What is the ICD 10 code for Raynaud syndrome with gangrene?
Raynaud's syndrome NON-BILLABLE | ICD-10 from 2011 - 2016 ICD Code I73.0 is a non-billable code. To code a diagnosis of this type, you must use one of the two child codes of I73.0 that describes the diagnosis 'raynaud's syndrome' in more detail. I73.0 Raynaud's syndrome I73.00 Raynaud's syndrome without gangrene
What is the ICD 10 code for secondary Raynaud's phenomenon?
Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for raynaud's syndrome: BILLABLE CODE - Use I73.00 for Raynaud's syndrome without gangrene BILLABLE CODE - Use I73.01 for Raynaud's syndrome with gangrene Tabular List of …
What is Raynaud’s disease?
Index Terms Starting With 'R' (Raynaud's disease, phenomenon or syndrome) Raynaud's disease, phenomenon or syndrome (secondary) I73.00 ICD-10-CM Diagnosis Code I73.00
What is the ICD 10 code for Neurologic diagnosis?
More specific codes: Billable - I73.00 Raynaud's syndrome without gangrene Billable - I73.01 Raynaud's syndrome with gangrene
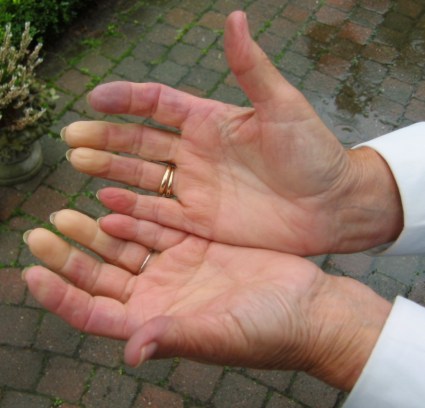
What is Raynaud syndrom?
Raynaud's phenomenon is a problem that causes decreased blood flow to the fingers. In some cases, it also causes less blood flow to the ears, toes, nipples, knees, or nose. This happens due to spasms of blood vessels in those areas. The spasms happen in response to cold, stress, or emotional upset.
What is the difference between Raynaud's disease and Raynaud's syndrome?
Primary Raynaud's(or Raynaud's disease) happens without any other illness behind it. The symptoms are often mild. Secondary Raynaud's (Raynaud's syndrome, Raynaud's phenomenon) results from another illness. It's often a condition that attacks your body's connective tissues, like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis.Aug 23, 2021
What is done for Raynaud's syndrome?
To widen blood vessels and increase blood flow, your doctor might prescribe: Calcium channel blockers. These drugs relax and open small blood vessels in your hands and feet, reducing the severity and number of attacks in most people with Raynaud's. These drugs can also help heal skin ulcers on your fingers or toes.Nov 6, 2020
What is the main cause of Raynaud?
Why does it happen? Raynaud's is usually triggered by cold temperatures, anxiety or stress. The condition occurs because your blood vessels go into a temporary spasm, which blocks the flow of blood. This causes the affected area to change colour to white, then blue and then red, as the bloodflow returns.Nov 23, 2021
Is Raynaud's an autoimmune disorder?
Summary. Raynaud's phenomenon is the short-term interruption of blood flow to the extremities, such as the fingers and toes. Raynaud's phenomenon may be a sign of an underlying autoimmune disorder such as scleroderma or lupus, so it's important to see your doctor for diagnosis.
How can you tell the difference between primary and secondary Raynaud's?
A major clinical distinction between primary and secondary Raynaud's is that patients with primary Raynaud's phenomenon do not get digital ulcers, gangrene, or signs of tissue injury. Only about one-third of scleroderma patients with severe secondary Raynaud's develop ischemic digital ulcers.Feb 19, 2015
What is the best medication for Raynaud's?
Calcium channel blockers are the class of drugs most widely used for treatment of Raynaud syndrome—especially the dihydropyridines (eg, nifedipine, nicardipine), which are the most potent vasodilators. Nifedipine is the customary first choice.Nov 23, 2020
How do you get tested for Raynaud's?
A cold stimulation test involves placing your fingers in an ice water bath to find out if you have Raynaud's syndrome.Jul 26, 2021
Is Raynaud's a neurological disorder?
(People exposed to cold weather are well aware of these mechanisms.) Cold, of course, is the main trigger in Raynaud's phenomenon, although roughly one-third of patients experience it in response to stress and anxiety -- another indication that the condition is neurological and even psychological in origin.Apr 11, 2019
Why are women's hands and feet always cold?
Women's circulation is centred around the female reproductive organs, thereby leaving the extremities, such as the hands and feet, feeling colder as the blood supply in these areas is reduced. This is also the reason that women complain that their partners feet are perfect whilst theirs are not.
What is the ICD code for Raynaud's disease?
The ICD code I730 is used to code Raynaud's phenomenon. In medicine, Raynaud's disease or Raynaud's phenomenon (pronunciation: /reɪˈnoʊz/ ray-NOHZ) is excessively reduced blood flow in response to cold or emotional stress, causing discoloration of the fingers, toes, and occasionally other areas. This condition may also cause nails ...
What is I73.0?
I73.0. Non-Billable means the code is not sufficient justification for admission to an acute care hospital when used a principal diagnosis. Use a child code to capture more detail. ICD Code I73.0 is a non-billable code.
What is inclusion term?
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
What is the ICD-10 code for Raynaud's syndrome?
Non-specific codes like I73.0 require more digits to indicate the appropriate level of specificity. Consider using any of the following ICD-10 codes with a higher level of specificity when coding for raynaud's syndrome: 1 BILLABLE CODE - Use I73.00 for Raynaud's syndrome without gangrene 2 BILLABLE CODE - Use I73.01 for Raynaud's syndrome with gangrene
What is secondary Raynaud?
It is called secondary when it is associated with another condition. Secondary Raynaud phenomenon is often associated with autoimmune disorders, which occur when the immune system malfunctions and attacks the body's own tissues and organs.
What does it mean when you have a Raynaud episode?
The vasospasms reduce blood circulation, leading to discomfort and skin color changes.Raynaud phenomenon is episodic, meaning that it comes and goes. A typical episode lasts about 15 minutes after the cold exposure or stressor has ended and involves mild discomfort such as numbness or a feeling of "pins and needles.".
When does the Raynaud phenomenon start?
Primary Raynaud phenomenon often begins between the ages of 15 and 25, while secondary Raynaud phenomenon usually starts after age 30.
Which disease is associated with the Raynaud phenomenon?
Autoimmune disorders with which Raynaud phenomenon can be associated include systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjögren syndrome.Primary Raynaud phenomenon is much more common and usually less severe than secondary Raynaud phenomenon.
What is the ICd 10 list of diseases and injuries?
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized "head to toe" into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code I73.0:
Why do my blood vessels turn red?
The affected areas usually turn white or blue when exposed to cold or when emotional stress occurs, and then turn red when re-warmed or when the stress eases .Raynaud phenomenon is categorized as primary when there is no underlying disorder that accounts for the exaggerated response of the blood vessels.

Popular Posts:
- 1. icd 10 code for fat containing left inguinal hernia
- 2. icd 10 code for type 2 diabetes mellitus with renal manifestations
- 3. icd 9 code for routine colonoscopy screening
- 4. icd 10 code for left lower extremity venous stasis ulcer
- 5. icd 10 dx code for urine culture
- 6. icd 10 code for migraine with nausea and photophobia
- 7. icd 10 code for arthralgia
- 8. icd 10 code for history of gilberts syndrome
- 9. icd 10 code for bilateral nephrolithiasis
- 10. icd 9 code for convulsions