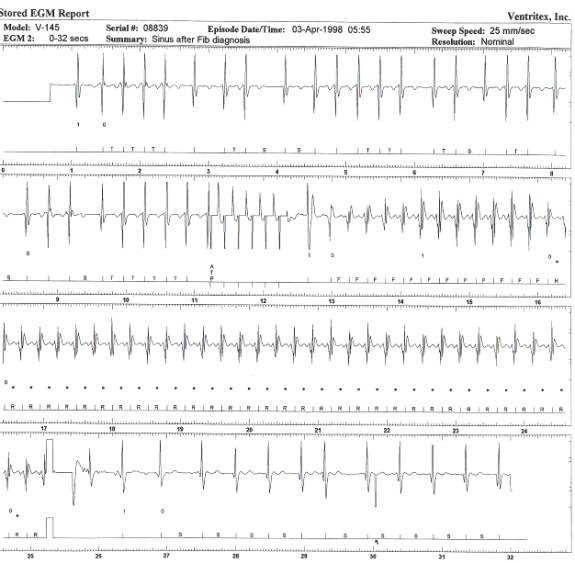
How to confirm atrial fibrillation?
When this happens, you may experience atrial fibrillation symptoms, including:
- Rapid and irregular heartbeat
- Fluttering or pounding in your chest
- Dizziness
How is atrial fibrillation diagnosed and treated?
Treatment is based on decisions made regarding when to convert to normal sinus rhythm vs. when to treat with rate control, and, in either case, how to best reduce the risk of stroke. For most patients, rate control is preferred to rhythm control. Ablation therapy is used to destroy abnormal foci responsible for atrial fibrillation.
Are You newly diagnosed with atrial fibrillation?
The patient with newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation. The NHFA’s AF guidelines recommend opportunistic AF screening in patients aged ≥65 years with either radial pulse palpation followed by a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) or a single-lead handheld ECG. 9 Therefore, AF can be diagnosed: during routine cardiac screening; because of new onset symptoms
What are signs and symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
You might feel:
- Heart palpitations -- a flutter in your chest
- Pain and pressure in your chest
- Confused
- Dizzy
- Faint
- Short of breath
- Sweaty
- Tired
- Weak

What is post operative AFIB?
Postoperative atrial fibrillation (POAF), defined as new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) in the immediate period after surgery, is the most important type of secondary AF (AF resulting from an identifiable, primary, acute condition)1.
What is the ICD 10 code for post op complication?
T88.9XXAICD-10-CM Code for Complication of surgical and medical care, unspecified, initial encounter T88. 9XXA.
What is the ICD 10 code for post surgery?
Encounter for other specified surgical aftercare Z48. 89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z48. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021.
How do you code new onset atrial fibrillation?
New Onset Afib ICD 10 is coded as I48. New onset AF is the most common scenario in which an AF diagnosis is made, as are asymptomatic patients with an abnormally irregular and often rapid pulse with an electrocardiogram consistent with AF.
Can you bill for post op complications?
Medicare says they will not pay for any care for post-operative complications or exacerbations in the global period unless the doctor must bring the patient back to the OR. This also applies to bringing the patient back to an endoscopy suite or cath lab.
What is the ICD-10 code for post op pain?
18.
How do you code post op visits?
Post-operative visits should be reported with CPT code 99024 when the visit is furnished on the same day as an unrelated E/M service (billed with modifier 24).
What is the ICD-10 code for attention to surgical wound?
Z48. 0 - Encounter for attention to dressings, sutures and drains. ICD-10-CM.
What is the ICD-10 code for non healing surgical wound?
998.83 - Non-healing surgical wound is a topic covered in the ICD-10-CM.
What is new onset atrial fibrillation?
New-onset atrial fibrillation (AF) is a new or first detectable episode of a chaotic and irregular atrial arrhythmia. Prevalence increases progressively with age.
What is atrial fibrillation with RVR ICD-10?
The code for “atrial fibrillation with RVR” is I48. 91 Unspecified atrial fibrillation.
What is unspecified atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (A-fib) is an irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots in the heart. A-fib increases the risk of stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications.
What causes atrial fibrillation?
The causes of atrial fibrillation is oftentimes unknown, but can be the result of damage to the heart’s electrical system caused by conditions such as uncontrolled hypertension and coronary artery disease.
What is the name of the heart that causes a patient to have a stroke?
Atrial fibrillation is an irregular heartbeat or arrhythmia sometimes called a quivering heart. This arrhythmia can cause a patient to develop blood clots, have a stroke, heart failure or other conditions. The heart rate is most often rapid and causes poor blood flow.
Is a patient with erratic heartbeat still atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation is still reported in patients that are not currently experiencing the erratic rhythm as long as the patient is requiring ongoing medication to help control the rate. Atrial fibrillation is very common in postoperative patients and should be verified as a complication before coding as such.
Does atrial fibrillation go away?
Sometimes treating and controlling the underlying cause will make the atrial fibrillation go away. If this does not help the erratic rhythm, then the patient may require treatment with beta blockers and calcium channel blockers to help slow the heart rate. The rhythm should be restored to a normal rhythm to reduce the high heart rate.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for intracranial mass
- 2. icd 10 cm code for trailer hitch dropped on right foot
- 3. icd 10 code for cramping in pregnancy
- 4. icd 10 code for fish test
- 5. icd 10 code for oa multiple sites
- 6. icd-9 code for acute myocardial infarction anterior wall episode
- 7. icd 10 code for concha bullosa right nasal turninate
- 8. icd 10 code for annual physical and have type 1 diabetes
- 9. icd 10 cm code for laceration torso
- 10. icd 10 code for right 5th toe amputation