What is the ICD 10 code for precipitous drop in hematocrit?
Precipitous drop in hematocrit. R71.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2019 edition of ICD-10-CM R71.0 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of R71.0 - other international versions of ICD-10 R71.0 may differ.
What is the ICD 10 code for abnormal hemoglobin?
Abnormal, abnormality, abnormalities - see also Anomaly. hemoglobin (disease) D58.2 - see also Disease, hemoglobin. Anemia (essential) (general) (hemoglobin deficiency) (infantile) (primary) (profound) D64.9. ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code D64.9.
What are the diagnosis index entries for hemoglobin R71?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to R71.0: Decrease (d) hematocrit R71.0 Drop (in) hematocrit R71.0 (precipitous) hemoglobin R71.0 Findings, abnormal, inconclusive, without diagnosis - see also Abnormal hematocrit drop R71.0 (precipitous)
Can you code drop in hematocrit in HCT?
Your saying if the patient is admitted with any dx of anemia and has a hct drop and your query does not get answered for ABLA you would not code drop in hct? I think the rule is that if the provider documents anemia of any type, the coding rules don't allow you to document a "precipitous drop in hematocrit".
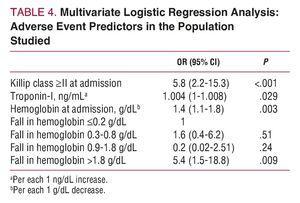
What is a precipitous drop in hematocrit?
There is another codeable condition called precipitous drop in hematocrit, R71. 0. This term can indicate several situations. In the first scenario, there is acute blood loss, but the patient never falls into anemic territory; therefore, acute blood loss anemia is not the appropriate term.
What does R71 mean?
Abnormality of red blood cellsR71- Abnormality of red blood cells ›
What is the ICD-10 code for abnormal hemoglobin?
ICD-10 code D58. 2 for Other hemoglobinopathies is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism .
What is the code for acute blood loss anemia?
ICD- 10-CM classifies acute blood loss anemia to code D62, Acute posthemorrhagic anemia, and chronic blood loss anemia to code D50. 0, Iron deficiency anemia secondary to blood loss (chronic). An Excludes1 note for “anemia due to chronic blood loss (D50.
What is diagnosis code R71 8?
ICD-10 code R71. 8 for Other abnormality of red blood cells is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Symptoms, signs and abnormal clinical and laboratory findings, not elsewhere classified .
What is the ICD 10 code for elevated hemoglobin and hematocrit?
ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code R97 R97.
What is icd10 code for low hemoglobin?
Code D64. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Anemia, Unspecified, it falls under the category of diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs and certain disorders involving the immune mechanism. Anemia specifically, is a condition in which the number of red blood cells is below normal.
What is abnormal hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin abnormalities are the group of blood disorders that affect the normal functioning of the hemoglobin in the red blood cells. These are genetic disorders that results in the altered size and shape of the red blood cells, thereby decreasing the oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood.
What makes hemoglobin low?
Not getting enough iron in your diet is the most common cause of low hemoglobin. Symptoms of low hemoglobin include headaches, fatigue, and pale skin. Treatments for low hemoglobin include iron supplements, iron therapy, and surgery. Adding more iron-rich foods to your diet is also important.
How much blood do you have to lose to drop hemoglobin?
In this study, 71 g of haemoglobin mass loss and 560 mL of blood volume loss were considered to be equivalent since they respectively correspond to approximately 10% of the total haemoglobin mass and 10% of the total blood volume of an average non-anaemic adult26.
The ICD code R71 is used to code Anisocytosis
Anisocytosis is a medical term meaning that a patient's red blood cells are of unequal size. This is commonly found in anemia and other blood conditions. False diagnostic flagging may be triggered by an elevated WBC count, agglutinated RBCs, RBC fragments, giant platelets or platelet clumps.
Coding Notes for R71.0 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'R71.0 - Precipitous drop in hematocrit'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code R71.0. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
Equivalent ICD-9 Code GENERAL EQUIVALENCE MAPPINGS (GEM)
This is the official exact match mapping between ICD9 and ICD10, as provided by the General Equivalency mapping crosswalk. This means that in all cases where the ICD9 code 790.01 was previously used, R71.0 is the appropriate modern ICD10 code.
What is a hemolytic disorder?
A disease characterized by compensated hemolysis with a normal hemoglobin level or a mild to moderate anemia. There may be intermittent abdominal discomfort, splenomegaly, and slight jaundice. A group of inherited disorders characterized by structural alterations within the hemoglobin molecule.
What does "type 1 excludes note" mean?
It means "not coded here". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as D58.2. A type 1 excludes note is for used for when two conditions cannot occur together, such as a congenital form versus an acquired form of the same condition. familial polycythemia (.
What is precipitous drop in hematocrit?
There is another codeable condition called precipitous drop in hematocrit, R71.0. This term can indicate several situations. In the first scenario, there is acute blood loss, but the patient never falls into anemic territory; therefore, acute blood loss anemia is not the appropriate term.
What is the normal range of hemoglobin?
For men, hemoglobin is usually somewhere between 13.5 and 17.5 g/dL, and for women, 12.0 to 15.5 g/dL.
How is blood loss determined?
The treatment of blood loss is determined by the rapidity by which the anemia develops, the degree of blood loss, whether symptoms have arisen, and whether there are high-risk clinical circumstances rendering the patient more vulnerable to harm.
What is the heme group in red blood cells?
Hemoglobin A is the protein in red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen. It is a complicated molecule composed of four folded subunits, two alpha and two beta chains, each with an incorporated heme group composed of an organic ring-like compound called porphyrin oriented around a central iron atom.
Does hematocrit lower red blood cell volume?
Since hematocrit is volume-dependent, if the patient receives significant fluid resuscitation, it can dilute the blood and lower the red blood cell volume. If the patient’s kidney function is normal, passage of time will allow for elimination of excess fluid and equilibration.
Is hemoglobin drop a quality measure?
It will trigger a quality measure PSI regarding hemorrhage. There is no absolute value of level of hemoglobin drop that defines ABLA. It occurs as a result of hemorrhage. If a blood transfusion is necessary due to hemorrhage, acute blood loss anemia is likely present and should be documented.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for congenital hydronephrosis
- 2. icd-10 code for right lung cancer
- 3. icd 10 code for face swelling rt side
- 4. icd-10-cm code for patient admitted for end of life hospice care
- 5. icd-10 code for osteoporosis with fracture
- 6. icd-10 code for automobile
- 7. what is the icd-10-cm code for acute cholecystitis with chronic cholecystitis
- 8. icd 10 code for ac arthritis
- 9. icd 10 code for right heart catheterization
- 10. icd-9 code for axillary breast tissue