Is pots a real illness?
Jan 15, 2020 · Besides, what is the ICD 10 code for POTS Syndrome? I49. 8 is a billable/specific ICD - 10 -CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD - 10 -CM I49.
What is the ICD 10 code for pots syndrome?
POTS has not been assigned a specific ICD-10 code; the following are commonly used: ICD-10 coding I49.8, Other specified cardiac dysrhythmia (POTS is listed as an example) I95.1, Orthostatic hypotension (sometimes occurs with POTS) G90.9, Disorder of the autonomic nervous system, unspecified R42, Dizziness R53.82, Chronic fatigue
How serious is pots syndrome?
PRESENT ICD-10-CM CODING • POTS often coded to I49.8: Other specified cardiac arrhythmias • Includes Brugada syndrome, coronary sinus rhythm disorder, ectopic rhythm disorder, nodal rhythm disorder • Inaccurate placement and description • POTS is not a cardiac arrhythmia • Arrhythmias are not associated with POTS •
What is the treatment for pots disease?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R80.2 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Orthostatic proteinuria, unspecified. Orthostatic proteinuria; Postural proteinuria. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R80.2. Orthostatic proteinuria, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. Applicable To. Postural proteinuria. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I95.1 [convert to ICD-9-CM]
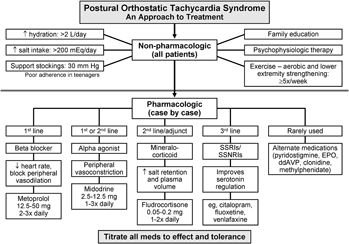
What is POTS Syndrome in adults?
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a condition that affects blood flow. POTS causes the development of symptoms -- usually lightheadedness, fainting and an uncomfortable, rapid increase in heartbeat -- that come on when standing up from a reclining position and relieved by sitting or lying back down.Oct 12, 2020
What disorders are comorbid with POTS?
Chronic symptoms and comorbidities that cannot physiologically be explained by orthostatic intolerance or tachycardia, but are common in patients with POTS include chronic fatigue, dizziness, syncope, migraines, functional gastrointestinal disorders, chronic nausea, fibromyalgia, and joint hypermobility.Mar 12, 2019
What type of disease is POTS?
POTS is a form of dysautonomia — a disorder of the autonomic nervous system. This branch of the nervous system regulates functions we don't consciously control, such as heart rate, blood pressure, sweating and body temperature.
What is the ICD-10 code for dysautonomia?
G90.1ICD-10 code G90. 1 for Familial dysautonomia [Riley-Day] is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the nervous system .
Is POTS a metabolic disease?
Hemodynamic and metabolic disorders are more prevalent in AN than in POTS, whereas condition like Fibromyalgia, CFS and IBS are more common in POTS, which suggests that POTS is a syndromic rather than a disease-based dysautonomia.Apr 9, 2014
Is POTS an endocrine disorder?
Abstract. Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a cardiovascular autonomic disorder with poorly understood etiology and underlying pathophysiology.Apr 21, 2021
How is POTS disease diagnosed?
To make an accurate diagnosis, he typically performs a physical exam and blood work to rule out other causes, as well as a tilt table test, the gold standard for diagnosing POTS. As patients transition from a prone to upright position on the table, those with POTS experience dramatic increases in heart rate.Nov 1, 2017
What autoimmune disease causes POTS?
Hypermobile Elhers‐Danlos syndrome has also been considered as secondary form of POTS. Our results support the hypothesis that POTS may be an autoimmune disorder affecting the autonomic nervous system.Sep 9, 2019
What is the difference between orthostatic intolerance and POTS?
Orthostatic intolerance was defined as the development of previously defined symptoms of cerebral hypoperfusion or sympathetic activation upon standing along with a heart rate (HR) increment <30 bpm on head-up tilt (HUT) [6], while those with symptomatic increase in heart rate on HUT ≥ 30 bpm were defined as POTS.Jun 1, 2013
What is pots chronic illness?
Postural tachycardia syndrome (PoTS) is an abnormal increase in heart rate that occurs after sitting up or standing. Some typical symptoms include dizziness and fainting. It's sometimes known as postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome.
What are the different types of dysautonomia?
There are at least 15 types of dysautonomia. The most common are neurocardiogenic syncope (NCS) and postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS)....Autonomic dysreflexiaheadaches.blotchy skin.a blocked nose.a slow pulse.nausea.goosebumps and clammy skin near the site of the injury.
What is Riley-Day syndrome?
Familial dysautonomia, also known as Riley-Day syndrome, is a disorder of autonomic nervous system with an autosomal recessive mode of inheritance. Reduction and/or loss of unmyelinated and small myelinated fibers is found, as reduction of dopamine beta-hydroxylase in blood.
What are the symptoms of a POTS?
Nausea and gastro-intestinal symptoms are common in POTS. Medication management of delayed gastric emptying and the dysmotility associated with irritable bowel syndrome (functional gastrointestinal disorder) are commonly experienced with POTS.
Why are there no practice guidelines for POTS?
There are no official practice guidelines, mostly because of a lack of comparative studies of treatment options. However, these review articles focus on the management of POTS in adolescents:
What is postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome?
Postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome (POTS) is a form of autonomic dysfunction with orthostatic intolerance that affects up to 1% of adolescents with chronic fatigue, dizziness, and, often, gastrointestinal discomfort or other forms of chronic pain. With treatment, most patients can fully recover and return to normal life activities.
What is a POTS?
Autonomic disorder (vague, but includes POTS)#N#Autonomic dysfunction (over-arching group of conditions of which POTS is a subset)#N#Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) (has diagnostic criteria for research use; over half of individuals with CFS likely have POTS or features thereof)#N#Dysautonomia (same as autonomic dysfunction)#N#Functional disorder (Lacking a specific diagnostic test, POTS is a functional disorder, as is migraine headache. Affected patients may have other functional disorders such as chronic pain or functional GI or neurologic disorder.)#N#Myalgic encephalopathy (ME) (British synonym for the American “CFS”)#N#Orthostatic intolerance (broad group of problems characterized by bothersome symptoms when upright that improve when lying down; POTS is the form that is chronic and associated with excessive postural tachycardia)#N#Postural tachycardia syndrome (preferred in Great Britain and abbreviated “PoTS.”)
What does it mean when you are dizzy when you lie down?
Typically, the dizziness is a sense of lightheadedness or instability, but sometimes patients report room-spinning vertigo. Chronic fatigue.
How to improve fluid and salt intake?
Instruct patients to increase fluid and salt intake, exercise daily, get adequate/appropriate sleep, and engage in cognitive behavioral therapy techniques. Prescription medications are most useful when the patient is fully engaged in these non-pharmacologic treatment modalities.
Is POTS a functional disorder?
Functional disorder ( Lacking a specific diagnostic test, POTS is a functional disorder, as is migraine headache. Affected patients may have other functional disorders such as chronic pain or functional GI or neurologic disorder.)

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for lumbar disc narrowing
- 2. icd 10 code for cerebellar cva
- 3. icd 10 code for ileocecectomy
- 4. icd 10 cm code for topamax
- 5. icd 10 code for fainting episodes
- 6. icd 10 code for acute pain of left knee
- 7. icd 10 code for left knee revision
- 8. icd 10 code for onychomycosis of toenail
- 9. icd 10 code for hit by hydraulics
- 10. icd 10 code for hpcd