What is the CPT code for hyperparathyroidism?
Oct 01, 2021 · Primary hyperparathyroidism. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. E21.0 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E21.0 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD 10 code for hyperthyroidism?
Oct 01, 2021 · Hyperparathyroidism, unspecified. 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 Billable/Specific Code. E21.3 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM E21.3 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the pathophysiology of hyperparathyroidism?
Primary hyperparathyroidism (E21.0) E21 E21.0 E21.1 ICD-10-CM Code for Primary hyperparathyroidism E21.0 ICD-10 code E21.0 for Primary hyperparathyroidism is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases . Subscribe to Codify and get the code details in a flash.
What is the diagnosis group for secondary hyperparathyroidism due to ESRD?
Oct 01, 2021 · E21.0 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Primary hyperparathyroidism. It is found in the 2022 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2021 - Sep 30, 2022 .
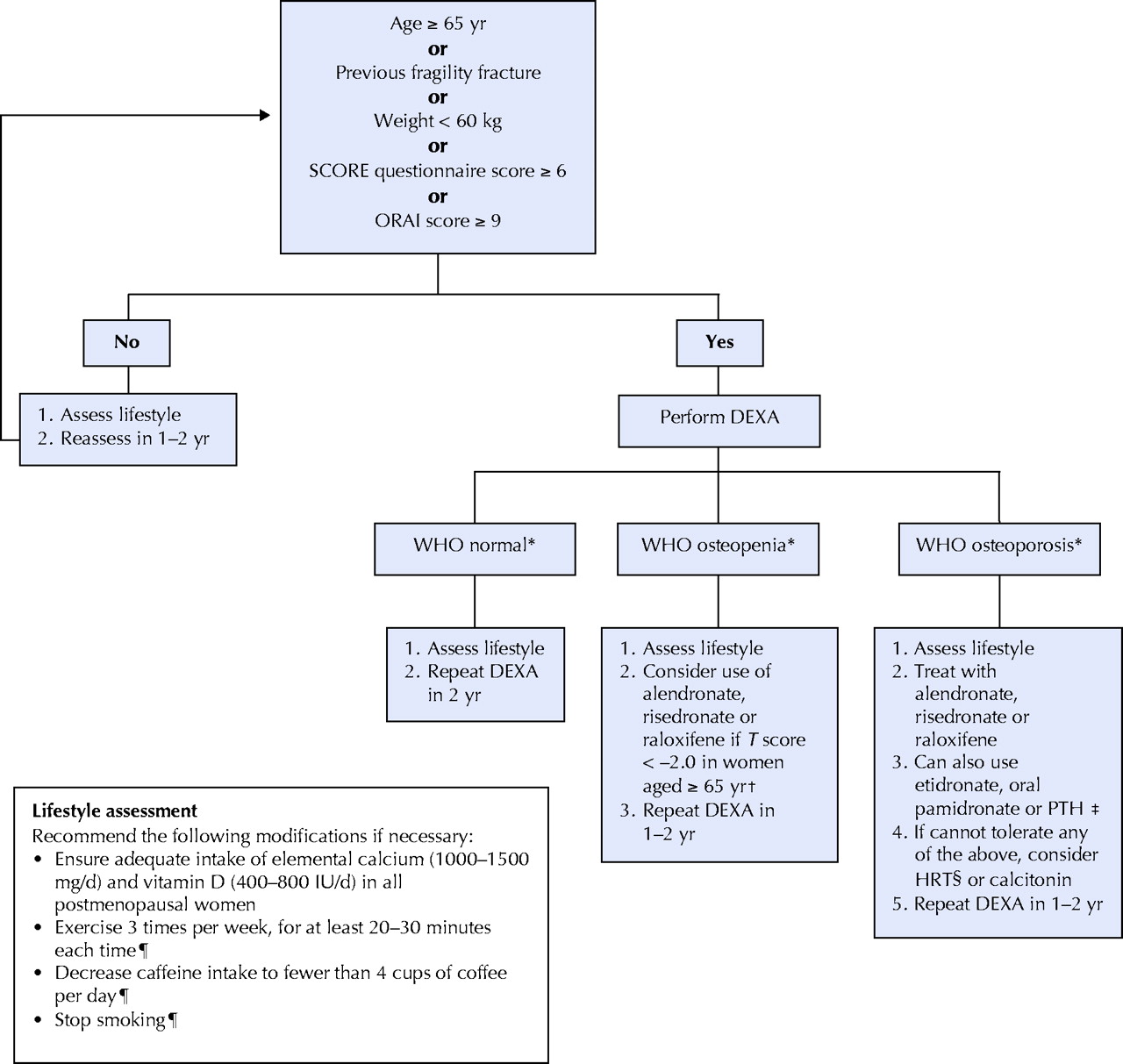
What is primary hyperparathyroidism?
Primary hyperparathyroidism is a condition in which one or more of the parathyroid glands makes too much PTH. This can lead to the loss of bone tissue. This condition is more common in women than in men. A job of PTH is to keep blood calcium levels from going too low.
What are the 3 types of hyperparathyroidism?
There are three types of hyperparathyroidism: primary, secondary, and tertiary.Primary Hyperparathyroidism. This type occurs when you have a problem with at least one of your parathyroid glands. ... Secondary Hyperparathyroidism. ... Tertiary Hyperparathyroidism.
What does code E21 3 mean?
3: Hyperparathyroidism, unspecified.
What is primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism?
Parathyroid glands can go crazy all on their own (called primary hyperparathyroidism) or when some other disease forces them to go crazy (called secondary hyperparathyroidism). Secondary hyperparathyroidism is a disease of the parathyroid glands that was caused by some other disease.
What is the most common type of hyperparathyroidism?
Primary hyperparathyroidismA noncancerous growth (adenoma) on a gland is the most common cause.Enlargement (hyperplasia) of two or more parathyroid glands accounts for most other cases.A cancerous tumor is a very rare cause of primary hyperparathyroidism.Jun 18, 2020
What causes primary hyperparathyroidism?
Causes. The most common cause of primary hyperparathyroidism is a tiny, benign tumor called an adenoma. Usually, one adenoma forms in one of the four parathyroid glands, but it is possible for more adenomas to form in multiple parathyroid glands. An adenoma causes the affected gland to become overactive.
What is E83 52?
ICD-10 code E83. 52 for Hypercalcemia is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Endocrine, nutritional and metabolic diseases .
What is ICD-10 code for osteoporosis?
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM CodesOsteoporosis ICD-9-CM & ICD-10-CM CodesOSTEOPOROSISOsteoporosis unspecified: 733.00M81.0Senile osteoporosis: 733.01M81.0Idiopathic osteoporosis: 733.02M81.812 more rows
What is hyperparathyroidism unspecified?
A condition of abnormally elevated output of parathyroid hormone (or pth) triggering responses that increase blood calcium. It is characterized by hypercalcemia and bone resorption, eventually leading to bone diseases. Primary hyperparathyroidism is caused by parathyroid hyperplasia or parathyroid neoplasms.
How do primary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism differ?
Unlike primary hyperparathyroidism, the tertiary form presents as a progressive stage of resolved secondary hyperparathyroidism with biochemical hallmarks that include elevated calcium ion levels in the blood, hypercalcemia, along with autonomous production of parathyroid hormone and adenoma in all four parathyroid ...
Can you have both primary and secondary hyperparathyroidism?
After treatment, there was a significant decrease of PTH levels in both groups. Conclusion: Patients with PA frequently have primary or secondary hyperparathyroidism, which is alleviated by correction of PA by surgical or medical means.
How does one differentiate between primary versus secondary versus tertiary hyperparathyroidism?
The increase may be due to a) primary hyperparathyroidism which is caused by adenoma of one or more parathyroid glands or hyperplasia of all four glands, b) secondary hyperparathyroidism, which may be caused by deficiency in vitamin D or uremia, and 3) tertiary hyperparathyroidism, which most often is the result of a ...
What is the ICd 10 code for hyperparathyroidism?
E21.0 is a valid billable ICD-10 diagnosis code for Primary hyperparathyroidism . It is found in the 2021 version of the ICD-10 Clinical Modification (CM) and can be used in all HIPAA-covered transactions from Oct 01, 2020 - Sep 30, 2021 .
What does NEC not elsewhere mean?
NEC Not elsewhere classifiable#N#This abbreviation in the Tabular List represents “other specified”. When a specific code is not available for a condition, the Tabular List includes an NEC entry under a code to identify the code as the “other specified” code.
What are the symptoms of osteotis fibrosa cystica of the tibia?
The symptoms of the disease are the consequences of both the general softening of the bones and the excess calcium in the blood, and include bone fractures, kidney stones, nausea, moth-eaten appearance in the bones, appetite loss, and weight loss. Osteitis fibrosa cystica of the tibia.
What is osteoclast cystica?
This surplus stimulates the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone, in a process known as osteoclastic bone resorption. The hyperparathyroidism can be triggered by a parathyroid adenoma, hereditary factors, parathyroid carcinoma, or renal osteodystrophy. Osteoclastic bone resorption releases minerals, including calcium, from the bone into the bloodstream. In addition to elevated blood calcium levels, over-activity of this process results in a loss of bone mass, a weakening of the bones as their calcified supporting structures are replaced with fibrous tissue (peritrabecular fibrosis), and the formation of cyst-like brown tumors in and around the bone. The symptoms of the disease are the consequences of both the general softening of the bones and the excess calcium in the blood, and include bone fractures, kidney stones, nausea, moth-eaten appearance in the bones, appetite loss, and weight loss.
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
What is the process of breaking down bone?
This surplus stimulates the activity of osteoclasts, cells that break down bone, in a process known as osteoclastic bone resorption. The hyperparathyroidism can be triggered by a parathyroid adenoma, hereditary factors, parathyroid carcinoma, or renal osteodystrophy.
Why does hyperparathyroidism cause thinning of bones?
Because calcium is removed from bones to be released into the bloodstream, hyperparathyroidism often causes thinning of the bones (osteoporosis). The age at which familial isolated hyperparathyroidism is diagnosed varies from childhood to adulthood.
What is the E21.0 code?
E21.0 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of primary hyperparathyroidism. The code E21.0 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What hormones are released into the bloodstream?
Parathyroid hormone stimulates the removal of calcium from bone and the absorption of calcium from the diet, and the mineral is then released into the bloodstream.In people with familial isolated hyperparathyroidism, the production of excess parathyroid hormone is caused by tumors that involve the parathyroid glands.
What hormones are involved in maintaining calcium and phosphorus levels?
The parathyroid glands make parathyroid hormone (PTH), which helps your body keep the right balance of calcium and phosphorous. If your parathyroid glands make too much or too little hormone, it disrupts this balance. If they secrete extra PTH, you have hyperparathyroidism, and your blood calcium rises.
Why is there too little calcium in my blood?
Your blood will have too little calcium and too much phosphorous. Causes include injury to the glands, endocrine disorders, or genetic conditions. Treatment is aimed at restoring the balance of calcium and phosphorous. NIH: National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases.
What is the tabular list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code E21.0:
Can parathyroidism cause cancer?
The tumors are usually noncancerous (benign), in which case they are called adenomas. Rarely, people with familial isolated hyperparathyroidism develop a cancerous tumor called parathyroid carcinoma.
When is the ICd 10 code for hyperparathyroidism effective?
The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM E21 became effective on October 1, 2020.
What does type 1 excludes mean?
Type 1 Excludes Help. A type 1 excludes note is a pure excludes. It means "not coded here ". A type 1 excludes note indicates that the code excluded should never be used at the same time as E21.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for physical for 17 year old
- 2. icd 10 code for unspecified eye injury to unspecified eye
- 3. icd 10 code for mass within the right parotid gland.
- 4. icd-10 code for attempted suicide
- 5. icd 10 code for status post esophageal cancer
- 6. what icd 9 code do i use for injection of birth control
- 7. icd 10 code for infected peritoneal dialysis catheter
- 8. icd-10 code for hypercapnia unspecified
- 9. icd 10 code for phthisis bulbi
- 10. icd 10 code for breakthrough bleeding with iud