What is the ICD 10 code for DVT prophylaxis?
Oct 01, 2021 · The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM I82.40 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of I82.40 - other international versions of ICD-10 I82.40 may differ. Applicable To Deep vein thrombosis NOS DVT NOS Type 1 Excludes acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of distal lower extremity ( I82.4Z-)
What is considered prediabetes A1C ICD 10?
ICD10 codes matching "Deep Vein Thrombosis" Codes: = Billable. I82.40 Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of lower extremity; I87.0 Postthrombotic syndrome; O22.3 Deep phlebothrombosis in pregnancy; O87.1 Deep phlebothrombosis in the puerperium
How to code deconditioning ICD 10?
Oct 01, 2021 · I82.401 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. Short description: Acute embolism and thombos unsp deep veins of r low extrem. The 2022 edition of ICD-10 …
How often is the ICD 10 coding books updated?
DVT on chronic anticoagulation therapy. I82.891 – Chronic embolism and thrombosis of other unspecified vein. The code does not match the documentation. Chronic anticoagulation or chronic use of medication does not mean DVT is chronic. Acuity should have been documented for clarity. I82.890 – Acute embolism and thrombosis of other unspecified vein.
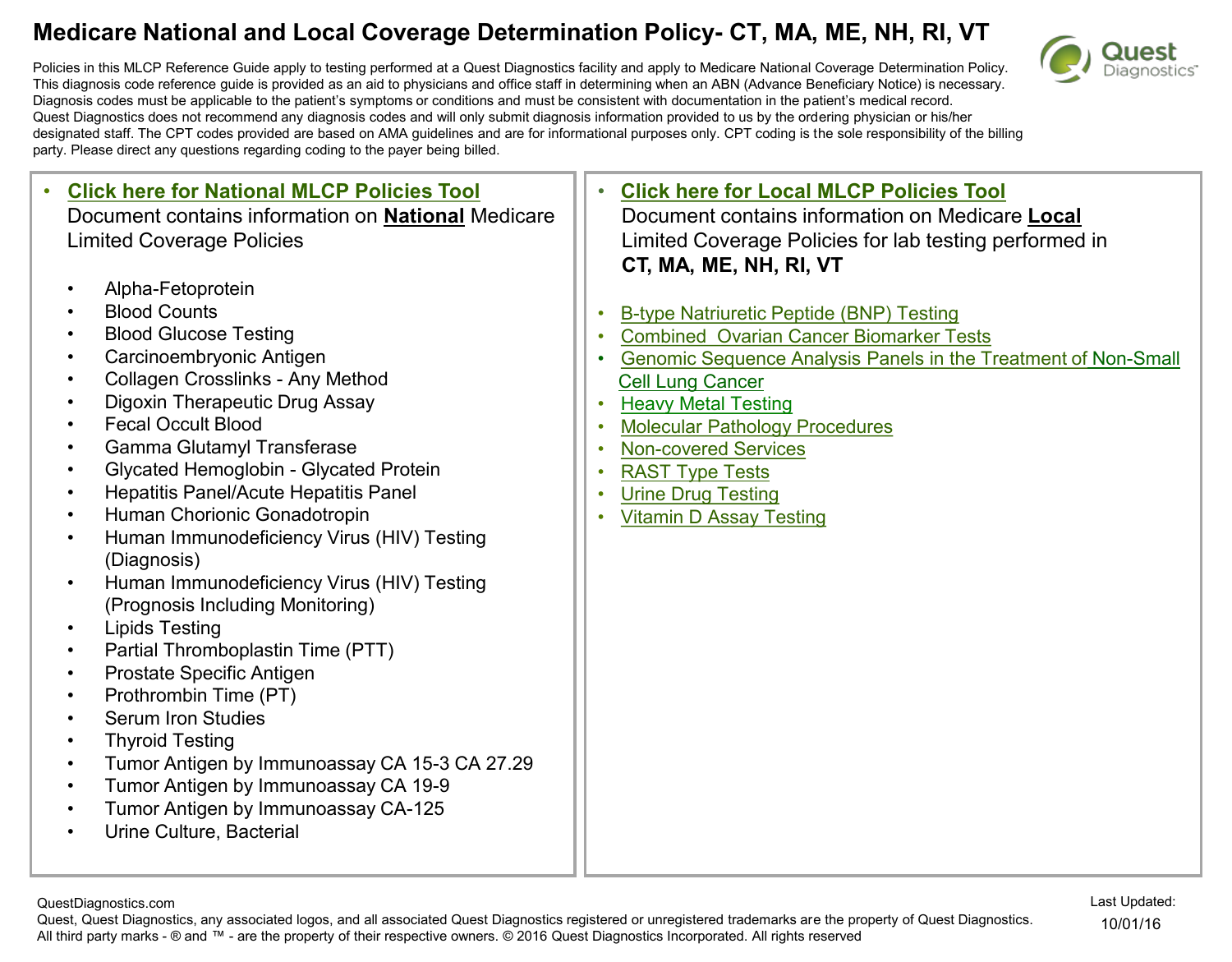
What is the ICD-10 code for unspecified DVT?
I82.409Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of unspecified lower extremity. I82. 409 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD-10 code for right DVT?
I82.4012022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I82. 401: Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of right lower extremity.
What is the ICD-10 code for DVT right lower extremity?
I82.401I82. 401 – Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of right lower extremity.May 15, 2020
What is the ICD-10 code I82 409?
ICD-10 | Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of unspecified lower extremity (I82. 409)
What is DVT medical term?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein. These clots usually develop in the lower leg, thigh, or pelvis, but they can also occur in the arm.
What is the ICD-10 code for left DVT?
I82.4022022 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I82. 402: Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of left lower extremity.
What is DVT prophylaxis?
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) prophylaxis consists of pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic measures to diminish the risk of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE).Mar 12, 2021
What is acute embolism and thrombosis?
Thrombosis occurs when a thrombus, or blood clot, develops in a blood vessel and reduces the flow of blood through the vessel. Embolism occurs when a piece of a blood clot, foreign object, or other bodily substance becomes stuck in a blood vessel and largely obstructs the flow of blood.
What is the ICD-10 code for PVD?
ICD-10 | Peripheral vascular disease, unspecified (I73. 9)
What is the ICD-10 code for bilateral DVT?
Chronic embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of lower extremity, bilateral. I82. 503 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the correct ICD-10 code for leukocytosis?
288.60 - Leukocytosis, unspecified. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 for CAD?
Code I25* is the diagnosis code used for Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease, also known as Coronary artery disease (CAD).
What is a DVT?
DVT occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more veins located deep inside the body. This serious condition occurs when the blood moves too slowly through the veins due to long periods of immobility or reduced mobility or other factors.
What are the symptoms of a DVT?
Symptoms of DVT can include. Swelling in the foot, ankle, or leg. Cramping and pain. swollen veins. Tenderness. Discoloration. Unusually hot skin in the affected area. If DVT occurs with no identifiable risk factor, the condition is called unprovoked DVT. There are many risk factors for DVT.
How to check for blood clots?
Methods use to diagnose DVT or check for a blood clot include: Venous Ultrasound: This standard test for DVT involves using sound waves to display how blood flows through the veins. Venography: This x-ray test involves injecting a dye into a large vein in the foot or ankle to detect clots.
What is DVT awareness month?
March is national Deep-Vein Thrombosis (DVT) Awareness Month. This public health initiative aims to raise awareness about this widely prevalent medical condition and its potentially life-threatening complication, pulmonary embolism (PE). The American Medical Association estimates that about 2 million people are affected by DVT each year, more than the numbers affected by heart attack or stroke annually. Billing and coding for these conditions is complex. An experienced medical billing and coding service provider would have proper knowledge of important diagnostic norms and documentation requirements to help physicians assign appropriate diagnoses and procedure codes on claims.
What is the treatment for a blood clot?
Therapies include: Anticoagulant Medications: Usually, heparin is prescribed first to prevent further clotting, which may be followed by warfarin to prevent another blood clot forming. Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) Filter: This small, cone-shaped filter is inserted into the inferior vena cava, the largest vein in your body.
What veins should be documented in a physician's diagnosis?
The specific vein such as femoral, iliac or tibial. The physician should also document the diagnostic method used, the anticoagulants administered and duration of treatment. The treatment and its goals should be linked to the diagnosis.
How many people are affected by DVT?
The American Medical Association estimates that about 2 million people are affected by DVT each year, more than the numbers affected by heart attack or stroke annually. Billing and coding for these conditions is complex.
What is the ICd 10 code for a complication of vein?
T81.72XS is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of complication of vein following a procedure, not elsewhere classified, sequela. The code T81.72XS is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.#N#The ICD-10-CM code T81.72XS might also be used to specify conditions or terms like acute deep vein thrombosis of left lower limb following procedure, acute deep vein thrombosis of left upper limb following procedure, acute deep vein thrombosis of right lower limb following procedure, acute deep vein thrombosis of right upper limb following procedure, acute deep venous thrombosis of left upper extremity , acute deep venous thrombosis of lower extremity as complication of procedure, etc. The code is exempt from present on admission (POA) reporting for inpatient admissions to general acute care hospitals.#N#T81.72XS is a sequela code, includes a 7th character and should be used for complications that arise as a direct result of a condition like complication of vein following a procedure not elsewhere classified. According to ICD-10-CM Guidelines a "sequela" code should be used for chronic or residual conditions that are complications of an initial acute disease, illness or injury. The most common sequela is pain. Usually, two diagnosis codes are needed when reporting sequela. The first code describes the nature of the sequela while the second code describes the sequela or late effect.
What are the different types of thrombosis?
The following clinical terms are approximate synonyms or lay terms that might be used to identify the correct diagnosis code: 1 Acute deep vein thrombosis of left lower limb following procedure 2 Acute deep vein thrombosis of left upper limb following procedure 3 Acute deep vein thrombosis of right lower limb following procedure 4 Acute deep vein thrombosis of right upper limb following procedure 5 Acute deep venous thrombosis of left upper extremity 6 Acute deep venous thrombosis of lower extremity as complication of procedure 7 Acute deep venous thrombosis of right upper extremity 8 Acute deep venous thrombosis of upper extremity as complication of procedure 9 Chronic deep vein thrombosis of left upper limb following procedure 10 Chronic deep vein thrombosis of right upper limb following procedure 11 Chronic deep venous thrombosis of upper extremity as complication of procedure 12 Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis 13 Phlebitis and thrombophlebitis of intracranial sinuses 14 Phlebitis as a complication of care 15 Phlebitis due to procedure 16 Phlebitis during procedure 17 Postoperative phlebitis and thrombophlebitis of intracranial sinuses 18 Postprocedural obstructed systemic venous pathway 19 Thrombophlebitis due to procedure 20 Thrombophlebitis during procedure
What is a pulmonary embolism?
Clinical Information. A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage in a lung artery. The cause is usually a blood clot in the leg called a deep vein thrombosis that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream to the lung. Pulmonary embolism is a serious condition that can cause. permanent damage to the affected lung.
What is a type 2 exclude note?
A type 2 excludes note indicates that the condition excluded is not part of the condition it is excluded from but a patient may have both conditions at the same time. When a type 2 excludes note appears under a code it is acceptable to use both the code ( I26) and the excluded code together. chronic pulmonary embolism (.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause death?
damage to other organs in your body from not getting enough oxygen. if a clot is large, or if there are many clots, pulmonary embolism can cause death. Half the people who have pulmonary embolism have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, they can include shortness of breath, chest pain or coughing up blood.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for encounter for urine drug screening
- 2. icd 10 code for gestational diabetes insulin controlled
- 3. icd 10 code for knee pain bilatera
- 4. icd 10 code for chronic hfpef
- 5. icd-10 code for left lower extremity dvt
- 6. assign the icd 10 pcs code for removal of an iud without the use of an endoscope
- 7. icd 9 code for hypertensive heart failure
- 8. icd 10 code for low self esteem
- 9. icd 9 code for lung carcinoid tumor
- 10. icd 10 code for ebv cmv igg/igm