How many codes in ICD 10?
- ICD-10 codes were developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) External file_external .
- ICD-10-CM codes were developed and are maintained by CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics under authorization by the WHO.
- ICD-10-PCS codes External file_external were developed and are maintained by Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. ...
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
The new codes are for describing the infusion of tixagevimab and cilgavimab monoclonal antibody (code XW023X7), and the infusion of other new technology monoclonal antibody (code XW023Y7).
What is the CPT code for potassium?
CPT code: Panel: 80047: Basic metabolic panel (Calcium, ionized) This panel must include the following: Calcium, ionized (82330) Carbon dioxide (bicarbonate) (82374) Chloride (82435) Creatinine (82565) Glucose (82947) Potassium (84132) Sodium (84295) Urea Nitrogen (BUN) (84520) 80048: Basic metabolic panel (Calcium, total)
What does ICD 10 mean?
ICD-10 is the 10th revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD), a medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). It contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases.
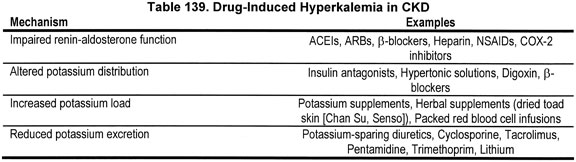
What is the ICD-10-CM code for Hypopotassemia?
Convert to ICD-10-CM: 276.8 converts directly to: 2015/16 ICD-10-CM E87. 6 Hypokalemia.
What is the medical code for potassium?
001180: Potassium | Labcorp.
How do you code hyperkalemia?
ICD-10-CM Code for Hyperkalemia E87. 5.
What is hypokalemia disease?
Hypokalemia is a metabolic imbalance characterized by extremely low potassium levels in the blood. It is a symptom of another disease or condition, or a side effect of diuretic drugs.
What diagnosis will cover potassium?
A potassium blood test is often included in a series of routine blood tests called an electrolyte panel. The test may also be used to monitor or diagnose conditions related to abnormal potassium levels. These conditions include kidney disease, high blood pressure, and heart disease.
What is I10 diagnosis?
ICD-Code I10 is a billable ICD-10 code used for healthcare diagnosis reimbursement of Essential (Primary) Hypertension.
What is severe hyperkalemia?
As background, severe hyperkalemia is a serum potassium concentration of >6.0 or >5.5 mmol/l with an arrhythmia or hyperkalemic electrocardiographic changes.
What is the ICD-10 code for anemia?
Code D64. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Anemia, Unspecified, it falls under the category of diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism. Anemia specifically, is a condition in which the number of red blood cells is below normal.
Why do you give calcium for hyperkalemia?
Calcium chloride Calcium prevents the deleterious cardiac effects of severe hyperkalemia that may occur before the serum potassium level is corrected. Because of its irritating effects when administered parenterally, calcium chloride is generally considered a second choice, after calcium gluconate.
What is the most common cause of low potassium?
Low potassium (hypokalemia) has many causes. The most common cause is excessive potassium loss in urine due to prescription medications that increase urination. Also known as water pills or diuretics, these types of medications are often prescribed for people who have high blood pressure or heart disease.
What causes a potassium deficiency?
Potassium deficiency, or Hypokalemia, is a condition in which a person does not get enough potassium for their body. It can be due to a poor diet or loss due to diarrhoea or vomiting. Potassium deficiency can result in medical conditions like high blood pressure, constipation, muscle weakness, and fatigue.
What causes low potassium in blood?
Low blood potassium typically occurs because of an excessive loss of potassium in your digestive tract. This may be due to frequent vomiting, diarrhea or laxative use. Other causes of hypokalemia include: Eating disorders, such as bulimia nervosa.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for acute on chronic anemia
- 2. icd 10 cm code for mdd recurrent moderate
- 3. icd 10 code for cellulitis upper back
- 4. icd 10 code for cardiomegaly with pulmonary vascular congestion
- 5. icd 10 code for suppurative otitis media
- 6. icd 9 code for flexor tendon laceration
- 7. icd 10 code for loss of a family member
- 8. icd 10 code for arthritis of thumb
- 9. 2021 icd 10 code for vertigo
- 10. icd 10 code for cauliflower ear