What is the ICD 10 code for renal failure?
ICD 10 code for Renal Failure. ICD 10 features multiple codes for renal failure as compared to ICD 9. The order of listing in ICD 10 is as follows: N00-N99 Diseases of the genitourinary system › N17-N19 Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease. It is important to note that ICD 10 distinguishes between acute renal insufficiency ...
What is the ICD 10 code for prerenal uremia?
Pre renal uremia syndrome; Prerenal uremia syndrome; uremia NOS (N19); Prerenal uremia ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code N17.9 [convert to ICD-9-CM] Acute kidney failure, unspecified
What is prerenal kidney failure (Aki)?
Prerenal kidney failure, also known as acute renal failure (ARF), or acute kidney injury (AKI), is an extensively researched concept that has undergone numerous revisions in the diagnosis over the last decade. There are at least 30 biochemical definitions that have existed for AKI.
What is the meaning of acute renal failure?
Acute or chronic condition, characterized by the inability of the kidneys to adequately filter the blood substances, resulting in uremia and electrolyte imbalances. Acute renal failure is usually associated with oliguria or anuria, hyperkalemia, and pulmonary edema.
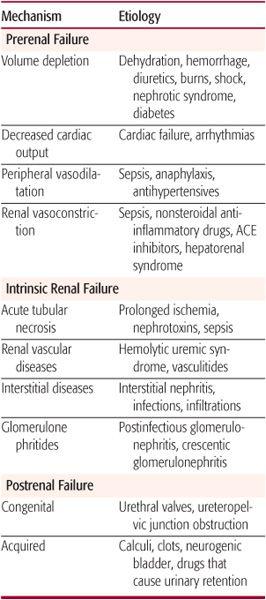
What is Prerenal acute renal failure?
Prerenal acute kidney injury (AKI) , (which used to be called acute renal failure), occurs when a sudden reduction in blood flow to the kidney (renal hypoperfusion) causes a loss of kidney function.
How do you code acute renal failure?
ICD-10-CM code N28. 9 is reported to capture the acute renal insufficiency. Based on your documentation, acute kidney injury/failure (N17. 9) cannot be assigned.
What is ICD-10 code N19?
ICD-10 code N19 for Unspecified kidney failure is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Diseases of the genitourinary system .
What does Prerenal state mean?
1. in front of the kidney. 2. occurring before the blood reaches the kidneys.
What is the ICD-10 code for Prerenal azotemia?
T28. 9 Corrosions of other and unspecified internal ...
What is the ICD-10 code for unspecified renal failure?
N19 - Unspecified kidney failure. ICD-10-CM.
What is diagnosis code N18 6?
Code N18. 6, end-stage renal disease, is to be reported for CKD that requires chronic dialysis. relationship between diabetes and CKD when both conditions are documented in the medical record.
What is R79 89?
R79. 89 - Other specified abnormal findings of blood chemistry | ICD-10-CM.
What is diagnosis code for acute on chronic renal failure?
N17-N19 Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney ...
How can you tell the difference between Prerenal and renal failure?
Response to fluid repletion is still regarded as the gold standard in the differentiation between prerenal and intrinsic AKI. Return of renal function to baseline within 24 to 72 hours is considered to indicate prerenal AKI, whereas persistent renal failure indicates intrinsic disease.
What is the most likely cause of pre-renal failure?
Intravascular volume depletion is the most common cause of pre-renal failure. Intravascular volume depletion can be the result of poor oral intake or excessive fluid loss.
What is the difference between Prerenal Intrarenal and Postrenal?
Pre-renal, generally in which decreased renal blood flow results in a drop in GFR. Intrinsic/intra-renal, in which a disease process causes damage to the kidney itself. Post-renal, in which a process downstream of the kidney prevents drainage of urine (urinary tract obstruction)
What is the ICd 10 code for renal failure?
ICD 10 features multiple codes for renal failure as compared to ICD 9. The order of listing in ICD 10 is as follows: N00-N99 Diseases of the genitourinary system › N17-N19 Acute kidney failure and chronic kidney disease. It is important to note that ICD 10 distinguishes between acute renal insufficiency and acute kidney injury/acute renal failure. There are additional codes to specify traumatic and non-traumatic kidney injury. Acute kidney disease and acute renal insufficiency cannot be reported as acute renal failure.
What causes clotting in the blood vessels in the kidney?
Clotting in the blood vessels within the kidney due to conditions like idiopathic thrombocytopenic thrombotic purpura (ITTP), malignant hypertension, hemolytic uremic syndrome, transfusion reaction, and scleroderma can also lead to acute renal failure.
What causes CKD?
Causes of CKD. The leading cause of CKD is diabetes. However, there are a number of factors that can lead to acute renal failure. Reduced blood flow to your kidneys due to conditions like low blood pressure, dehydration, burns, injury, hemorrhage, serious illness, septic shock and surgery can cause damage leading to acute renal failure.
Can kidney failure be life threatening?
The loss of the filtering ability of your kidney, leads to accumulation of waste material and electrolytes in your body, eventually leading to acute renal failure which can be life threatening. However, proper and timely treatment can reverse the damage and help you recover from the problem.
What is acute renal failure?
Acute renal failure is usually associated with oliguria or anuria, hyperkalemia, and pulmonary edema.
Can kidney failure lead to full life?
But with the help of healthcare providers, family and friends, most people with kidney failure can lead full and active lives. Inability of a kidney to excrete metabolites at normal plasma levels under conditions of normal loading or inability to retain electrolytes under conditions of normal intake.
Can chronic renal failure be cured?
Chronic renal failure develops over many years, may be caused by conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes, and cannot be cured. Chronic renal failure may lead to total and long-lasting renal failure, called end-stage renal disease (esrd).

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for absence of parotid gland
- 2. icd 9 code for aortic atherosclerosis
- 3. icd 10 code for lumbar failed back surgery syndrome
- 4. icd 10 cm code for recurrent mdd
- 5. icd 10 code for burn to foot
- 6. icd code for knee surgery
- 7. what is the icd-10 cm code for admission for adjustment of artificial leg
- 8. icd 10 code for alcoholic malnutrition
- 9. icd 10 code for status post icd
- 10. icd 10 cm code for pediactric ccontusion on head