How do you diagnose mental retardation?
Some of the symptoms of mild intellectual disability include:
- taking longer to learn to talk, but communicating well once they know how
- being fully independent in self-care when they get older
- having problems with reading and writing
- social immaturity
- increased difficulty with the responsibilities of marriage or parenting
- benefiting from specialized education plans
- having an IQ range of 50 to 69
What are 3 factors that may cause mental retardation?
What is the cause of mental retardation?
- Various genetic disorders (e.g. Down’s Syndrome, phenylketonuria)
- Certain maternal infections during pregnancy (e.g. rubella)
- Mother who abuses substances such as alcohol during pregnancy
- Certain psychosocial conditions (e.g. ...
- Maternal exposure to various drugs (e.g. ...
- Maternal exposure to environmental chemicals (discussed in detail later)
What are the signs of mental retardation?
Some of the most common signs of intellectual disability are:
- Rolling over, sitting up, crawling, or walking late
- Talking late or having trouble with talking
- Slow to master things like potty training, dressing, and feeding themselves
- Difficulty remembering things
- Inability to connect actions with consequences
- Behavior problems such as explosive tantrums
- Difficulty with problem-solving or logical thinking
How is a basic diagnosis of mental retardation made?
language and motor skills may be apparent. A diagnosis of mental retardation, however, is often not made until the child is in elementary school and has difficulty in mastering academic skills. Although children with Down Syndrome are mentally retarded, there are a number of other causes of mental retardation. Real Life Stories
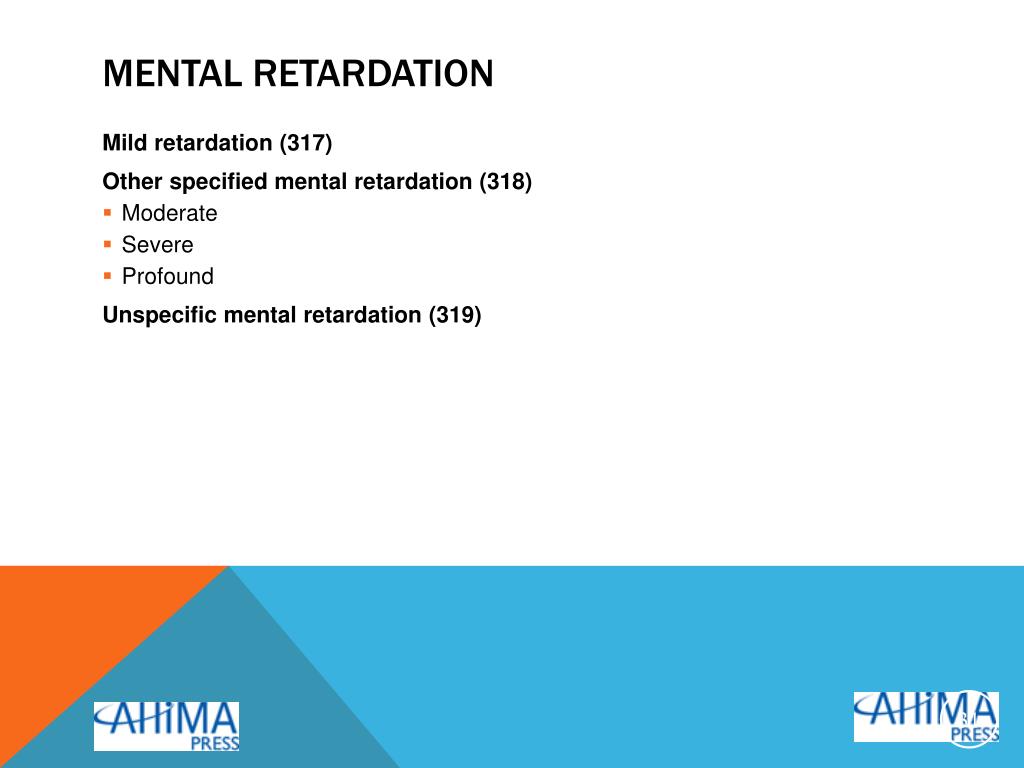
What is the ICD-10 code for profound intellectual disability?
F73 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F73 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for mental retardation?
The following ICD-10-CA codes were used to select and exclude ID cases: F70 = Mild mental retardation. F71 = Moderate mental retardation. F72 = Severe mental retardation.
How do you code intellectual disability?
F79 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM F79 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for IQ 27 intellectual disabilities?
Iq 20-34.
What is profound mental retardation?
Profound Mental Retardation (MR) is defined by the presence of significantly sub average general intellectual functioning as well as significant limitations in adaptive functioning present prior to the age of 18 years. Individuals with a diagnosis of Severe MR generally obtain IQ scores below 20–25 [1, 3, 4].
What is mental retardation called now?
intellectual disabilityIn the fifth edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), the APA replaced “mental retardation” with “intellectual disability (intellectual developmental disorder).” The APA included the parenthetical name “(intellectual developmental disorder)” to indicate that the diagnosed deficits ...
What is a profound intellectual disability?
Profound Intellectual Disability These individuals cannot live independently, and they require close supervision and help with self-care activities. They have very limited ability to communicate and often have physical limitations.
What are the severity codes of intellectual disability?
Most epidemiological surveys generally categorize the severity of intellectual disability as mild (IQ ≥50) or severe (IQ ≤50), with 75% of individuals recognized to have mild intellectual disability (1,2,4,9-11).
What is considered a severe intellectual disability?
Severe intellectual disability severe damage to, or abnormal development of, their central nervous system. generally having an IQ range of 20 to 34.
What are the 3 main diagnostic criteria for intellectual disability?
There are three major criteria for intellectual disability: significant limitations in intellectual functioning, significant limitations in adaptive behavior, and onset before the age of 18.
What is the IQ range for intellectual disability?
Diagnosing Intellectual Disability A full-scale IQ score of around 70 to 75 indicates a significant limitation in intellectual functioning.
What does an IQ of 63 mean?
intellectual impairment: ● 317 Mild Mental Retardation: IQ level 50 55 to. ● 317 Mild Mental Retardation: IQ level 50–55 to. approximately 70. ● 318.0 Moderate Mental Retardation: IQ level 35–40.
What is the billable code for acute care?
Billable codes are sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. F73 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of profound intellectual disabilities. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.
What is intellectual disability?
Intellectual disability (ID), also called intellectual development disorder (IDD) or general learning disability, and formerly known as mental retardation (MR), is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significantly impaired intellectual and adaptive functioning. It is defined by an IQ score below 70 in addition to deficits in two or more adaptive behaviors that affect everyday, general living. Once focused almost entirely on cognition, the definition now includes both a component relating to mental functioning and one relating to individuals' functional skills in their environments. As a result of this focus on the person's abilities in practice, a person with an unusually low IQ may not be considered intellectually disabled. Intellectual disability is subdivided into syndromic intellectual disability, in which intellectual deficits associated with other medical and behavioral signs and symptoms are present, and non-syndromic intellectual disability, in which intellectual deficits appear without other abnormalities. Down syndrome and fragile X syndrome are examples of syndromic intellectual disabilities.
What is the difference between syndromic and non-syndromic intellectual disability?
Intellectual disability is subdivided into syndromic intellectual disability, in which intellectual deficits associated with other medical and behavioral signs and symptoms are present, and non-syndromic intellectual disability, in which intellectual deficits appear without other abnormalities.
What is the F73 code?
F73 is a billable ICD code used to specify a diagnosis of profound intellectual disabilities. A 'billable code' is detailed enough to be used to specify a medical diagnosis.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for iliac tube malfuntion
- 2. icd 10 cm code for estrace
- 3. icd 10 code for chondral loss lateral facet patella
- 4. 2016 icd 10 code for compression deformity t12
- 5. icd 10 code for inguinal hernia repair with mesh
- 6. 2015 icd 10 code for brewer's infarct
- 7. icd 10 code for bee stings
- 8. icd 10 code for partial replacement (synthetic) of left shoulder (humeral head)
- 9. icd code for eye pain
- 10. icd-9 code for pain in finger