What is the ICD 10 code for injury of right ankle?
ICD-10 code S99.911A for Unspecified injury of right ankle, initial encounter is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is the ICD 10 code for fracture of right leg?
Unspecified fracture of right lower leg, initial encounter for closed fracture. S82. 91XA is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM S82. Click to see full answer.
What is the ICD 10 code for calcaneus fracture?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes S99-* S99.0 Physeal fracture of calcaneus S99.1 Physeal fracture of metatarsal S99.2 Physeal fracture of phalanx of toe S99.8 Other specified injuries of ankle and foot S99.9 Unspecified injury of ankle and foot
What is the ICD 10 code for open wound?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Codes S91-* S91.0 Open wound of ankle S91.1 Open wound of toe without damage to nail S91.2 Open wound of toe with damage to nail S91.3 Open wound of foot
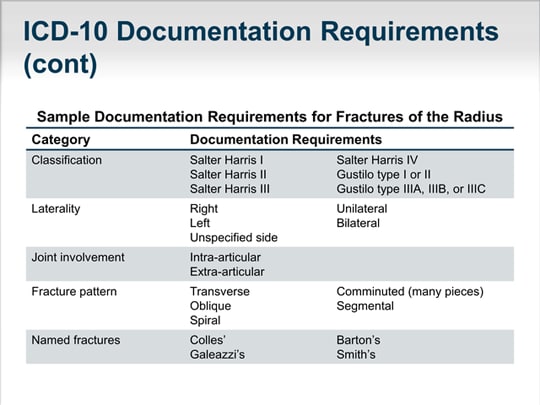
What is the ICD 10 code for aftercare of orthopedic surgery?
ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for other orthopedic aftercare Z47. 89.
What is the ICD 10 code for status post surgery?
ICD-10-CM Code for Encounter for surgical aftercare following surgery on specified body systems Z48. 81.
What is the ICD 10 code for aftercare following surgery?
81: Encounter for surgical aftercare following surgery on specified body systems.
What is the ICD 10 code for ORIF right ankle?
891B: Other fracture of right lower leg, initial encounter for open fracture type I or II.
How do you code surgical aftercare?
Use Z codes to code for surgical aftercare. Z47. 89, Encounter for other orthopedic aftercare, and. Z47.
What is the ICD-10 code for surgical wound?
ICD-10 Code for Disruption of external operation (surgical) wound, not elsewhere classified, initial encounter- T81. 31XA- Codify by AAPC.
What is considered orthopedic aftercare?
Z aftercare codes are used in office follow-up situations in which the initial treatment of a disease is complete and the patient requires continued care during the healing or recovery phase or for long-term consequences of the disease.
What is the difference between follow-up and aftercare?
Follow-up. The difference between aftercare and follow-up is the type of care the physician renders. Aftercare implies the physician is providing related treatment for the patient after a surgery or procedure. Follow-up, on the other hand, is surveillance of the patient to make sure all is going well.
What is Encounter for other orthopedic aftercare?
Encounter for other orthopedic aftercare 89 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Z47. 89 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is Orif ankle surgery?
Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is a type of surgery used to stabilize and heal a broken bone. You might need this procedure to treat your broken ankle. Three bones make up the ankle joint. These are the tibia (shinbone), the fibula (the smaller bone in your leg), and the talus (a bone in your foot).
What is the CPT code for ORIF ankle?
CPT® Code 27822 in section: Open treatment of trimalleolar ankle fracture, includes internal fixation, when performed, medial and/or lateral malleolus.
What is the ICD-10 for ankle fracture?
ICD-10 code S82 for Fracture of lower leg, including ankle is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Injury, poisoning and certain other consequences of external causes .
Open Approach
Cutting through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to expose the site of the procedure
Percutaneous Approach
Entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach the site of the procedure
Percutaneous Endoscopic Approach
Entry, by puncture or minor incision, of instrumentation through the skin or mucous membrane and any other body layers necessary to reach and visualize the site of the procedure
External Approach
Procedures performed directly on the skin or mucous membrane and procedures performed indirectly by the application of external force through the skin or mucous membrane
What is the code for postoperative pain?
Postoperative pain not associated with a specific postoperative complication is reported with a code from Category G89, Pain not elsewhere classified, in Chapter 6, Diseases of the Nervous System and Sense Organs. There are four codes related to postoperative pain, including:
What is code assignment in coding?
The key elements to remember when coding complications of care are the following: Code assignment is based on the provider’s documentation of the relationship between the condition and the medical care or procedure.
Is postoperative pain normal?
Determining whether to report postoperative pain as an additional diagnosis is dependent on the documentation, which, again, must indicate that the pain is not normal or routine for the procedure if an additional code is used. If the documentation supports a diagnosis of non-routine, severe or excessive pain following a procedure, it then also must be determined whether the postoperative pain is occurring due to a complication of the procedure – which also must be documented clearly. Only then can the correct codes be assigned.
Is postoperative pain a part of recovery?
Postoperative pain typically is considered a normal part of the recovery process following most forms of surgery. Such pain often can be controlled using typical measures such as pre-operative, non-steroidal, anti-inflammatory medications; local anesthetics injected into the operative wound prior to suturing; postoperative analgesics;
Is postoperative pain a reportable condition?
Only when postoperative pain is documented to present beyond what is routine and expected for the relevant surgical procedure is it a reportable diagnosis. Postoperative pain that is not considered routine or expected further is classified by whether the pain is associated with a specific, documented postoperative complication.

Popular Posts:
- 1. 2018 icd 10 code for enlarged pituitary
- 2. icd 10 code for left diabetic foot ulcer
- 3. icd 10 code for croup
- 4. icd 9 code for bacteriuria
- 5. icd 10 code for vegan diet
- 6. icd 10 code for contact dermatitis of abdomen
- 7. icd 10 code for colon adenocarcinoma
- 8. icd 10 code for bilateral eye
- 9. icd 9 code for eca stenosis
- 10. icd 10 code for right scapula injury