What is the ICD 10 code for colon polyps?
2018/2019 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K51.40. Inflammatory polyps of colon without complications. 2016 2017 2018 2019 Billable/Specific Code. K51.40 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
What is the ICD 10 code for hyperplastic colon?
If a colon polyp is specified as hyperplastic, assign K63.5 even if greater specificity is provided regarding the location, per Coding Clinic for ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS (Second Quarter 2015, pages 14-15). The ICD-10 code for rectal polyp is K62.1 Rectal polyp. Example: A 53-year-old-male presents for colonoscopy.
What is the ICD 10 code for inflammation of the colon?
Diagnosis Index entries containing back-references to K51.40: Inflammation, inflamed, inflammatory (with exudation) polyp, colon K51.40 - see also Polyp, colon, inflammatory Polyp, polypus colon K63.5 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code K63.5
What is the ICD 10 code for K51 40?
K51.40 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes. The 2018/2019 edition of ICD-10-CM K51.40 became effective on October 1, 2018. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K51.40 - other international versions of ICD-10 K51.40 may differ.

What is Pseudopolyposis of colon?
There is a type of polyp that may be found in the colon of a person who has inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), either Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis, that is actually not really a true polyp. These growths are called pseudopolyps because they are not polyps at all; rather, they are "false" polyps.
How do you code a tortuous colon in ICD-10?
560.2 is correct. Your documentation states tortuous not congenital.
What is the ICD-10 code for redundant colon?
Other specified congenital malformations of intestine The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM Q43. 8 became effective on October 1, 2021. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of Q43.
What does quiescent colitis mean?
Quiescent (inactive) colitis refers to architectural abnormalities of chronic colitis in the absence of significant neutrophilic crypt injury. These changes include atrophy, irregularity and shortening of crypts, thickening of the muscularis mucosae, or metaplasia (Paneth cell or pyloric metaplasia) (Figure 11B).
What is a tortuous colon?
Summary. If your colon measures longer than five feet, it will contort itself so that it can fit into your abdomen. The extra loops and bends that form result in a condition known as tortuous or redundant colon. You may have some digestive discomfort such as constipation and cramping, but often there are no issues.
What is a redundant colon?
However, an individual with a redundant colon has an abnormally long colon, especially in the final section (called the descending colon). A redundant colon often has additional loops or twists. Other names for a redundant colon include tortuous colon or elongated colon.
Is a redundant colon always congenital?
A redundant loop of sigmoid colon is a scarce congenital anatomic variation that is associated with serious chronic and acute clinical and functional implications. This variation is difficultly diagnosed or suspected preoperatively. Its presence though, complicates surgical maneuvers and radiographic analysis.
Is tortuous colon congenital?
A Redundant Colon or a 'Tortuous colon' is a congenital abnormality of the intestines such that the colon is longer than what is considered normal. Though not necessarily dangerous, it is usually diagnosed as a result of a colonoscopy and may make it a more difficult procedure.
What is angulation of the colon?
Loops or angulation in the colon are possibly the most common patient-related source of difficulty. Some bends require additional skill to navigate. Loops, particularly in the sigmoid colon, can result in loss of control of the endoscope as well as patient discomfort.
What are the 3 types of colitis?
Colitis is inflammation of your colon, also known as your large intestine....1. Ulcerative colitisproctosigmoiditis, which affects the rectum and lower portion of the colon.left-sided ulcerative colitis, which affects the left side of the colon beginning at the rectum.pancolitis, which affects the entire large intestine.
What is the difference between colitis and ulcerative colitis?
What's the difference between colitis and ulcerative colitis? Colitis means your colon is inflamed, or irritated. This can be caused by many things, such as infections from viruses or bacteria. Ulcerative colitis is more severe because it is not caused by an infection and is lifelong.
What is Lymphoplasmacytosis?
Noun. lymphoplasmacytosis. (pathology) A condition in which there is an unusually large proportion of lymphocytes in tissues, exudates, or blood.
What is the code for inflammatory colon polyps?
Codes for inflammatory colon polyps, found in category K51, include a description of complications: K51.40 Inflammatory polyps of colon without complications. K51.411 Inflammatory polyps of colon with rectal bleeding. K51.412 Inflammatory polyps of colon with intestinal obstruction.
Is colon cancer benign?
Print Post. Colorectal cancer typically develops from colon polyps, which are abnormal growths of tissue (neoplasms). Most polyps are benign, but may become cancerous. When selecting an ICD-10 diagnosis code for polyp (s) of the colon, you will need to know the precise location of the polyp (s) and the type of polyp (e.g., benign, inflammatory, ...
What is a polypoid lesion?
A polypoid lesion that arises from the colon and protrudes into the lumen. This group includes adenomatous polyps, serrated polyps, and hamartomatous polyps. Abnormal growths of tissue in the lining of the bowel. Polyps are a risk factor for colon cancer.
What is an adenomatous colon polyp?
Adenomatous colon polyps are considered to be precursor lesions of colon cancer. An extra piece of tissue that grows in the large intestine, or colon. Discrete tissue masses that protrude into the lumen of the colon. These polyps are connected to the wall of the colon either by a stalk, pedunculus, or by a broad base.
What is a mass of tissue that bulges or projects into the lumen of the colon?
This is a descriptive term referring of a mass of tissue that bulges or projects into the lumen of the colon. The mass is macroscopically visible and may either have a broad base attachment to the colon wall, or be on a pedunculated stalk. These may be benign or malignant.
Is a polyp of the intestine dangerous?
Polyp colon, hyperplastic. Polyp of intestine. Clinical Information. A polyp is an extra piece of tissue that grows inside your body. Colonic polyps grow in the large intestine, or colon. Most polyps are not dangerous . However, some polyps may turn into cancer or already be cancer.
Can colon polyps cause diarrhea?
most colon polyps do not cause symptoms. If you have symptoms, they may include blood on your underwear or on toilet paper after a bowel movement, blood in your stool, or constipation or diarrhea lasting more than a week. nih: national institute of diabetes and digestive diseases.
Can you have pseudopolyposis if you have a benign lymphoid?
benign lymphoid pseudopolyp of colon. AuntJoyce said: Absolutely...to be considered to have pseudopolyposis, you must first have the offending pseudopolyp and vice versa, if you have a pseudopolyp, you are considered as having pseudopolyposis.
Is pseudopolyposis pre malignant?
Pseudopolyps are NOT pre- malignant polyps but have the characteristics of them and hats off to the many docs who call it as ...
Not Valid for Submission
556.4 is a legacy non-billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of pseudopolyposis of colon. This code was replaced on September 30, 2015 by its ICD-10 equivalent.
Information for Medical Professionals
References found for the code 556.4 in the Index of Diseases and Injuries:
Information for Patients
Also called: Colitis, Distal colitis, Pancolitis, Ulcerative proctitis
ICD-9 Footnotes
General Equivalence Map Definitions The ICD-9 and ICD-10 GEMs are used to facilitate linking between the diagnosis codes in ICD-9-CM and the new ICD-10-CM code set. The GEMs are the raw material from which providers, health information vendors and payers can derive specific applied mappings to meet their needs.
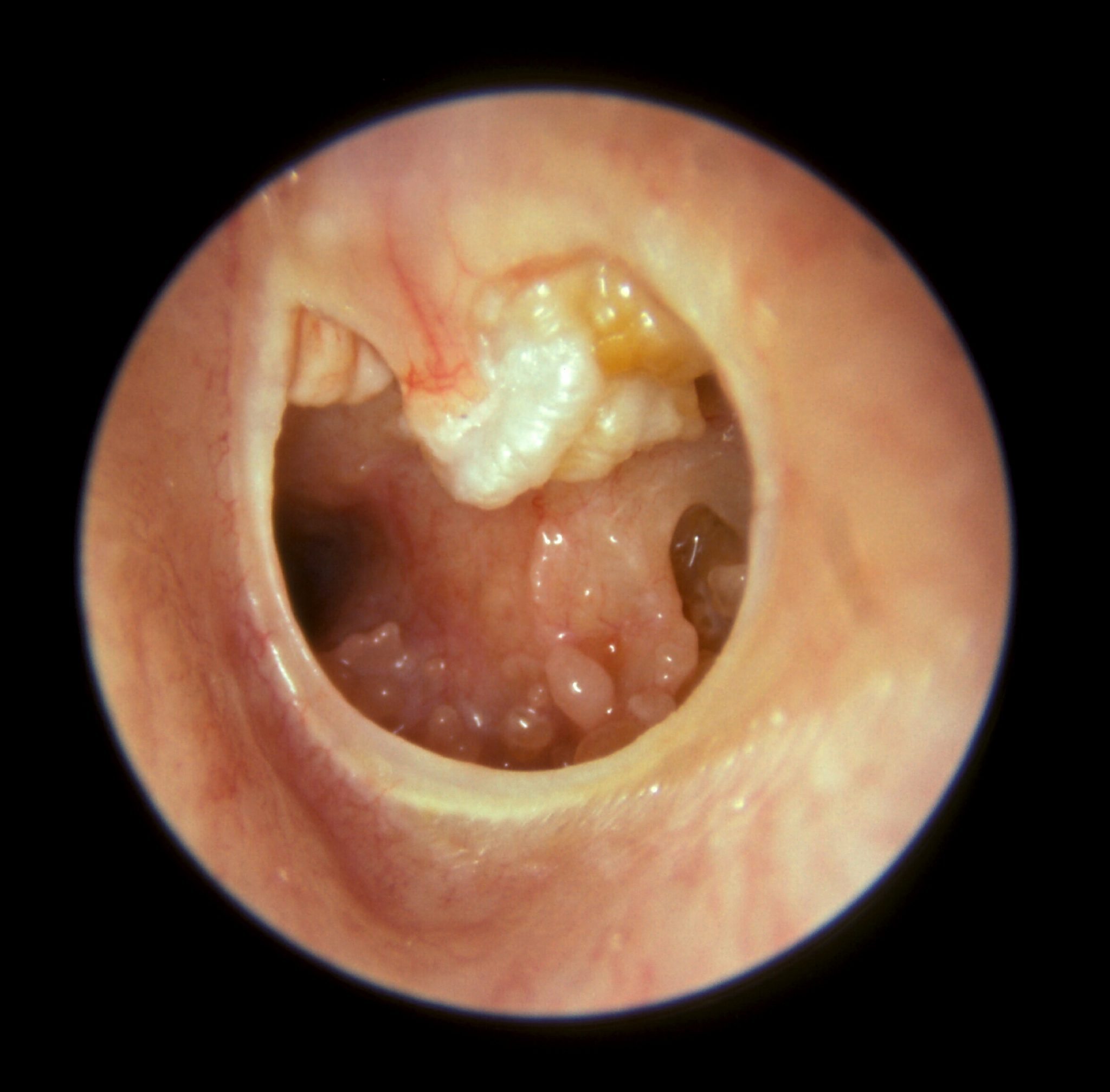
Benign Colon Polyps
Inflammatory Polyps
- Codes for inflammatory colon polyps, found in category K51, include a description of complications: Per ICD-10 guidelines, you should use an additionalcode with category K51 to identify manifestations (e.g., pyoderma gangrenosum).
Other Polyps
- Polyps of the colon not documented as adenomatous, benign, or inflammatory are reported using K63.5 Polyp of colon. If a colon polyp is specified as hyperplastic, assign K63.5 even if greater specificity is provided regarding the location, per Coding Clinic for ICD-10-CM and ICD-10-PCS (Second Quarter 2015, pages 14-15). The ICD-10 code for rectal ...
Malignant Neoplasms
- For malignant neoplasm(s) of the colon and rectum, refer to ICD-10 categories C18-C20. Example: A 70-year-old patient with a family history of colon cancer complains of abdominal pain and rectal bleeding. During colonoscopy, the physician finds a mass at the hepatic flexure, which pathology confirms as malignant. The primary diagnosis is cancer of the hepatic flexure. Scan t…
Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for teen pregnancy
- 2. icd 10 code for aki unspecified
- 3. icd 10 code for edema to lower extremities
- 4. icd 9 code for lateral column pain with peroneal tendonitis
- 5. what icd-10 code covers psa for medicare
- 6. icd 10 code for decubitus ulcer of sacral region unstageable
- 7. icd 10 cm code for blurred vision bilateral
- 8. icd code for cerebrovascular disease
- 9. icd 10 code for failed right tka s/p revision
- 10. icd 10 code for acute retroviral syndrome