What is the ICD-10 code for shunt revision?
Presence of dentures (complete) (partial) ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code T85.02XA [convert to ICD-9-CM] Displacement of ventricular intracranial (communicating) shunt, initial encounter. Displacement of ventricular intracranial shunt, init; Ventricular …
What is the ICD 10 code for displacement of intracranial shunt?
What is the ICD 10 code for VP shunt? Z98. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM Z98.
What is the ICD 10 code for cerebrospinal fluid drainage?
Feb 08, 2022 · What is the ICD 10 code for VP shunt? ICD-10:Z98.2Short Description:Presence of cerebrospinal fluid drainage deviceLong Description:Presence of …
What is a ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt?
Apr 02, 2020 · What is the ICD 10 code for VP shunt? Presence of cerebrospinal fluid drainage device. Z98. 2 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2020 edition of ICD-10-CM Z98.
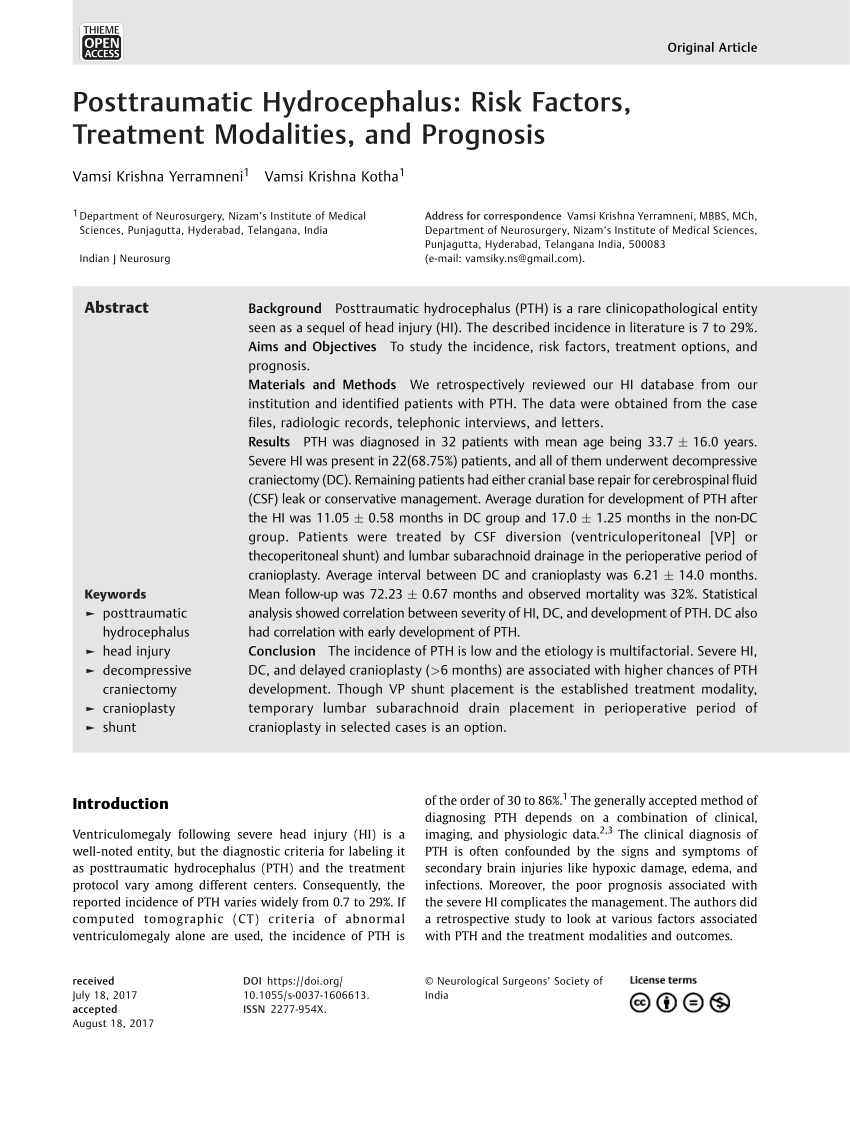
What is a VP shunt?
A ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt is a thin plastic tube that helps drain extra cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the brain. CSF is the saltwater that surrounds and cushions the brain and spinal cord.
What is VP shunt status?
Ventriculoperitoneal shunting is surgery to treat excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the cavities (ventricles) of the brain (hydrocephalus).Oct 6, 2019
What is VP shunt malfunction?
Cerebral shunt malfunction also referred to as shunt failure, is a partial or complete blockage (obstruction) of the shunt that causes it to function intermittently or not at all. When a blockage occurs, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) accumulates and can result in symptoms of untreated hydrocephalus.
What is a permanent VP shunt?
A ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt is a medical device that relieves pressure on the brain caused by fluid accumulation. VP shunting is a surgical procedure that primarily treats a condition called hydrocephalus. This condition occurs when excess cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) collects in the brain's ventricles.
What is an indwelling shunt?
✓ The authors describe an indwelling intraluminal shunt for carotid endarterectomy. The device is equipped with balloons at both ends to prevent bleeding and to hold the tube in place.
What is a VP shunt made of?
A ventriculoperitoneal shunt drains excess brain fluid, reducing brain pressure to a safe level. Ventriculoperitoneal shunts consist of a valve and two tubes, called catheters, which drain the fluid. One catheter drains fluid from the brain out of a small hole the doctor makes in the skull.Jan 8, 2019
How do you assess a VP shunt?
Examine for conscious state, pupillary size/reactivity, papilloedema. In a child with an open fontanelle, this should be soft and pulsatile. A sunken fontanelle may be due to low pressure. Fluid tracking along subcutaneous shunt tubing may indicate shunt blockage.
What is obstructed VP shunt?
VPS obstruction, which is most often occurs in the proximal catheter, is the most common cause of VPS malfunction. Hardware infection is the second most common cause of VPS malfunction, and this is a complication is most often observed in infants, with premature infants being the most susceptible.
How do you assess shunt?
The shunt patency is a study to determine if cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is actually flowing through the shunt system (valves and proximal and distal catheters). By injecting a small volume (about 0.3 ml) of a radiotracer into the shunt reservoir, the flow of CSF through the catheters and valve can be measured.
What are the different types of shunts?
A ventriculoperitoneal shunt moves fluid from the ventricles of the brain to the abdominal cavity. A ventriculoatrial shunt moves fluid from the ventricles of the brain to a chamber of the heart. A lumboperitoneal shunt moves fluid from the lower back to the abdominal cavity.
How is a VP shunt placed?
The long catheter is placed under your skin, behind your ear, down your neck, and into your abdomen. As the VP shunt drains extra CSF and lessens the pressure in your brain, it may ease some of your symptoms. Some symptoms will stop right after the VP shunt is inserted.Feb 8, 2022
What is shunt in anatomy?
In medicine, a shunt is a hole or a small passage that moves, or allows movement of, fluid from one part of the body to another. The term may describe either congenital or acquired shunts; acquired shunts (sometimes referred to as iatrogenic shunts) may be either biological or mechanical.
What is a VP shunt?
A ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt is a medical device that relieves pressure on the brain caused by fluid accumulation. VP shunting is a surgical procedure that primarily treats a condition called hydrocephalus.
What is the condition where there is an abnormal build up of CSF in the cavities of the brain?
Hydrocephalus, also called water in the brain, is a condition where there is an abnormal build up of CSF (cerebrospinal fluid) in the cavities (ventricles) of the brain. The build-up is often caused by an obstruction that prevents proper fluid drainage.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for allergy to cats
- 2. percutaneous abdominoplasty for cosmetic purposes icd pcs code
- 3. icd 10 code for hepatitis a
- 4. icd 10 code for lower lip mucocele
- 5. icd 10 code for acute meniere's disease
- 6. icd-10 code for chronic small vessel ischemic white matter disease
- 7. icd 10 code for dti left great toe
- 8. icd 10 code for early dementia
- 9. icd 10 code for sci incomplete tetraplegia
- 10. icd 10 code for superglue to eyelid