How ICD 10 is different from ICD 9 codes?
Oct 01, 2021 · The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M11.2 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of M11.2 - other international versions of ICD-10 M11.2 may differ. Presence of calcium salts, especially calcium pyrophosphate, in the cartilaginous structures of one or more joints. When accompanied by attacks of goutlike symptoms, it is …
How to ICD 10 code pseudoobstruction?
Apr 15, 2022 · AHA Coding Clinic ® for ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS - 2018 Issue 3; Ask the Editor Pseudogout of Knee. A 91-year-old with a significant history of multiple medical problems presents with left knee pain and swelling. The provider diagnosed pseudogout of the left knee, due to the patient’s previous x-ray finding of chondrocalcinosis.
What are the new ICD 10 codes?
M1A.059 Idiopathic chronic gout, unspecified hip. M1A.0590 Idiopathic chronic gout, unspecified hip, wit... M1A.0591 Idiopathic chronic gout, unspecified hip, wit... M1A.06 Idiopathic chronic gout, knee. M1A.061 Idiopathic chronic gout, right knee. …
Where can one find ICD 10 diagnosis codes?
Feb 15, 2016 · Feb 15, 2016. #2. I looked up pseudogout last week, and I used a code for Chondrocalcinosis. I looked up what Chondrocalcinosis meant, and it said also known as pseudogout. So, for pseudogout of the L knee, I would use dx code M11.262. Hope this helps! You must log in or register to reply here. Forums. Medical Coding.

Is Pseudogout the same as chondrocalcinosis?
Synonyms. Pseudogout and calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease are synonyms for chondrocalcinosis.
Is chondrocalcinosis the same as arthritis?
Chondrocalcinosis, also known as calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) and pseudogout, is a condition where calcium pyrophosphate crystals build up in the joints. It is a type of arthritis that causes inflammation, stiffness, tenderness, redness, and warmth of the joints.Apr 8, 2021
What is the ICD-10 code for left knee swelling?
ICD-10 code M25. 462 for Effusion, left knee is a medical classification as listed by WHO under the range - Arthropathies .
What is the ICD-10 code for right knee chondrocalcinosis?
M11.261ICD-10 | Other chondrocalcinosis, right knee (M11. 261)
What is another name for pseudogout?
Also called calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease or CPPD, the common term "pseudogout" was coined for the condition's similarity to gout. Crystal deposits within a joint cause both conditions, although the type of crystal differs for each condition.Jul 16, 2020
What is difference between gout and pseudogout?
In pseudogout, or CPPD, crystals of pyrophosphate dihydrate form in your joints causing pain. Gout, on the other hand, is caused by the formation of monosodium urate crystals due to high levels of uric acid. The crystals form around your joints, causing pain.
What is the ICD-10 code for arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis, unspecified M06. 9 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM M06. 9 became effective on October 1, 2021.
What is the ICD-10 code for right shoulder pain?
ICD-10 | Pain in right shoulder (M25. 511)
What is the ICD-10 code for joint pain?
Code M25. 50 is the diagnosis code used for Pain in the Unspecified Joint. It falls under the category of Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue.
What is crystal arthropathy?
Crystalline arthropathies are a group of joint disorders caused by deposits of crystals in joints and the soft tissues around them. The most common types are gout and calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD). Over time, crystalline arthropathies can lead to joint damage and occasionally kidney disease.
What is the ICD-10 code for gout?
M10.9Code M10. 9 is the diagnosis code used for Gout, Unspecified. It is a common, painful form of arthritis. It causes swollen, red, hot and stiff joints and occurs when uric acid builds up in your blood.
Is Pseudogout hereditary?
In some families, a predisposition for developing pseudogout is hereditary. These people tend to develop pseudogout at younger ages. Mineral imbalances. The risk of pseudogout is higher for people who have excessive calcium or iron in their blood or too little magnesium.Jul 16, 2020
What is gouty tophus?
Gouty tophus of right olecranon bursa. Clinical Information. A condition marked by increased levels of uric acid in the blood, joints, and tissue. The buildup of uric acid in the joints and tissues causes arthritis and inflammation. Gout is a common, painful form of arthritis.
Why does gout make my joints swell?
It causes swollen, red, hot and stiff joints. Gout occurs when uric acid builds up in your blood. This happens if your body produces extra acid or does not eliminate enough, or if you eat too many foods with purines, such as liver and dried beans. Pseudogout has similar symptoms and is sometimes confused with gout.
The ICD code M112 is used to code Chondrocalcinosis
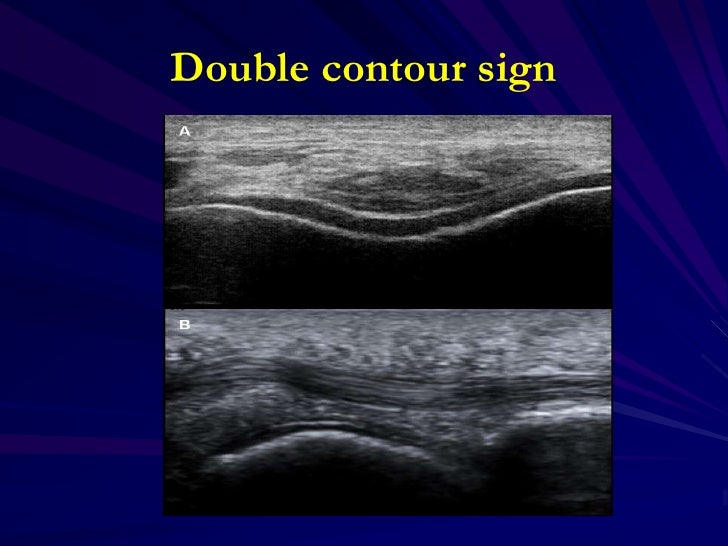
Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD) crystal deposition disease, also known as chondrocalcinosis, pseudogout and pyrophosphate arthropathy is a rheumatologic disorder with varied symptoms and signs arising from the accumulation of crystals of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate in the connective tissues.
Coding Notes for M11.2 Info for medical coders on how to properly use this ICD-10 code
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index References for 'M11.2 - Other chondrocalcinosis'
The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index links the below-listed medical terms to the ICD code M11.2. Click on any term below to browse the alphabetical index.
What is pseudogout?
Pseudogout (or "false gout") is a form of arthritis that results from deposits of calcium pyrophosphate crystals (its medical term is calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease, or CPPD). It commonly affects the knees and wrists.
What is CPPD in medical terms?
What is calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CPPD, or pseudogout)? Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease (CPPD) is a form of arthritis that causes pain, stiffness, tenderness, redness, warmth and swelling (inflammation) in some joints. It usually affects one joint at a time, ...
Is Cleveland Clinic a non profit?
Less often, CPPD may cause persistent swelling, warmth and pain in several joints, and can even mimic rheumatoid arthritis. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cle veland Clinic products or services.
How do steroids work?
Steroids also work by decreasing inflammation. Steroids can be injected into the affected joint or given as pills. (Steroids shouldn't be used in certain cases.) Certain medications, such as anakinra and canakinumab, have been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of the acute attack.
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for c diff colonization
- 2. icd-10 code for re-exam
- 3. icd 10 code for drug-induced obesity
- 4. what are the icd 10 code for squamous cell carcinoma in situ
- 5. icd 10 code for low o2 sat
- 6. icd 10 code for coccyx mass
- 7. icd 10 code for cut injury of finger
- 8. icd 10 code for finger laceration left third digit
- 9. icd 10 code for papillary carcinoma of the thyroid
- 10. 2020 icd 10 code for shortness of breath with exertion