isn't the same as simple kidney cysts, which are usually harmless. PKD is a serious type of chronic kidney disease.Feb 3, 2021
What is the ICD code for polycystic kidney?
Q61.2 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of polycystic kidney, adult type. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease?
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD, autosomal dominant PKD or adult-onset PKD) is the most prevalent, potentially lethal, monogenic human disorder. It is associated with large interfamilial and intrafamilial variability, which can be explained to a large extent by its genetic heterogeneity and modifier genes. It is also the most common of the inherited cystic kidney diseases — a group of disorders with related but distinct pathogenesis, characterized by the development of renal cysts and various extrarenal manifestations, which in case of ADPKD include cysts in other organs, such as the liver, seminal vesicles, pancreas, and arachnoid membrane, as well as other abnormalities, such as intracranial aneurysms and dolichoectasias, aortic root dilatation and aneurysms, mitral valve prolapse, and abdominal wall hernias. Over 50% of patients with ADPKD eventually develop end stage kidney disease and require dialysis or kidney transplantation. ADPKD is estimated to affect at least 1 in every 1000 individuals worldwide, making this disease the most common inherited kidney disorder with a diagnosed prevalence of 1:2000 and incidence of 1:3000-1:8000 in a global scale.
How many people have ADPKD?
ADPKD is estimated to affect at least 1 in every 1000 individuals worldwide, making this disease the most common inherited kidney disorder with a diagnosed prevalence of 1:2000 and incidence of 1:3000-1:8000 in a global scale. Specialty:
What is billable code?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. The Center for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) requires medical coders to indicate whether or not a condition was present at the time of admission, in order to properly assign MS-DRG codes.
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 cm code for chest wall contusion
- 2. 2015 icd 10 code for pleural based density
- 3. icd 10 code for peg tube exchange
- 4. 2018 icd 10 code for iud insertion
- 5. icd 10 code for fibroma back skin
- 6. icd 10 code for status post surgical acute postoperative pain
- 7. icd 10 code for atypical syncope
- 8. icd 10 code for severe methamphetamine
- 9. icd 10 code for bucket-handle tear
- 10. icd 10 code for murmur systolic