How to strengthen the posterior tibial tendon?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code M67.969 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Unspecified disorder of synovium and tendon, unspecified lower leg. Unsp disorder of synovium and tendon, unspecified lower leg; Disorder of synovium of knee; Disorder of tendon of lower leg; Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction; Synovial disorder of lower leg; Unspecified tendon disorder of lower leg.
What are the stages of posterior tibial tendon dysfunction?
Oct 01, 2021 · Posterior tibial tendinitis, right leg 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code M76.821 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M76.821 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What are good walking shoes for a tibial tendon tear?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S76.311. Strain of muscle, fascia and tendon of the posterior muscle group at thigh level, right thigh. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code S76.312. Strain of muscle, fascia and tendon of the posterior muscle group at thigh level, left thigh.
What causes a tendon to tear?
Sadly, there is no code for PTTD. There is not even a code for rupture of this specific tendon. There is a diagnosis code for posterior tibial tendinitis: M76.82. 11 However, this would only be applicable to stage 1 PTTD, which precedes attenuation and rupture of the posterior tibial tendon which occurs in stage 2 PTTD. 2
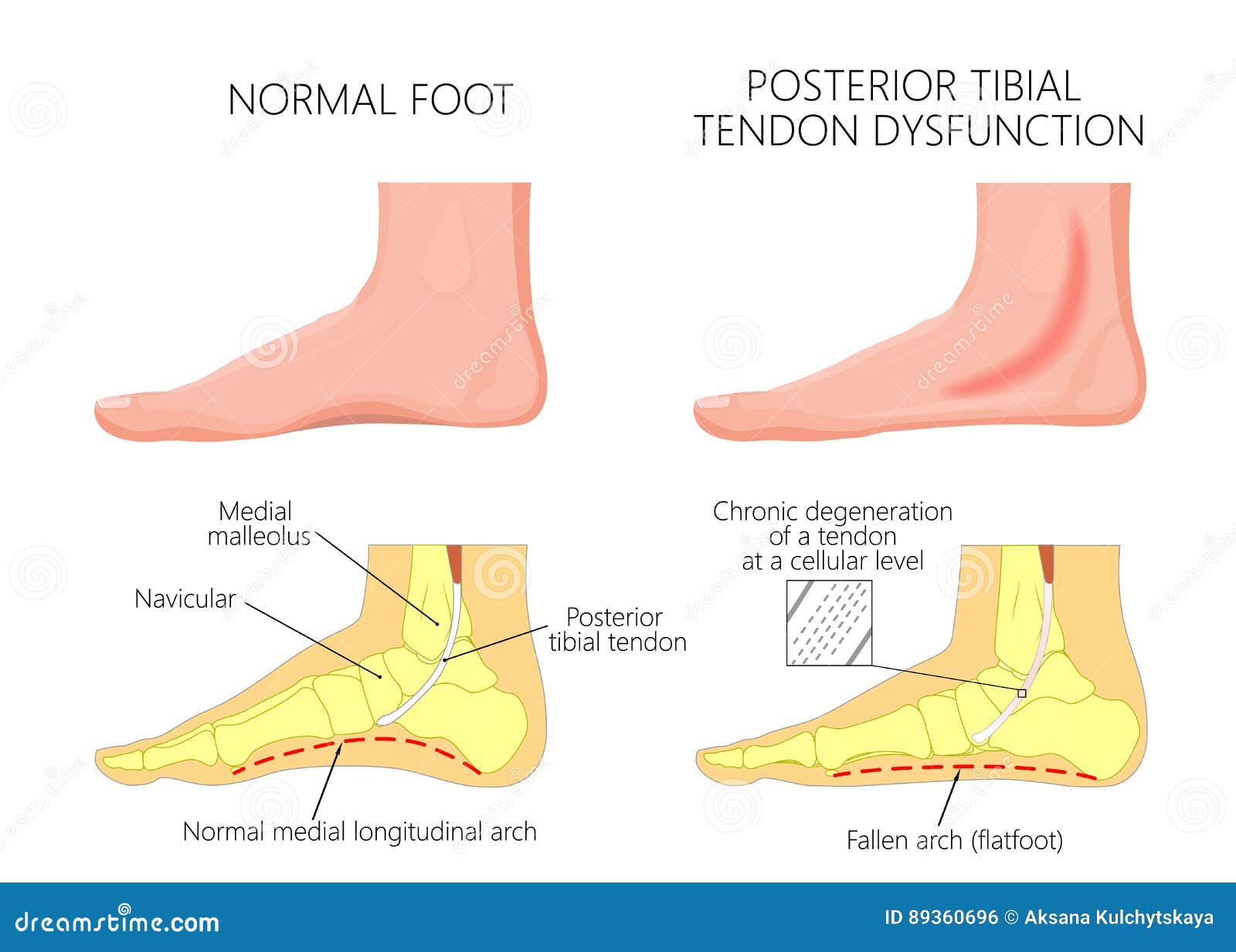
What is posterior tibial tendon dysfunction?
Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is one of the most common problems of the foot and ankle. It occurs when the posterior tibial tendon becomes inflamed or torn. As a result, the tendon may not be able to provide stability and support for the arch of the foot, resulting in flatfoot.
What is diagnosis code M76 822?
Posterior tibial tendinitis822: Posterior tibial tendinitis, left leg.
Where is the posterior tibial tendon?
The posterior tibialis tendon is a strong cord of tissue. It is one of the most important tendons in your leg. It attaches the posterior tibialis muscle on the back of your calf to the bones on the inside of your foot. It helps support your foot and hold up its arch when you are walking.
Is the posterior tibial tendon a flexor or extensor?
Because the tibialis posterior (TP) originates from the posterior compartment of the lower leg, the tibialis posterior is also a secondary plantar flexor of the foot along with the gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles.Aug 17, 2021
What is the ICD 10 code for ankle pain?
Pain in unspecified ankle and joints of unspecified foot M25. 579 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M25. 579 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for plantar fasciitis?
ICD-10 | Plantar fascial fibromatosis (M72. 2)
What is the tibial tendon?
The posterior tibial tendon connects your calf muscle to bones on the inside of your foot. The main purpose of the tendon is to support the arch on the inside of your foot. When the tendon is injured or breaks down, it may no longer be able to support the arch.Nov 4, 2021
How do you test for posterior tibial tendon?
1:403:04Simple Test: Is Your Foot Pain "Posterior Tibial Tendonitis"??YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAgain is that tendon that's where you're going to feel that that tenderness if you're going to pushMoreAgain is that tendon that's where you're going to feel that that tenderness if you're going to push in there it may make you jump in sure that kind of thing and up here's where the muscle belly is and
What is dorsalis pedis?
The dorsalis pedis artery (dorsal artery of foot), is a blood vessel of the lower limb that carries oxygenated blood to the dorsal surface of the foot. It arises at the anterior aspect of the ankle joint and is a continuation of the anterior tibial artery.
What Innervates the posterior tibialis?
Tibialis posterior is innervated by the tibial nerve which arises from the L4 and L5 spinal nerves. The tibial nerve is the larger of the two branches of the sciatic nerve.Jun 30, 2020
What Innervates posterior tibialis?
the tibial nerveIn addition to the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle, the tibial nerve innervates the plantaris, soleus, popliteus, posterior tibialis, flexor digitorum longus, and flexor hallucis longus muscles (Fig. 1).
Which is the origin of the tibialis posterior?
The tibialis posterior muscle originates on the inner posterior border of the fibula laterally. It is also attached to the interosseous membrane medially, which attaches to the tibia and fibula.
What is the most common ankle problem?
Your muscles and tendons move it. The most common ankle problems are sprains and fractures. A sprain is an injury to the ligaments.
How many bones are in the ankle?
Ankle fracture - aftercare (Medical Encyclopedia) Ankle sprain - aftercare (Medical Encyclopedia) Foot, leg, and ankle swelling (Medical Encyclopedia) Each of your feet has 26 bones, 33 joints, and more than 100 tendons, muscles, and ligaments. No wonder a lot of things can go wrong.
How long does it take for a sprain to heal?
A sprain is an injury to the ligaments. It may take a few weeks to many months to heal completely. A fracture is a break in a bone. You can also injure other parts of the ankle such as tendons, which join muscles to bone, and cartilage, which cushions your joints.
What bones make up the ankle joint?
Ankle Injuries and Disorders. Your ankle bone and the ends of your two lower leg bones make up the ankle joint. Your ligaments, which connect bones to one another, stabilize and support it. Your muscles and tendons move it.
How many bones are there in the foot?
Foot Injuries and Disorders. Each of your feet has 26 bones, 33 joints, and more than 100 tendons, muscles, and ligaments. No wonder a lot of things can go wrong. Here are a few common problems: Bunions - hard, painful bumps on the big toe joint.
How long does it take for a sprain to heal?
A sprain is an injury to the ligaments. It may take a few weeks to many months to heal completely. A fracture is a break in a bone. You can also injure other parts of the ankle such as tendons, which join muscles to bone, and cartilage, which cushions your joints.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for screening for diabetes mellitus
- 2. icd 10 code for nonresponsive
- 3. icd-9-cm code for cortical visual
- 4. icd 10 code for osteomyelitis left femur
- 5. icd 10 code for sternum sprain
- 6. icd 9 code for history of cabg
- 7. icd 10 code for chip fracture right distal fibula
- 8. icd code for afib with rvr
- 9. icd 10 code for family history of esophageal cancer
- 10. icd 10 code for over extended bladder